
The fastest and most secure way to protect the watches and jewelry you love.
We've minimized the paperwork and maximized protection, so you can stop worrying about your watches and jewelry and focus on enjoying them.
In most cases, you'll get a personalized quote in seconds and your policy kicks in immediately.
Wherever you are on planet Earth, your watches and jewelry are protected. Rest easy and travel safely.
If you suffer a covered loss, there's no deductible and no gimmicks. Ever.
Each of your watches and jewelry is covered up to 150% of the insured value (up to the total value of the policy).

Popular Searches

Introducing The S.T. Dupont x Franck Muller Lighter That's Reigniting The Fire For Franck (Live Pics)

Happenings The Horological Society Of New York To Hold Classes In Seattle And Vancouver

Introducing Urwerk's Very Limited EMC SR-71 Uses Pieces Of A Real 'Blackbird'

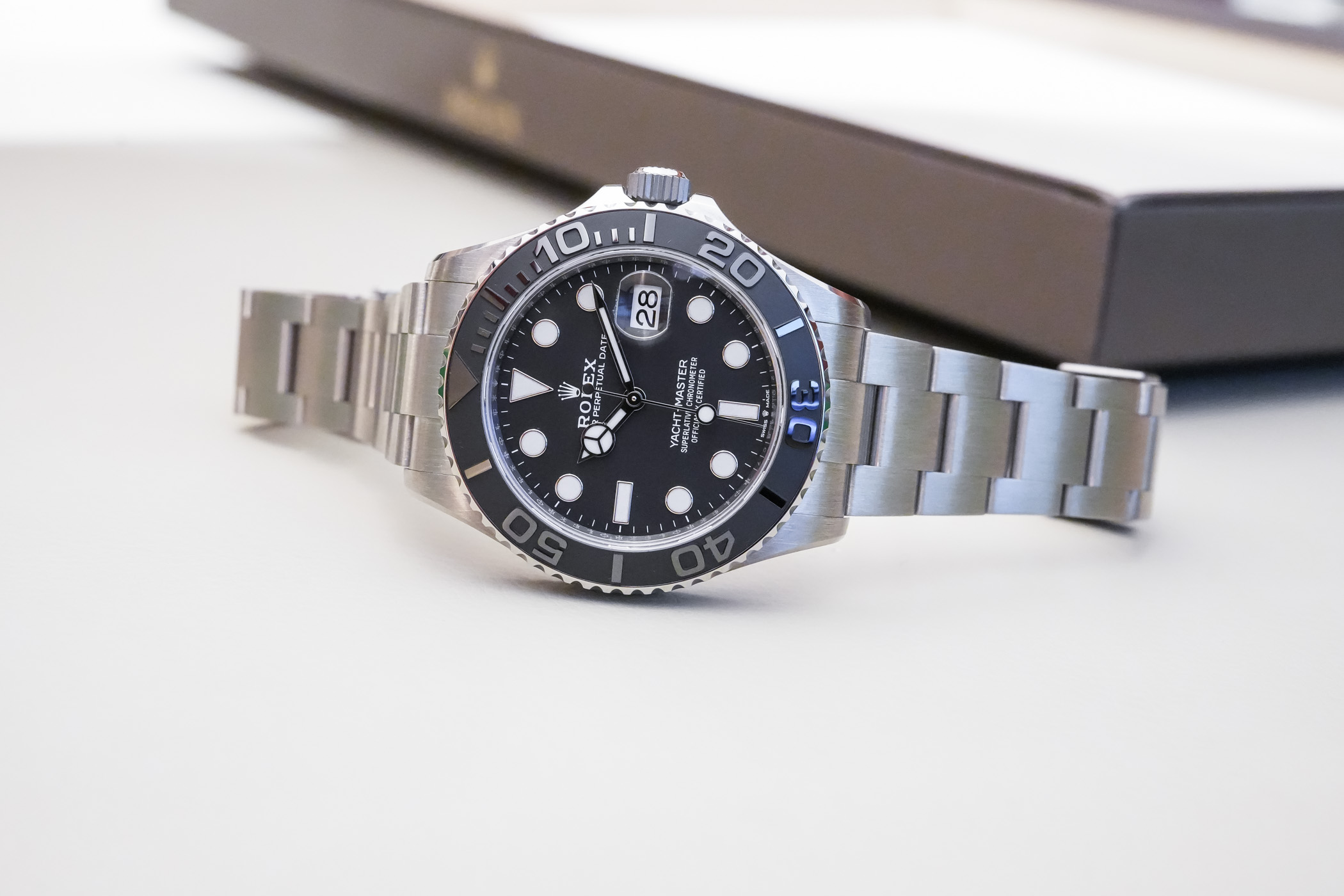
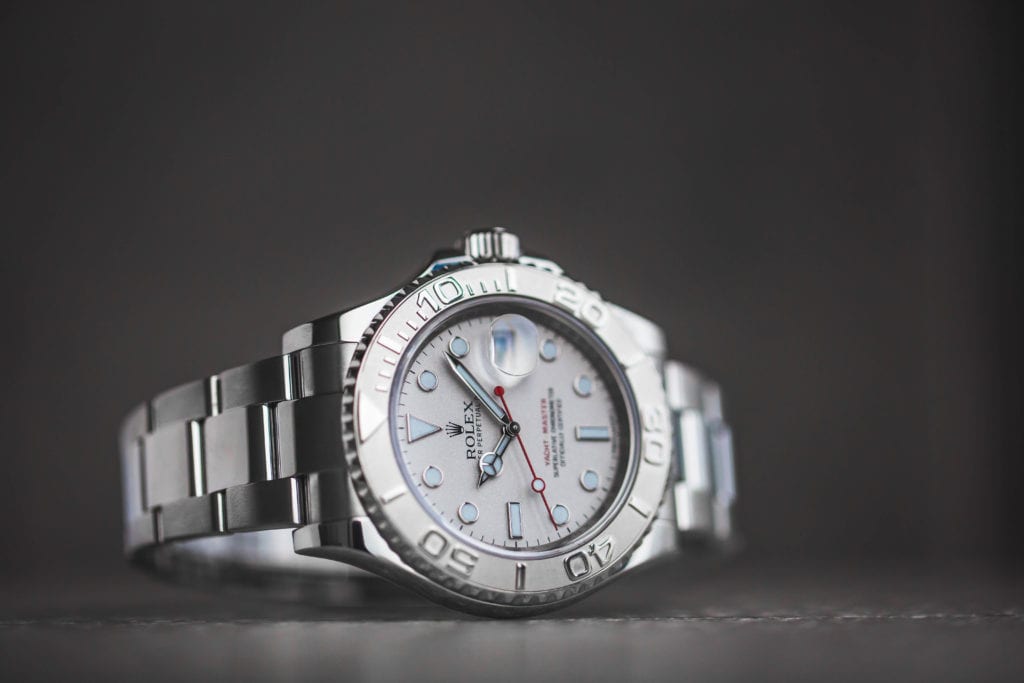
A Week On The Wrist The Rolex Yachtmaster 40mm With Oysterflex Bracelet
For the first time, rolex is delivering a watch on a rubber strap – except in classic rolex fashion it's not a rubber strap at all. it's a beautifully over-engineered bracelet called the oysterflex..

Editors’ Picks

How To Wear It The Cartier Tank Cintrée

In-Depth Examining Value And Price Over Time With The ‘No Date’ Rolex Submariner

Watches In The Wild The Road Through America, Episode 1: A Model Of Mass Production
There is big news, and there is Rolex big news, and in some ways, ne'er the twain shall meet. At Baselworld this year, Rolex debuted a first for the company: the very first, ever, Rolex delivered on a rubber strap. Now, for most companies this would have little effect on watch enthusiasts other than to evoke (very) tepid interest at best, and boredom at worst – but this is not an ordinary rubber strap, this is an official, designed-and-tested-and-thoroughly-obsessed-over-by-Rolex rubber strap. And thereby hangs a tale.
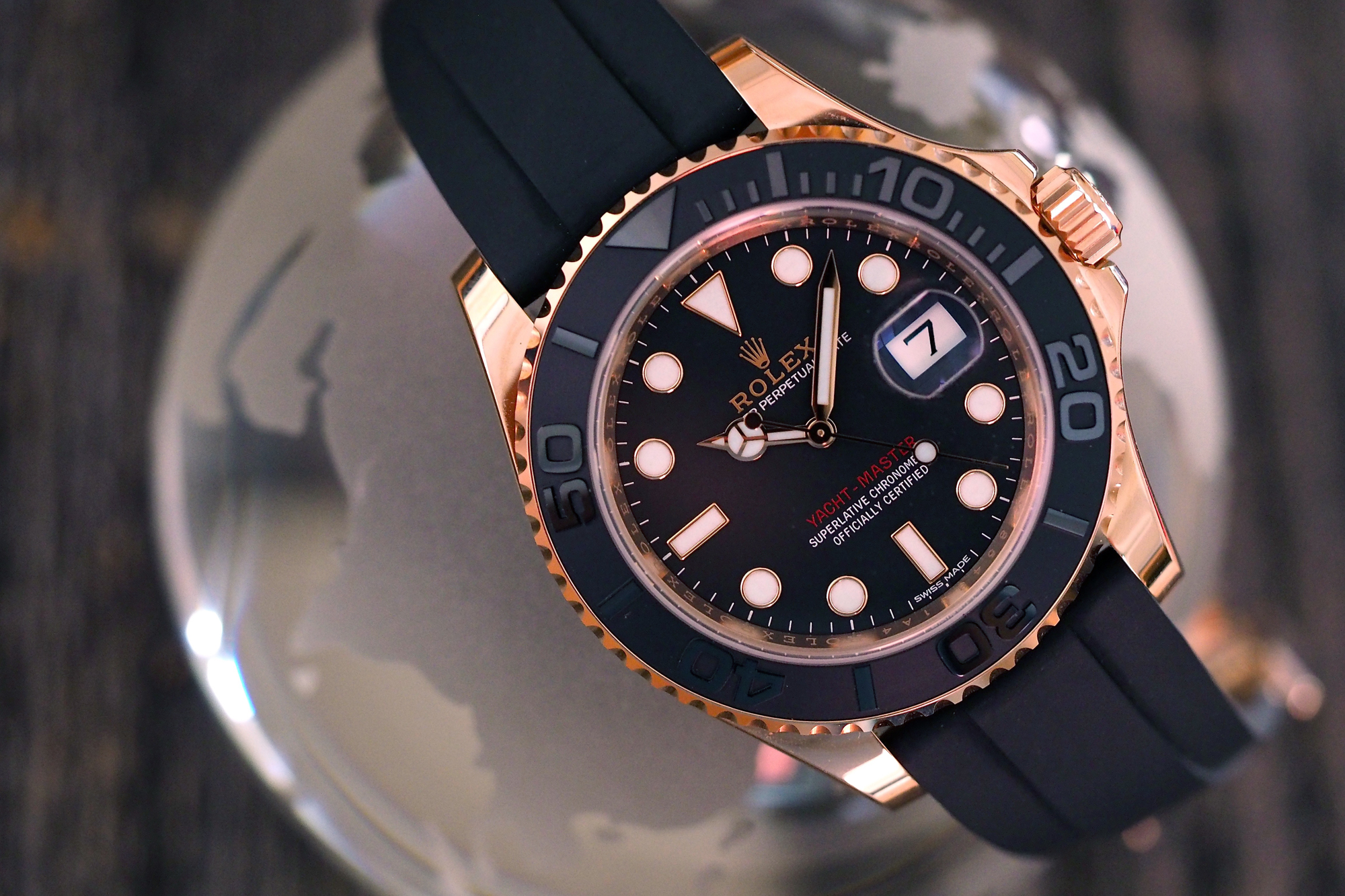

The Yachtmaster, as we have mentioned in some of our previous coverage , occupies a somewhat particular place in Rolex’s lineup of sports watches; it shares water-resistance and a turning bezel with the Submariner (the latter is water resistant to 300 m while the Yachtmaster standard model is water resistant to 100 m). It is certainly not a tool watch; the Yachtmaster is offered in either platinum and steel, or gold and steel (that’s Rolesium and Rolesor, lest we forget) and is either quietly or unequivocally luxurious depending on what size and metal you go for (Rolex makes the Yachtmaster in both 35 mm and 40 mm sizes).
The Yachtmaster’s history goes back to the first introduction of the watch in 1992, although the name, interestingly enough, appears on the dial of a prototype Yachtmaster Chronograph from the late 1960s (a watch so legendary I am actually forced to use the word; one of three known is in the collection of Mr. John Goldberger; we covered it – and a host of other remarkable ultra-rare watches from his collection – in a very memorable episode of Talking Watches ).

The term “Yachtmaster” is also, incidentally, used for a certificate of competency in yachting which is issued by the Royal Yachting Association, although we’re unaware of any specific association between the RYA and the Yachtmaster watch.
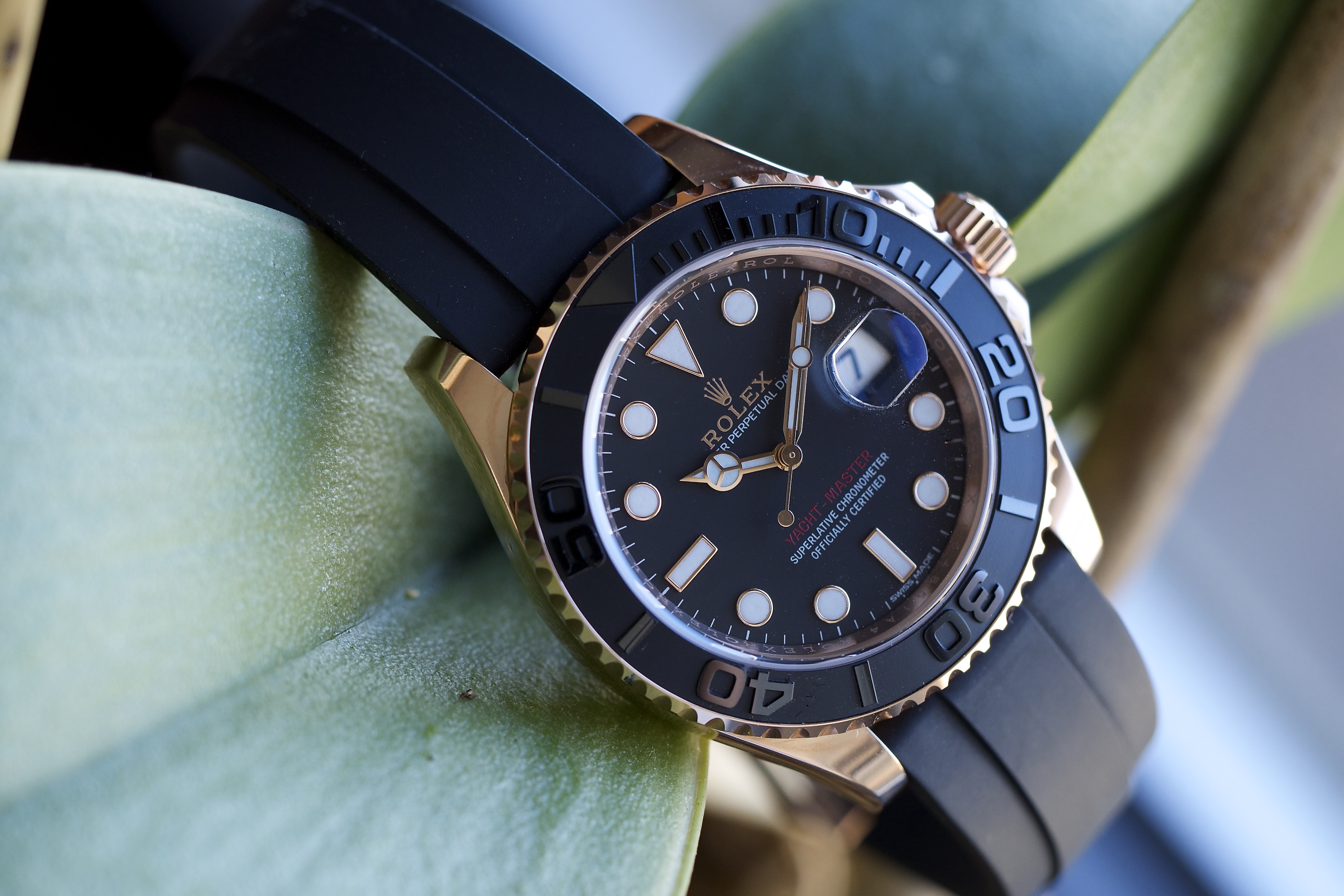
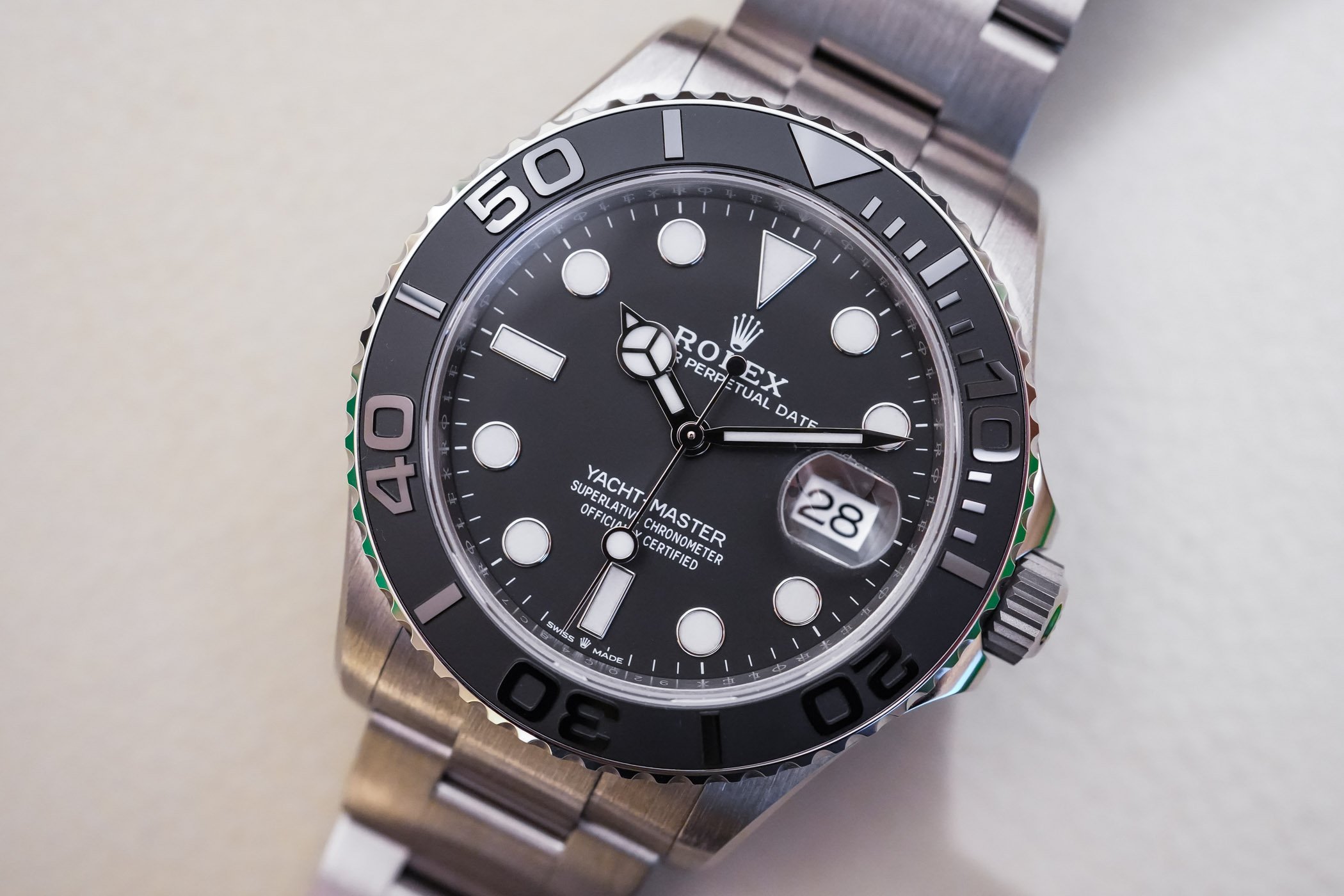
Now, this newest version of the Yachtmaster does take a few pages from the existing Yachtmaster playbook: 100-meter water resistance, a bidirectional turning bezel, and a dial and hands that echo the Submariner. There are also a couple of features that may make vintage Sub enthusiasts wonder if Rolex mightn’t have an exceedingly subtle sense of humor; the gilt coronet and “Rolex,” and the red lettering, both features which according to HODINKEE founder Ben Clymer would have, had they appeared on a Rolex dive watch, made it instantly the single most popular watch in the modern Rolex inventory. The case is rose gold – Rolex famously makes their own, called Everose, in their own foundry, with a bit of platinum mixed in to prevent discoloration – and the bezel, rather than being some other precious metal (as is the case in the “standard” Yachtmasters) is in black Cerachrom – a very technical-looking matte black that contrasts sharply with the gold case. Somehow, between the rose gold, the Cerachrom bezel, and the new Oysterflex bracelet this manages to be the most luxurious and at the same time most technical Yachtmaster yet (leaving aside the Yachtmaster II, which we recently reviewed right here , but that is a watch that marches to the beat of a different drummer entirely).
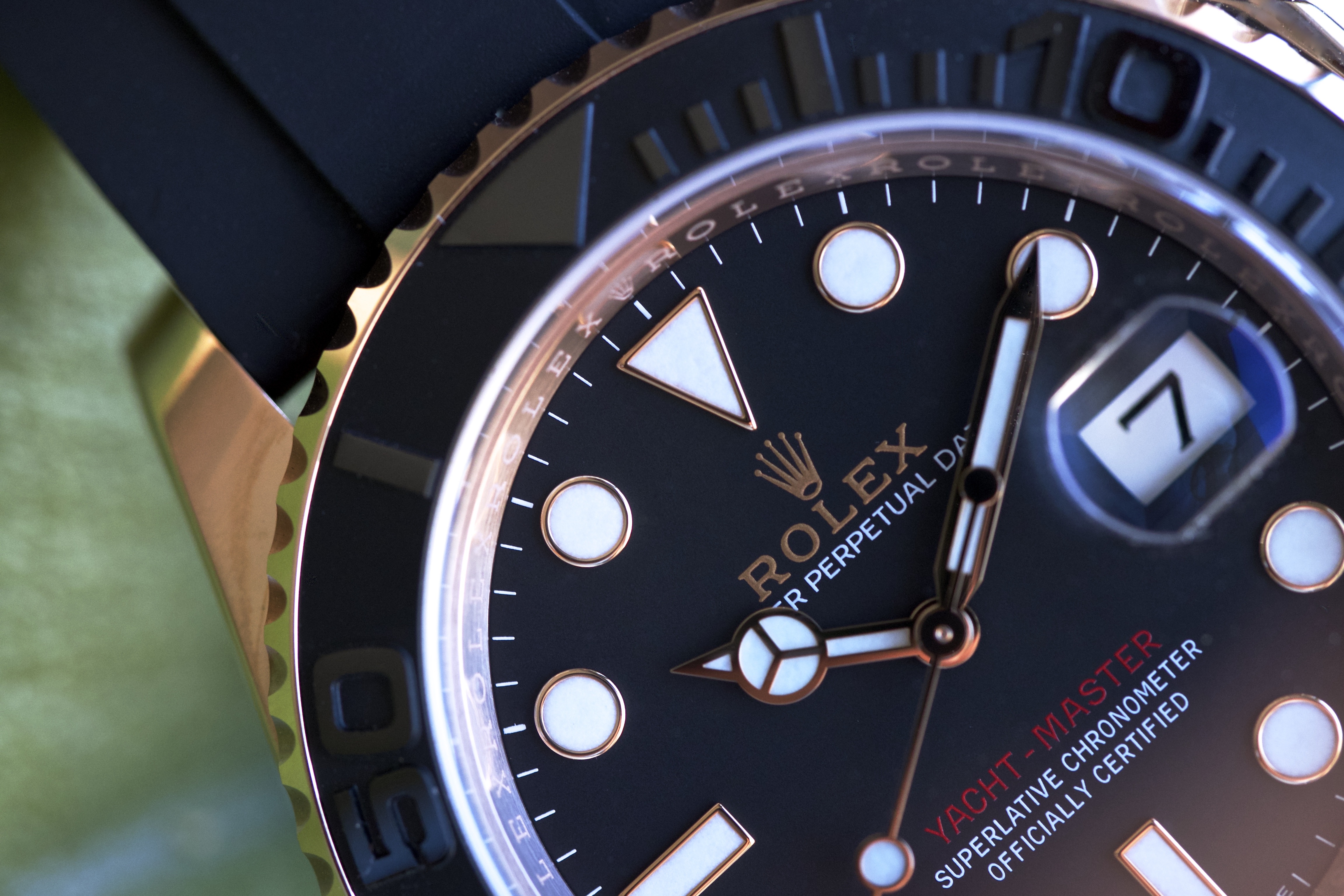

The two different versions of the Everose Yachtmaster (40 mm and 37 mm) sport different movements; the larger uses the caliber 3135 and the smaller, the newer 2236, which sports the “Syloxi” silicon balance spring (first used by Rolex in 2014).
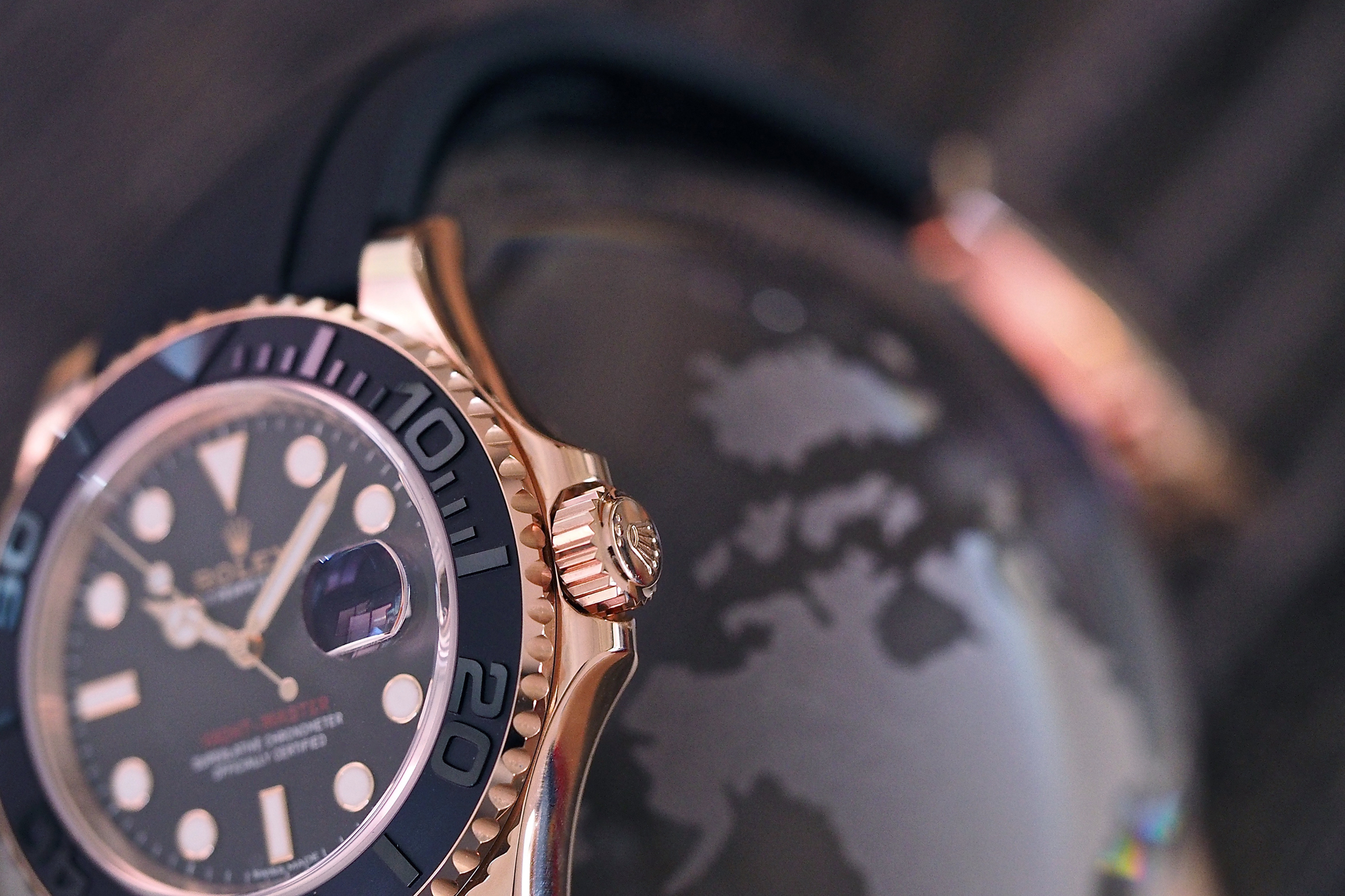

The Oysterflex bracelet is, in a nutshell, quite a piece of work. One of the most endearing traits of Rolex as a company is that it tends to demonstrate what we can only describe as a laudable degree of corporate obsessive-compulsive disorder when it comes to research and development, and it does so, often, without making any sort of fanfare about it at all. In this case we do know a little bit about the Oysterflex, however – it is basically designed to have the hypoallergenic and comfort properties of a rubber strap and the durability and shape-retention properties of a bracelet.
At the core of the Oysterflex bracelet are metal inserts made of titanium and nickel, which are used to affix the bracelet to the clasp and watch case; over those is a sheathing of “high-performance black elastomer.” “Elastomer” is a portmanteau word, formed from “elastic” and “polymer” and is a general term for natural and synthetic rubbers. In addition to the materials complexity of the Oysterflex bracelet, it is also shaped in a rather unusual fashion – there are ridges molded into the the wristward face of the bracelet, which are intended to allow the bracelet when worn to better approximate the natural curvature of the wrist.
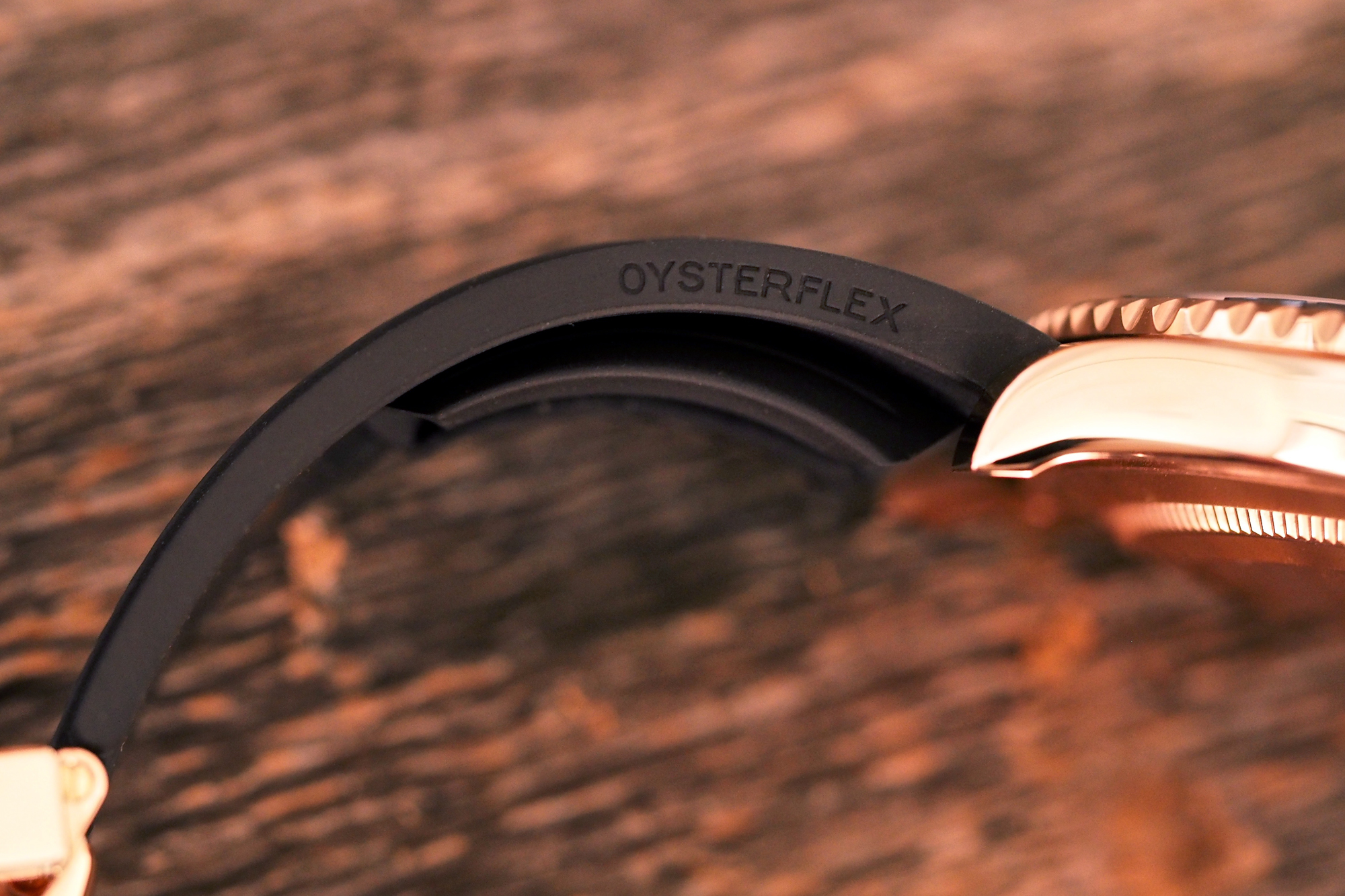

They might look a bit odd but in practice, the design works out quite wonderfully; this is easily the most downright comfortable and organic-feeling rubber strap I have ever worn, and like the entire watch manages to be both extremely technical in feel, and very luxurious at the same time; I doubt whether any company has ever taken so much trouble over the design of a strap (for all that Rolex prefers the term “bracelet” in describing the Oysterflex, habit dies hard and you’ll probably find yourself calling it a strap, just as we did). On the wrist, the two stabilizing ridges do exactly what they are supposed to: keep the watch from shifting, as heavier watches on rubber straps are wont to do, without requiring you to have the strap uncomfortably tight. The Everose Oysterlock clasp does a superb job mechanically and also looks fabulous into the bargain; the quality of finish on the clasp and case may not seem terribly elaborate at first, but it is as technically flawless as anything I have ever seen at any price, on any watch.
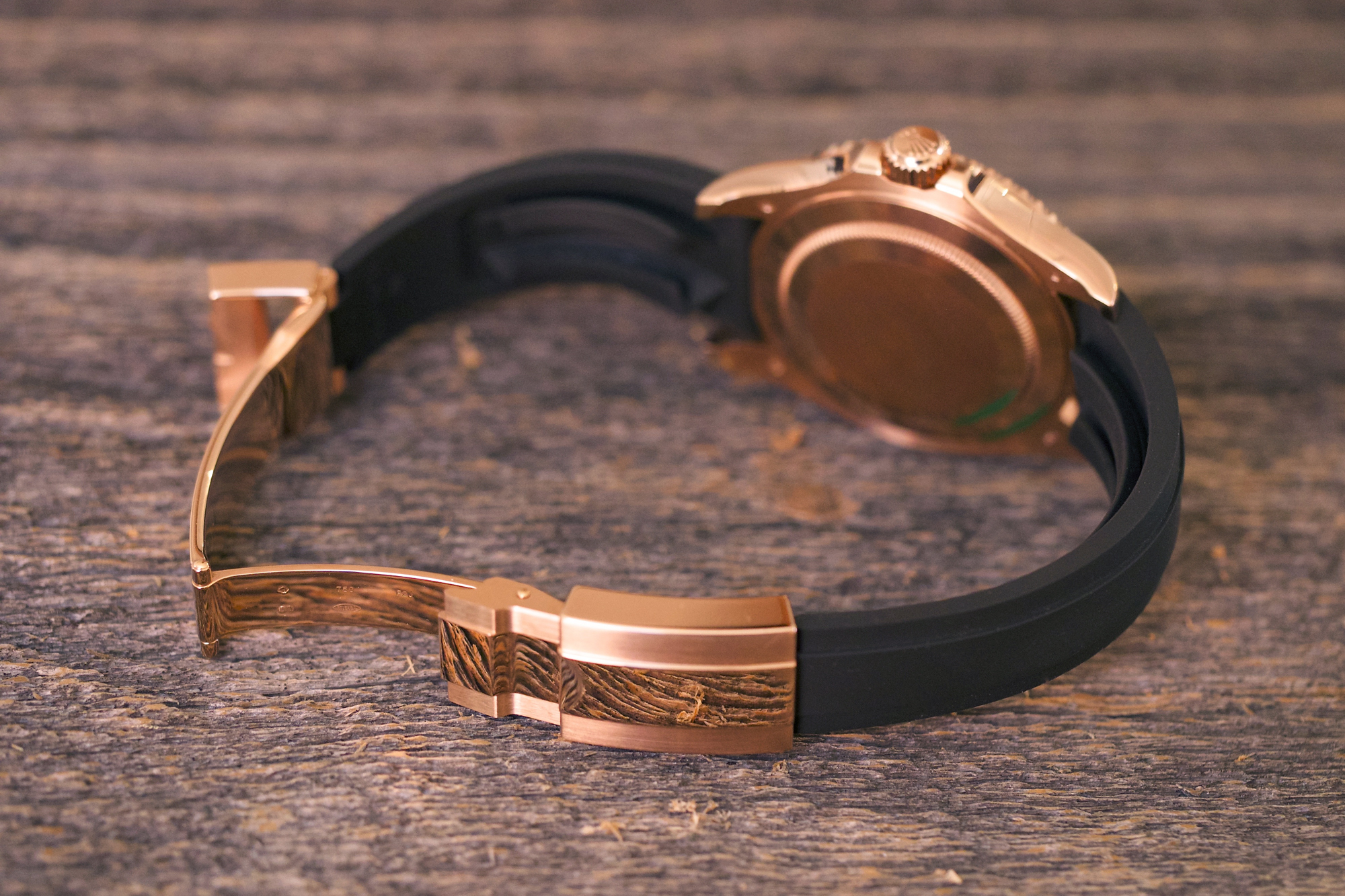

What we have here, in other words, is a very Rolex interpretation of luxury. Yes, this is a gold watch, and a gold Rolex, and wearing a gold Rolex always carries with it, shall we say, certain semiotic complexities. However there is also another side to the watch, and to the Rolex approach to luxury in general: the taking of such pains to produce technical perfection that technical perfection becomes a luxury in itself.
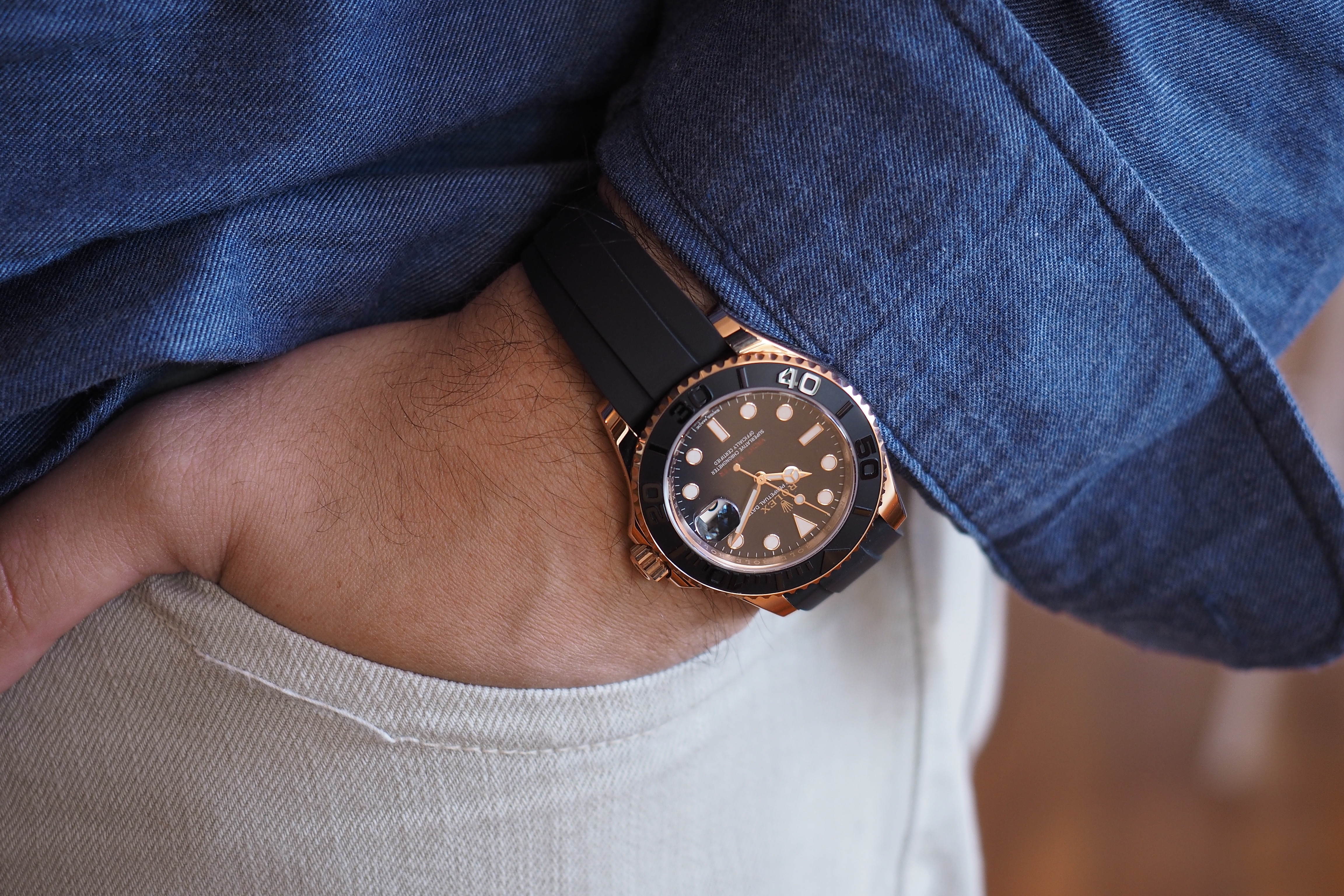

The Everose Rolex Yachtmaster, in Rolex Everose, with Everose Oysterclasp and Oysterflex bracelet, as shown, $22,000 in 37 mm, and $24,950 in 40 mm. For more info, check out Rolex.com.

Watching Movies Tom Selleck's Tiny Timex And Two-Tone Rolex In 'Three Men And A Baby'
By Danny milton

Seven Of Our Favorite Watches To Engrave
By James stacey
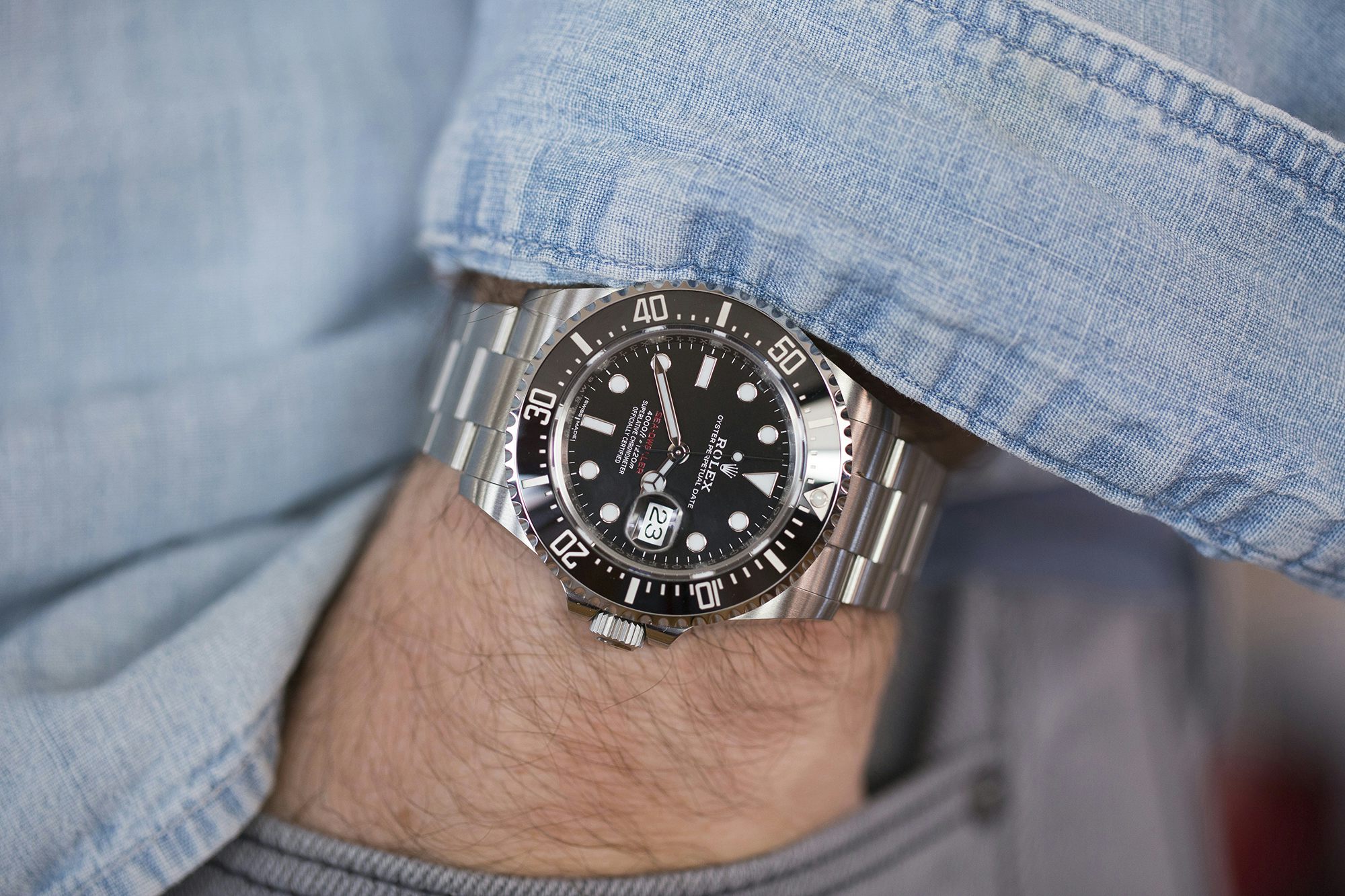

Sunday Rewind Take A Deep Dive With The Rolex Sea-Dweller 126600
By Hodinkee

Pre-Owned Picks A Patek Philippe Nautilus Ref. 5711/1A, An Audemars Piguet Royal Oak Offshore Chronograph, And An IWC Portugieser Chronograph Rattrapante
By Hodinkee shop

Last Week’s Top Stories

Editors' Picks The Watches We'd Wear To Our Best Friend's Wedding

Introducing Audemars Piguet Announces Three Colorful New Royal Oak Offshores
By Anthony traina

Hands-On Two Unlikely Watches That Became The Face Of Omega's Olympics – The BG859 And The Aqua Terra 150 'Ultra Light' 'Duplantis'
By Mark kauzlarich

New Rolex Short Film Highlights The Worldwide Impact Of The Perpetual Planet Initiative

The Value Proposition The Habring² Erwin 'Tuxedo'
By Tantan wang
The Rolex Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium, Very Rolex Yet Surprisingly Disturbing
It is undoubtedly a rolex from head to toe, yet it felt very surprising on the wrist....
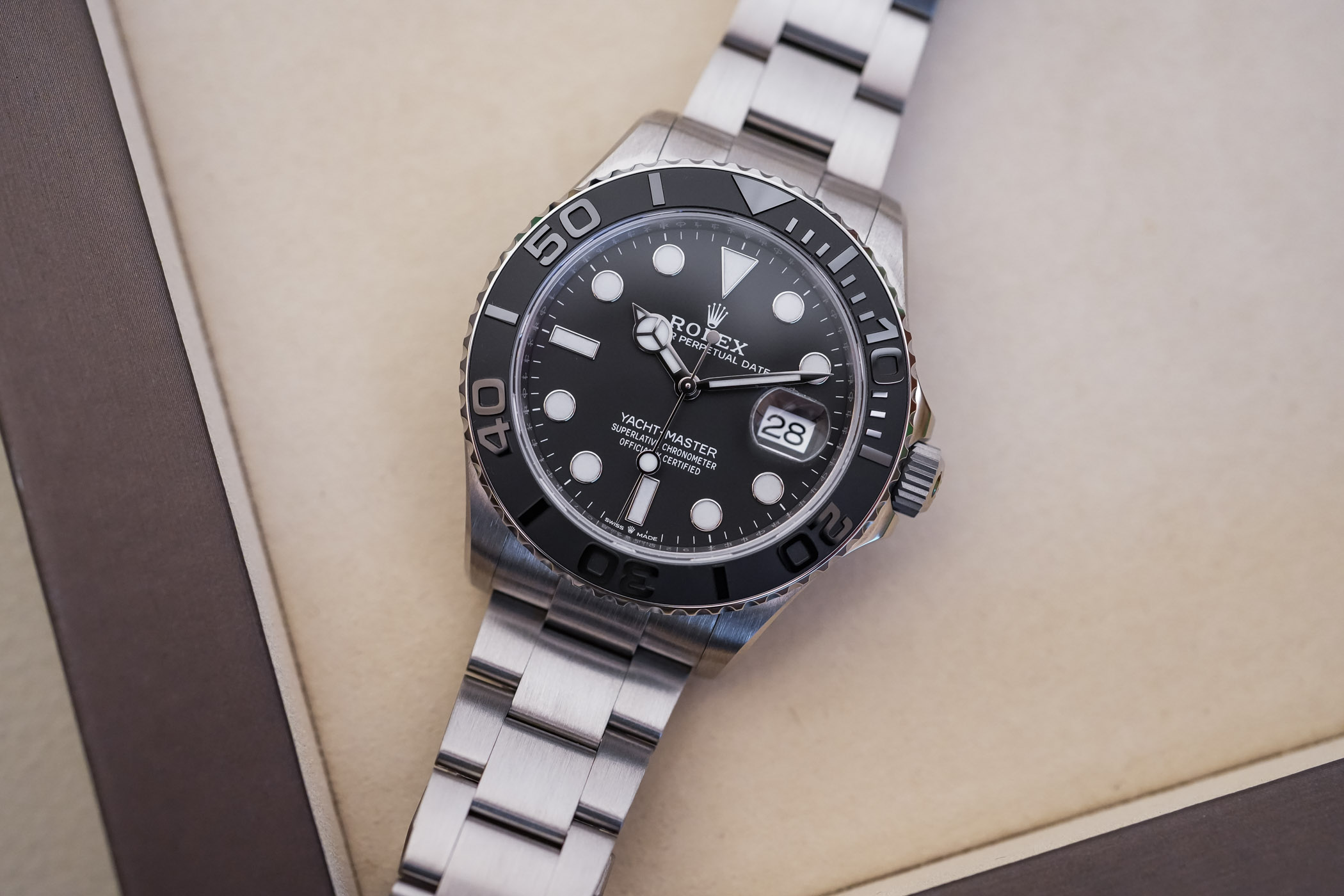

Launched in 1992, the Rolex Yacht-Master has undoubtedly enjoyed a long shelf life but has never attained the same cult status as a Submariner. A watch inspired by the nautical world and meant to be used as a luxury yachting watch, its vocation and looks have always been slightly confusing. It looks somewhat like a Submariner but without the diving credentials. It has sporty specifications, yet it is truly luxurious and has often appeared in precious metals. Recent versions, with the enlarged 42mm diameter and the matte black bezel, changed this perception. But clearly, it’s the new Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium that signs the independence act of the collection. We’re taking a closer look at this watch that feels extremely familiar and, at the same time, left us with contradictory thoughts. Good or not, let’s check this out.
Some context
The Yacht-Master collection was introduced at the 1992 edition of the Baselworld Fair. And believe me, this was quite an event. Rolex is known for its strategy of incremental updates and rarely presents new watches. In fact, when the YM was launched, it was one of the very few entirely new collections since the launch of the Daytona in 1963. However, despite the new name (well, not entirely, as it was first used in the late 1960s on a prototype watch based on a Daytona) and its unprecedented vocation within the Rolex portfolio, the watch felt familiar.
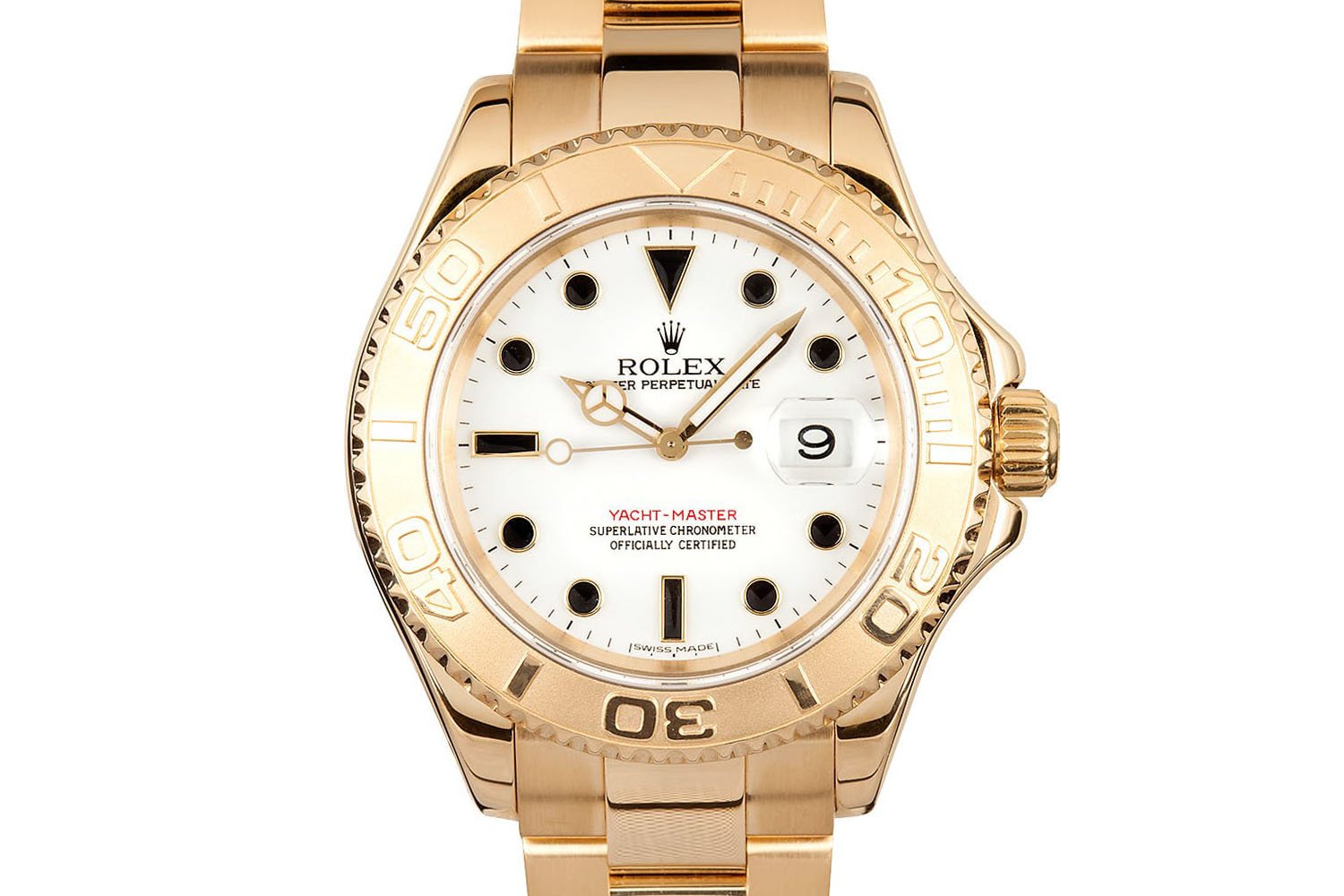

The modern-day version of the Yacht-Master made its first appearance with the reference 16628, an 18k yellow gold version with a white dial and black-filled hour markers. Looking at it, the resemblance with the Submariner and other aquatic models at Rolex is… obvious. Some say (nothing official here) that during the 1980s, the brand experimented with many different options to revamp its iconic Submariner. Several attempts later, something close to the Yacht-Master appeared; however, Rolex felt that redesigning the Sub was probably not the right move. Yet, the design caught people’s attention but had to be slightly updated so as not to cannibalise the all-important Submariner. The decision was made to position this design as a higher-end, luxurious nautical model.
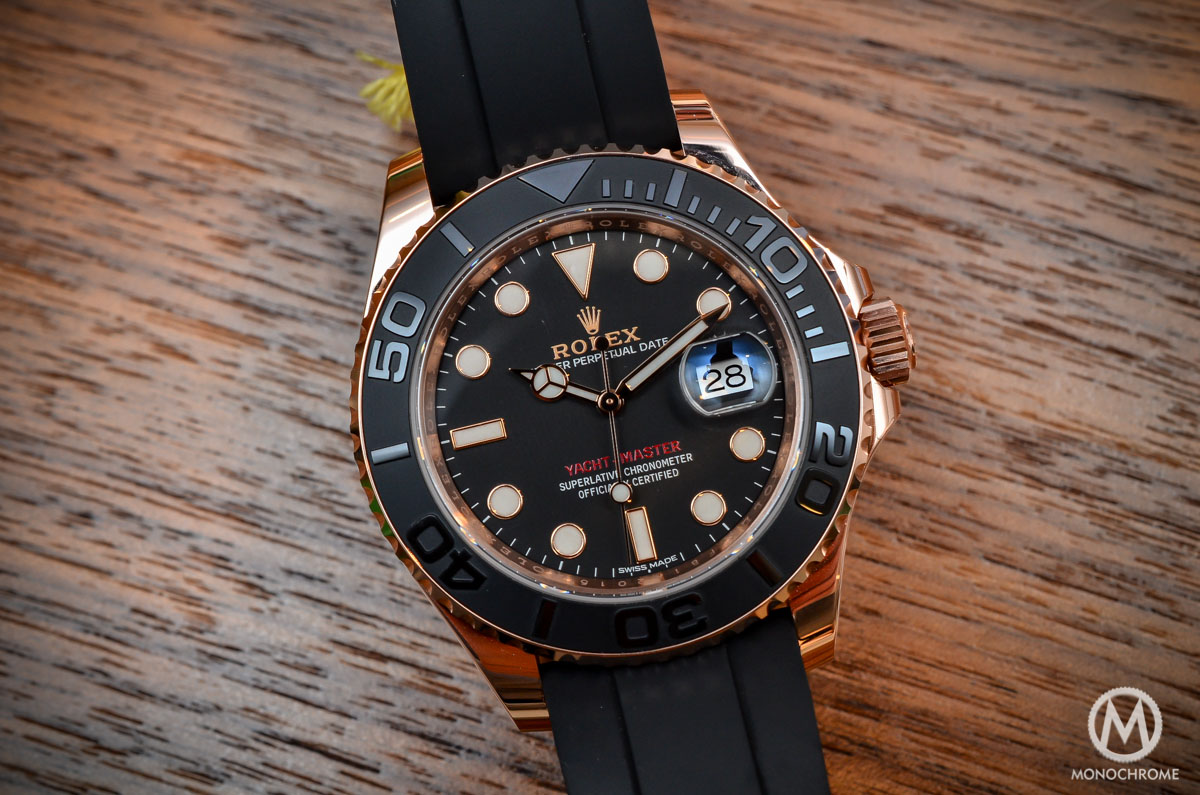

The differences were straightforward: steel, 300m water-resistant case, black bezel, black dial and instrumental characteristics for the Submariner compared to the gold; 100m water-resistant case, bright dial, solid gold bezel, more rounded shapes and luxurious touches for the Yacht-Master. However, the visual resemblance persisted, which is probably why it took many years for the YM to become a model on its own. An important moment in the history of this watch is, to me, the introduction of the reference 116655 , an Everose model with a matte black dial, a matte ceramic bezel with raised numerals and the Oysterflex rubber bracelet. This is the moment when the YM became different… and much more attractive.

Since then, Rolex has gradually improved its nautical watch with the release of the Yacht-Master 42 – a new size, larger than a Submariner, to differentiate the collection. It would later be followed by a very appealing yellow gold edition .
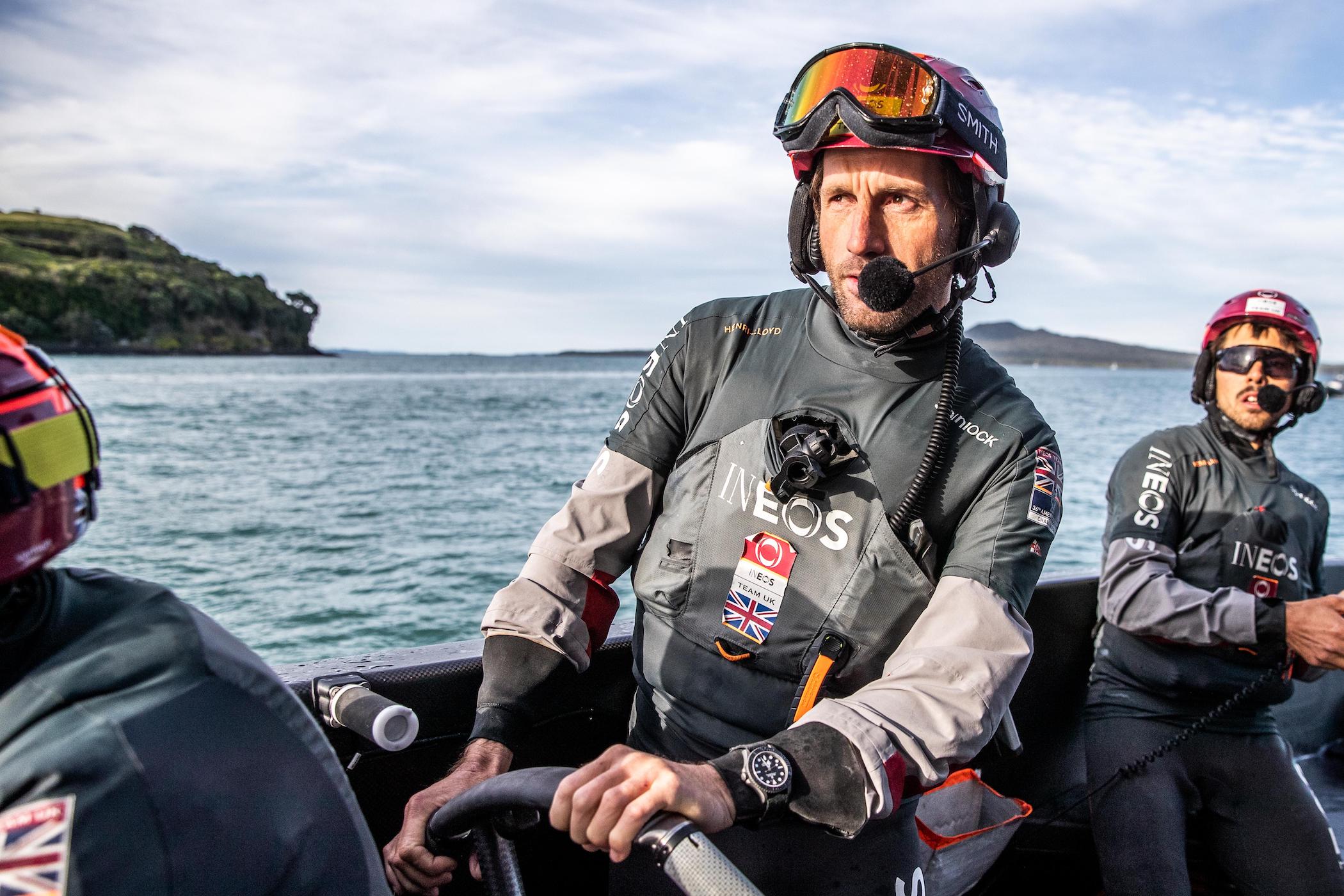
The Prototype Yacht-Master 42 of Sir Ben Ainslie… In titanium
The current RLX Titanium edition of the Yacht-Master 42 doesn’t spring out of nowhere. It has existed for about three years already, but only as a prototype, on the wrist of legendary sailor Sir Ben Ainslie – winner of the 34th America’s Cup with Oracle Team USA in 2013, four-time Olympic champion, CEO and Skipper of INEOS Britannia and skipper of the Great Britain SailGP Team. This watch came to us as a surprise long after its creation in 2020. Despite appearing in the wild repeatedly, we only noticed its existence in late 2021, after it was mentioned in an interview on October 2020 in The Week . It was also mentioned in the official Rolex print magazine.

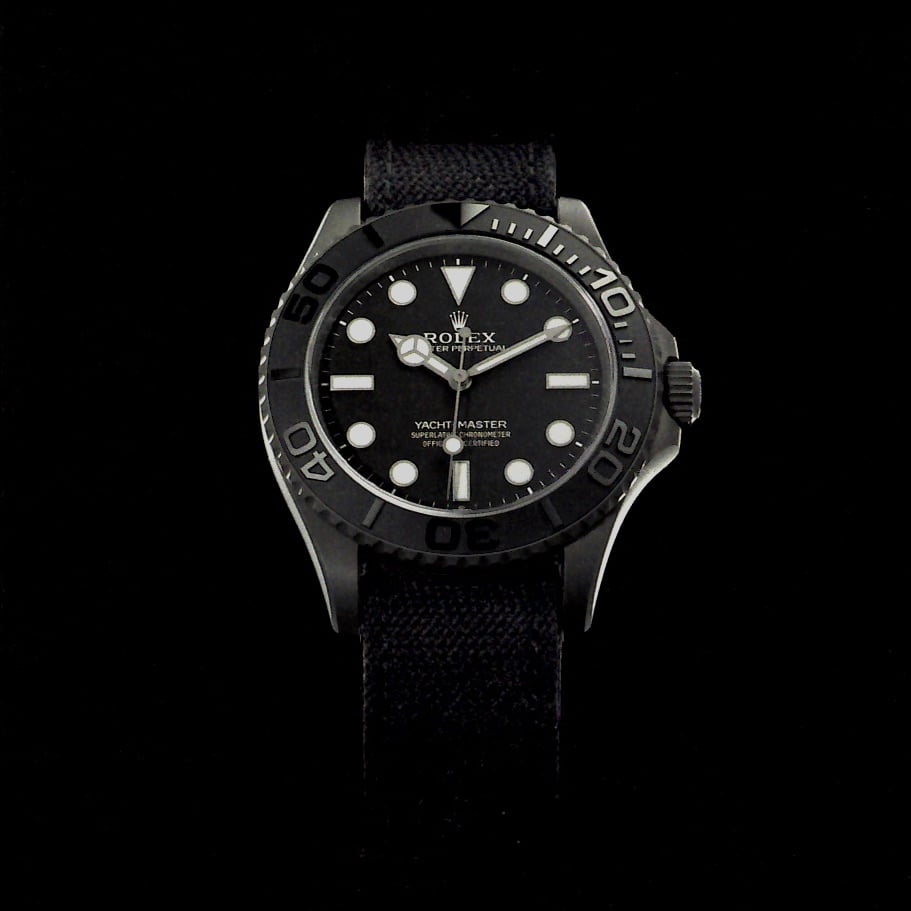
The watch in question, a prototype made exclusively for Ainslie for a very specific purpose and designed to be tested on the field, was made in RLX Titanium (back then an unprecedented material for Rolex, which would later be used on the Deepsea Challenge ) and looked like a deluxurised version of a well-known watch. Entirely matte, equipped with a black dial and black bezel and with a no-date display, it was worn on a technical NATO strap, which according to the brand, combines Cordura with high-performance elastomer and is closed by a Velcro for easy adjustments.

The existence of this watch immediately gave us some ideas, incorporated in our 2022 Rolex Predictions featuring a titanium Yacht-Master . And as we anticipated, it became a reality this year .
The Rolex Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium
This year, Rolex launched its commercial version of the Yacht-Master 42 Titanium, which resulted in a slightly different watch from what we’ve seen on the wrist of Ainslie. More in line with the current white gold and yellow gold YM42 , the watch has many distinctive features. It isn’t just a titanium attire; it is a standalone model with its specificities and unique features.
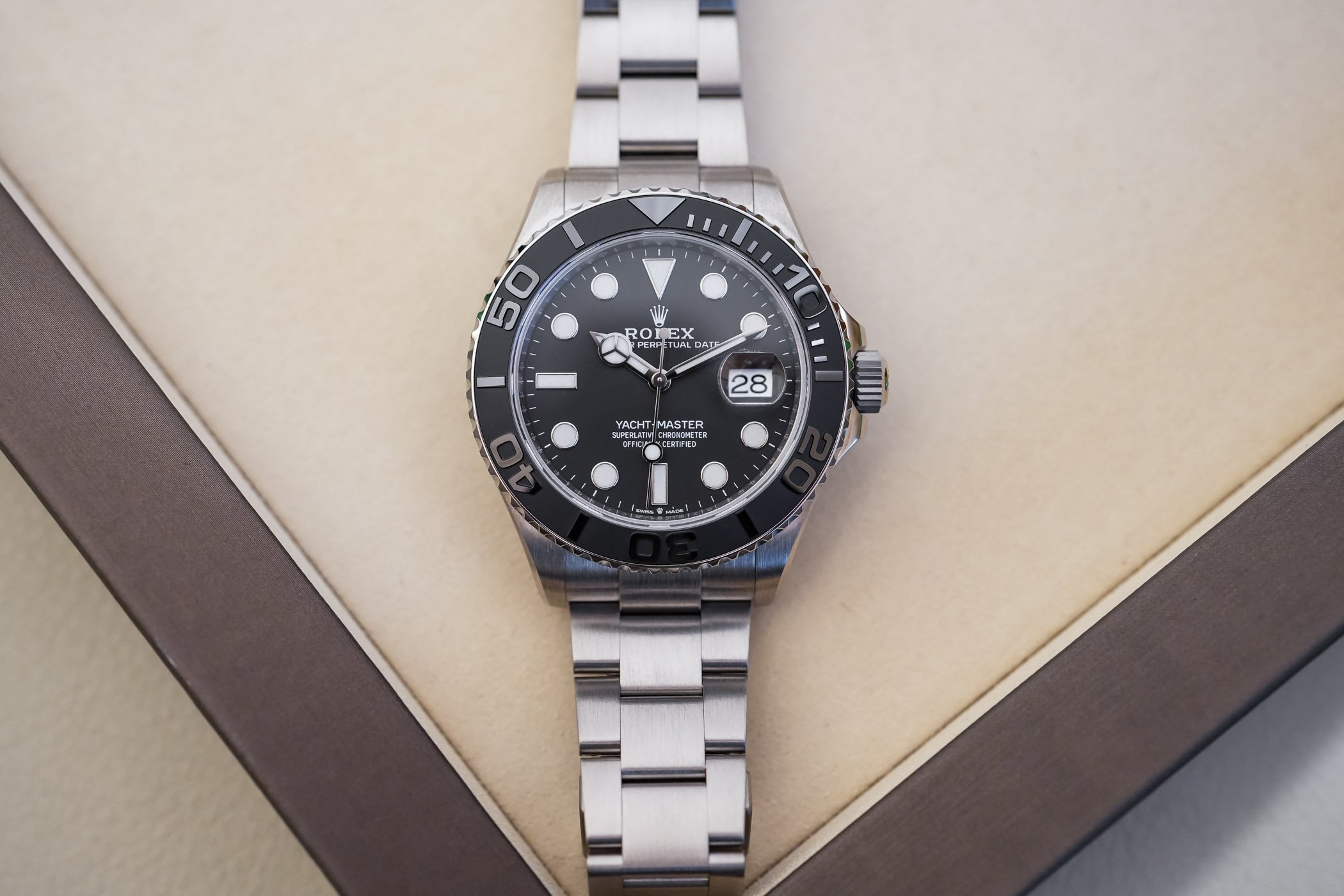

First of all, let’s talk titanium at Rolex. The brand, over the years, has been using an array of metals – steel, with its own Oystersteel alloy (904L), gold in all possible colours and even proprietary alloys and platinum. Ceramic has long been used too, but only for bezel inserts. Rolex has never used ceramic or any other high-tech material for its cases. Until the recently introduced Deepsea Challenge , titanium has remained a rarity, used for the caseback of the Sea-Dweller Deepsea and for the Pelagos , which isn’t a Rolex but a Tudor, so it doesn’t really count.

Now, in less than six months, Rolex has released two watches made entirely of titanium, with an alloy named RLX – which is grade 5 titanium. One is a beast, a gigantic timepiece made to explore the deepest point of the oceans – a watch, objectively speaking, that is hardly wearable. The other one, the Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium reference 226627, is certainly one of the most comfortable models in the brand’s collection.
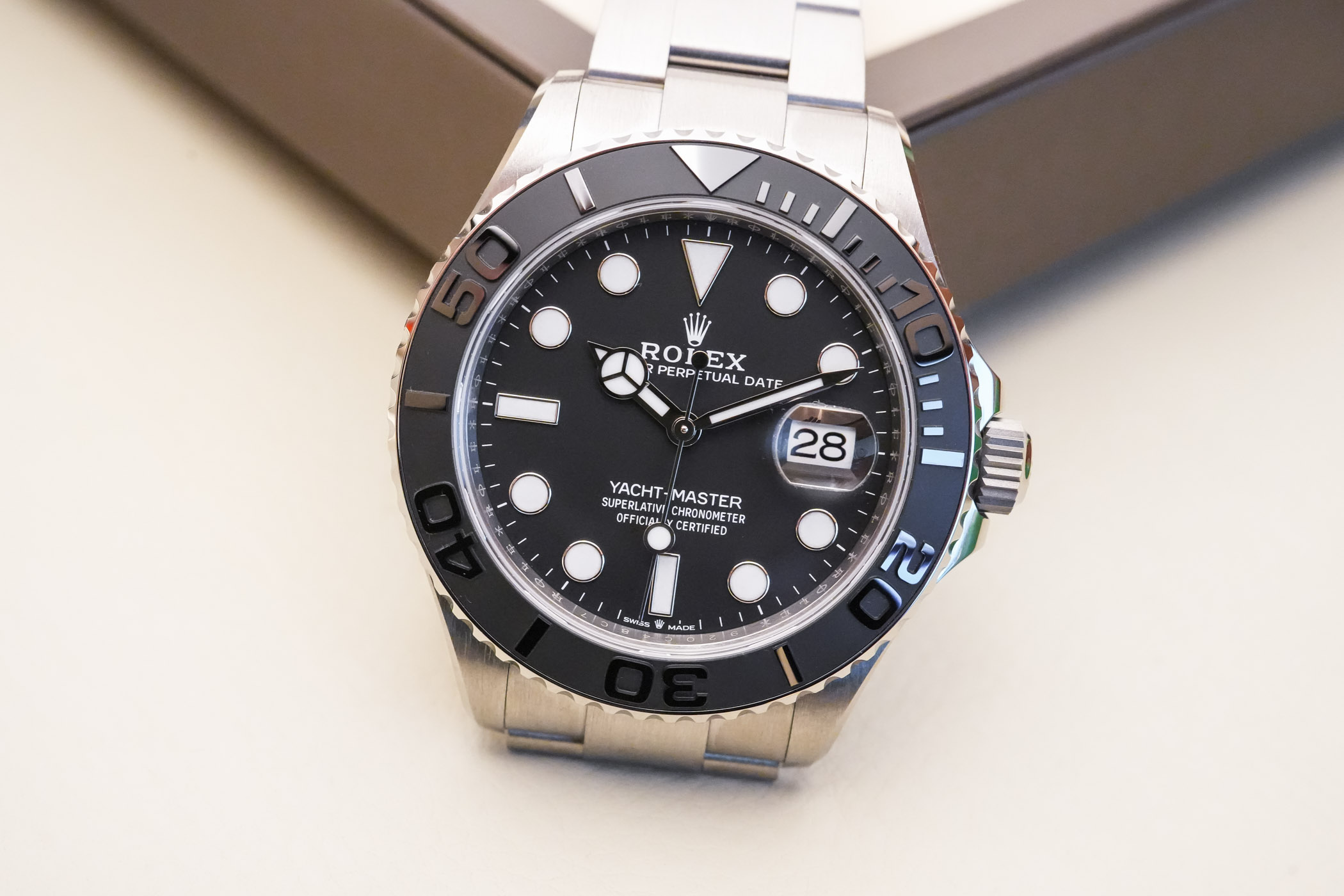

As said, the YM42 Titanium is more than just a new material applied to an existing watch. Of course, it shares multiple elements with its gold siblings, but some details truly set it apart. The case measures 42mm in diameter with a fairly contained 11.60mm thickness. Measuring 50.3mm from lug-to-lug, it’s not the smallest watch in the brand’s portfolio and wears slightly larger than a classic Submariner (40.5mm x 12.5mm x 47.6mm). All parts of the habillage are made of titanium, from the monobloc middle case to the crown, the rotating bezel, the caseback and the bracelet. The specifications are classic Rolex Yacht-Master, with a Triplock crown with integral guards, a screwed back, a sapphire crystal with AR coating and a Cyclops lens over the date and 100m water-resistance.

Classic features of the YM have been retained, such as the bidirectional bezel with a 60-minute Cerachrom insert. The latter sticks to the classic look of the collection, with a matte base and raised, polished numerals and markers without a lumed index. What makes the Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium so special, then? Well, first of all, the case features one very appealing detail: bevelled lugs. A nod to the past, this feature is exclusive to this titanium version and brings more dynamism to the case, as well as providing a nice historical reference – something that Rolex fanboys will surely appreciate (I do…). The second specificity of this model is its matte look. But I’ll come back to that point later.

The dial of this titanium YM42 is, however, classic. It retains most of the attributes of the white gold reference 226659, with oversized applied markers and hands in polished white gold and all tracks and printings in white. There is not a single touch of colour on this dial, which comes in a new colour named intense black, with a fine satin finish. Matte, with a velvet-like texture, this dial isn’t pure black like most of the watches in the brand’s collection but feels more like a very dark anthracite. Combined with a flat sapphire crystal with AR coating, the result is an almost complete lack of reflections. And the overall legibility, thanks to large markers and great contrast, is superb.

Inside the case is a classic Rolex movement, the calibre 3235 – used in the Submariner Date , the Datejust 41 and 36 , the Sea-Dweller or the Deepsea . A Superlative Chronometer (meaning certified by COSC and then by Rolex once the movement is encased), this automatic movement comes with all the recent innovations of Rolex: a bidirectional rotor on ball bearings, a Chronergy escapement, a paramagnetic nickel-phosphorus pallet fork and escape wheel and a paramagnetic blue Parachrom hairspring. It beats at 4Hz, stores a comfortable 70h power reserve and features an instantaneous date and a stop-seconds mechanism. Simply one of the best time-and-date engines on the market.

The bracelet of this new Yacht-Master 42 is also made of RLX Titanium. A classic 3-link Oyster style, it is also entirely matte with a so-called technical satin finish . Contrary to most Oyster bracelets, the sides are also matte, and only the Coronet on the clasp is polished. As you would expect, it is on par with Rolex quality standards, with an Oysterlock folding safety clasp and the Easylink comfort extension link to adjust the bracelet length by approximately 5mm. Also, this bracelet includes patented ceramic inserts inside the links to enhance its longevity and flexibility on the wrist.
Some thoughts… It is a disturbing watch (but a good one)
When you’ve been into watches for some years, you develop some preconceived notions about Rolex timepieces and the way they look and feel on the wrist. There’s a certain heft, a presence on the wrist, consolidating the perception of quality and solidity. There’s also a sheen that is unique to Rolex, with glossy bezels and dials. Rolex watches are so emblematic that your brain is pre-formatted to a certain conception of what they should look and feel like on the wrist. The Rolex Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium changes everything and breaks the norm. And it left me with mixed feelings, but not necessarily in a bad way.
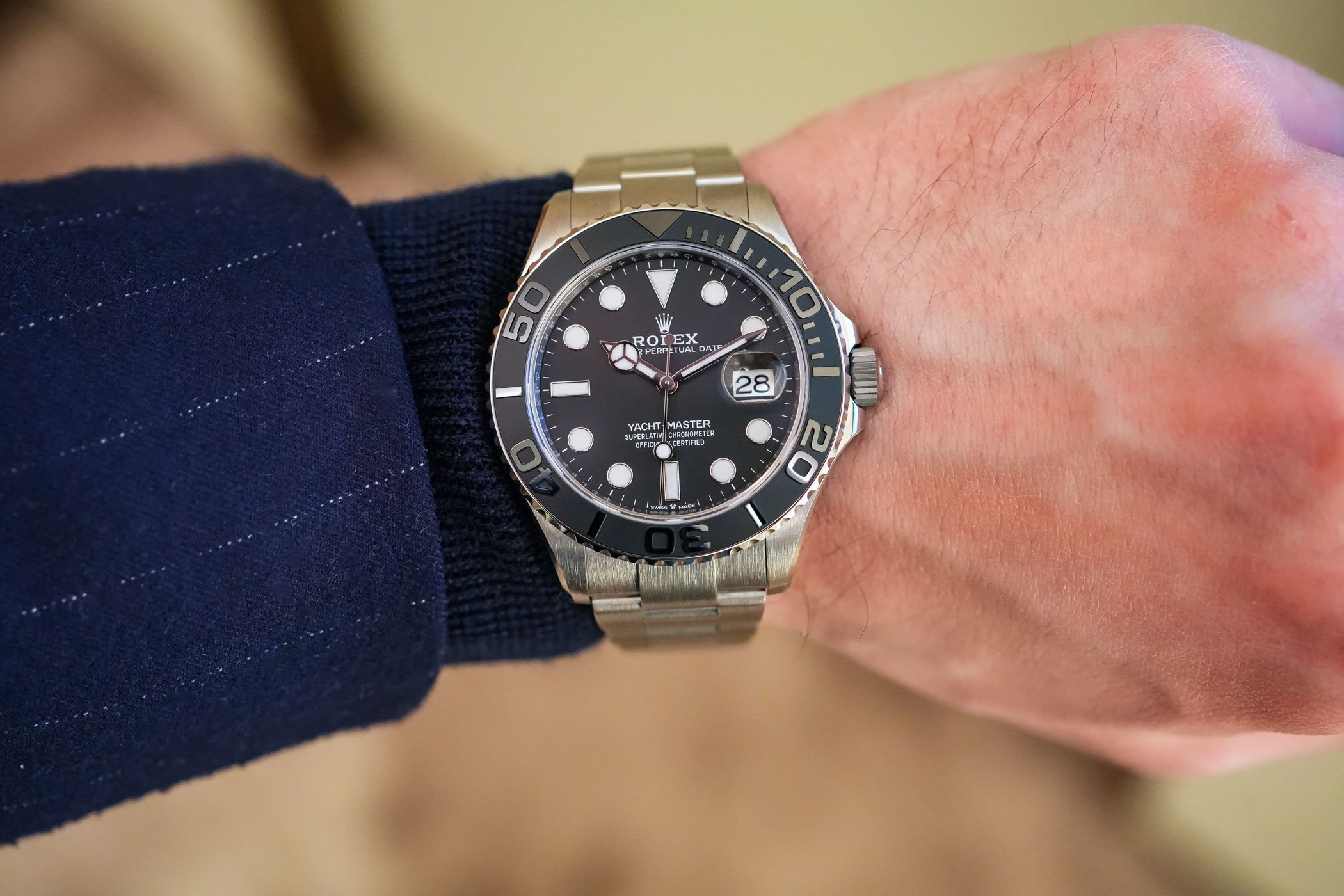

When you take a Submariner and strap it around your wrist, it feels like home… It’s reassuringly heavy yet comfortable. Even though weight might be a bit irrational, weight adds to the feeling of quality and weight robustness. Having worn Rolex sports watches on so many occasions in my personal and professional life, I expect a watch from the Crown to weigh about 150/160 grams on a bracelet. It is a construction that is so deeply embedded in my brain that the moment I strapped the YM42 Titanium, I was left with a very disturbing sensation.

Yes, the watch looks like a Rolex, but it doesn’t feel like one on the wrist. It’s about 35% lighter than steel (around 100 grams), and everything I associated with how a Rolex should feel on the wrist simply vanished. I don’t want to sound too dramatic, but believe me when I say that it was a rather special experience at first. But the beauty is that you soon forget about this first impression and enjoy a watch that is surprisingly light. Despite its size, it is extremely comfortable and balanced. A watch that you’ll forget in about 30 seconds after you strapped it on the wrist. The initial feeling of a lack of robustness is, of course, just a misinterpretation of a pre-formatted brain and has nothing to do with the actual heft of the watch.
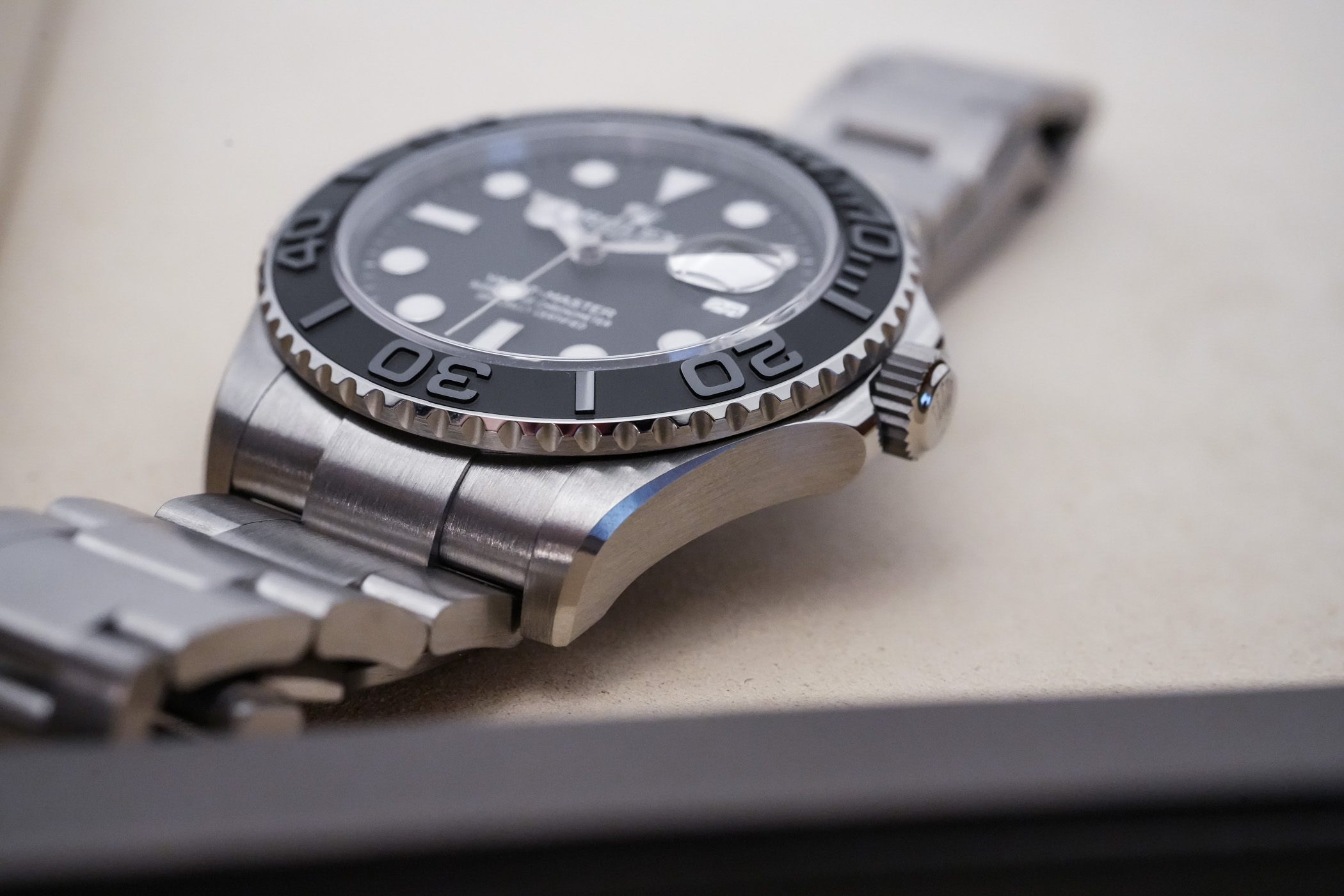

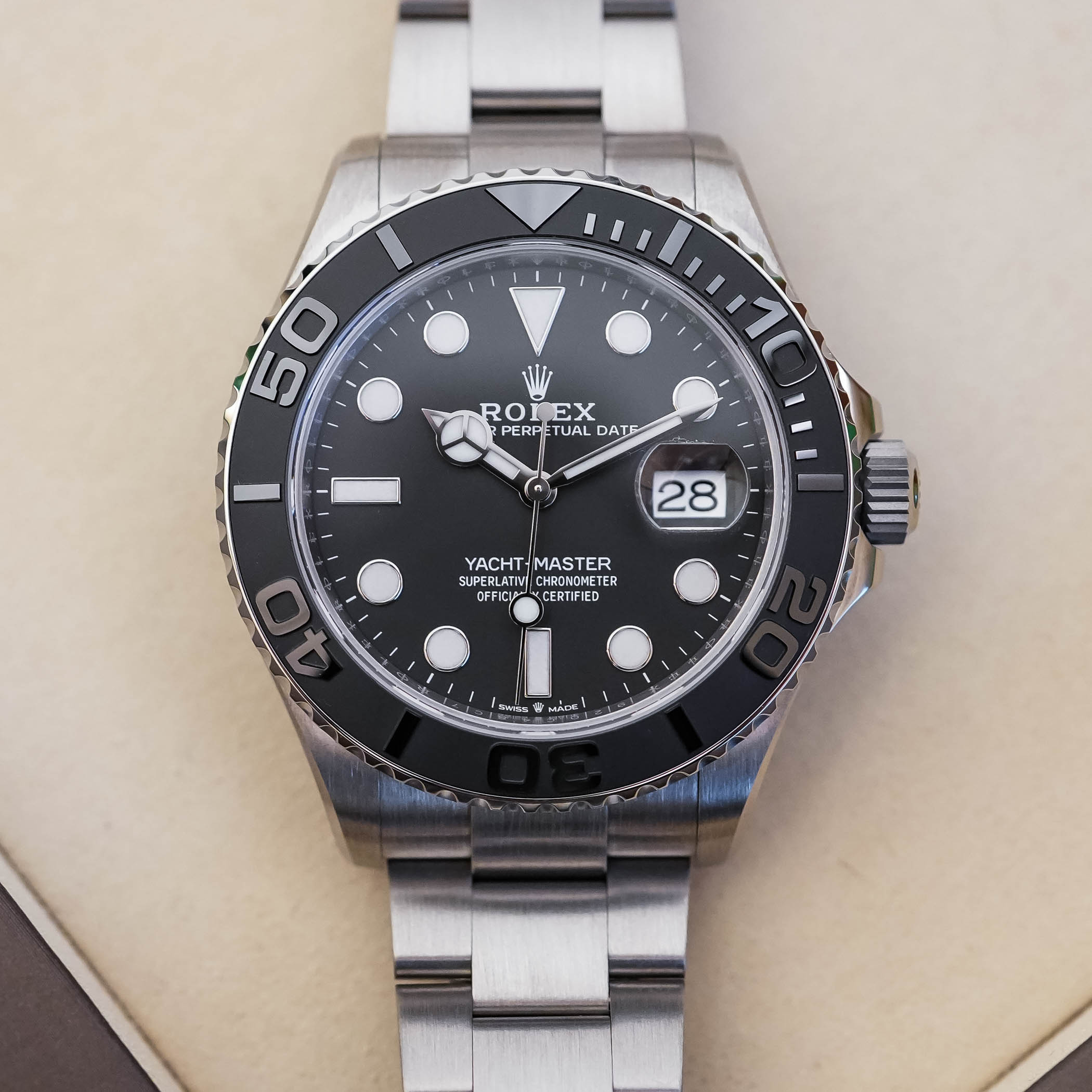
The second surprise with this watch is how it plays with the light and its lack of reflections. As said, most sports Rolex have a certain sheen. Even a Submariner or a Deepea feature glossy, reflective parts, such as the bezel and the sides of the case and the bracelet. The Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium is the most matte watch in the brand’s collection, with only a few polished accents (numerals on the bezel, bezel rim, and crown guards). Even the bevel on the side of the lugs is satin finished. This lack of sheen is definitely something new to Rolex and, far from me to complain, makes this model one of the most discreet and instrumental in the collection. It’s monochromatic, light on the wrist, and despite a size that I would have loved to be a bit smaller, a real joy to wear. It’s not a poser’s watch. The Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium is a tribute to when Rolex watches were made for a job. Yes, I’m very positive about this new release.
Availability & Price
The Rolex Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium 226627 isn’t yet available at retailers but will be soon. At least, on paper, as it won’t be easily accessible, even by Rolex standards. The brand doesn’t communicate production numbers, but we’ve heard that this will remain, for now, a rather exclusive model. It is priced at EUR 13,900 , CHF 13,400 or USD 14,050 . More details at rolex.com .
Technical specifications – Rolex Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium 226627
10 responses.
RLX, which is Grade 5 Titanium. 🙂 I laughed out loud, because it’s just so typical for the obfuscation the brand foists upon us via their marketing behemoth on an annual basis.
A “Piece Unique” is more common than this model ….
I have been looking forward to this for a while. But, I was hoping/expecting a more adjustable bracelet. If they can do it on the Pelagos at 1/3 the price, there’s no excuse they can’t do it for this
I only know that the so-called special steel Rolex uses on the bezel of their regular models was soft and easily scratched on the Rolex I owned. My humble Tissot which I wore every day for years, was much more scratch resistant. I wasn’t impressed with the materials Rolex uses. They make them look impressive in photos.I thought Rolex was the watch to have, until I got one.Sold and moved on.
IWC Mark XX vs new Ingenuier – the internet melts down at how expensive the watch is using the same movement.
DJ36 vs YM42 RLX- the internet would do anything (deranged Sxual favors included) to pay double for the YM even though they have the same movement.
Quite like the look of this one on its own, but on the wrist it looks genuinly gigantic..
Old dog doing new trick? It’s tough
Well, it really looks nice, and if it is that big and only weights 100 grams, that is really awesome!!!! I love Titanium watches more than any gold watch. But I am of the opinion that although Rolex is a brand producing excellent watches with a QC second to none, it is still too expensive for my taste. I own since 2017 as part of my watch collection, an Ocean 7 Diver chronometer with an ETA 2824-2, saphire crystal, ceramic bezel, 2000m WR with He Valve, and it had never failed me as my daily watch, and I only paid for it 365.00 USD including taxes new. I also have a 1971 Submariner, and I use both daily,one on each wrist, and I don’t see any difference on the accuracy/function. But I have to pay a fortune every time the Rolex is serviced, not with the Ocean 7 that I can service myself- I am a pretty good amateur watchmaker myself, is one of my hobbies. And when I am working at the Hospital near the MRI machines with that strong magnetic field, I then use my Speedmaster Master Chronometer with cal.3861, and it works flawlessly, and it is less expensive than this YM. I like expensive watches, but still look for the best bang of my buck. And I am an owner of a JLC Deep Sea 40mm, a Blancpain Fifty Fatoms, a Zodiac Super Sea Wolf, a Juvenia 200M Diver’s, and an Omega SMPO as part of my diver’s watch collection. But I like this Titanium YM a lot more than the Submariner or the Sea Dweller. That is what I can say.
best thing about this watch is it’s an alternative to the biG piLLowized case of the redesigned submariner a few years back. softer scratchable titanium and no bezel lume (guess people only yacht in the daytime) are reasons not to buy.
Really, why does one need a 42mm titanium Rolex watch when sailing his uber racing yacht!?! One need to keep your eyes on the gyro compass, or the magnetic compass including (always) the trim of the sails including the large readout on the on the E-chart display which includes instantly time, speed, direction and position. Last: Why does one need a watch when sailing in a corrosive salt sea and air environment? Answer: Beats me unless one wishes to show off his wealth at the yacht club dinner during post racing presentations where a 42mm titanium Rolex is a must.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Top stories.

Introducing Hajime Asaoka Revives Extinct Japanese Brand Takano and Presents the Chateau…

Introducing The Omega Paris 2024 Bronze Gold Edition

Editorial An Analysis of a Struggling Watch Market, New and Secondary, for…
Subscribe to our newsletter, subscribe to our newsletter.

Rolex Yacht-Master Watch Review
Rolex yacht-master review.
Rolex has built a reputation on their classic and timeless designs. They’re not one to release a new model every other year. In fact, after the launch of the Daytona in 1963, it would be nearly another 30 years before they’d debut an entirely new model. That model was the Rolex Yacht-Master. Here, we’ll provide a Rolex Yacht-Master review, including key features of the Rolex Yacht-Master, the history of the Rolex Yacht-Master through the years, and notable wearers.

List of Key Features of the Rolex Yacht-Master
- Case: Available in three different sizes – 37mm, 40mm, and 42mm – and two materials – gold or two-tone gold and platinum
- Bezel: Bidirectional, rotatable, 60-minute graduated bezel
- Crown: Screw-down, Triplock, water-resistant crown system
- Depth Rating: 100 meters of water resistance
- Movement: Perpetual, mechanical, self-winding movement manufactured by Rolex
- Band: Offered with either an Oyster bracelet or Oysterflex strap
History of the Rolex Yacht-Master through the Years
The very first Rolex Yacht-Master was the Reference 16628. The brand only offered the model in a 40mm, 18-karat yellow gold case with a white dial. The Ref. 16628 also came equipped with a screw-down, Triplock crown and boasted 100 meters of water resistance. Inside, it housed the Caliber 3135 movement.
For the first several years, Rolex only made minor changes to the Yacht-Master line. In 1994, they released a slightly different iteration of the Yacht-Master: the Reference 68628. This variation was smaller, with a 35mm case. That same year, they also added a women’s version of the Yacht-Master: the Reference 69628. It showcased an even more modest case size, measuring just 29mm.
In 1999, Rolex introduced the first major update to the Yacht-Master collection. That year, they debuted an all-new, patented combination of metals created specifically for the Yacht-Master. They called this two-tone combination of stainless steel and platinum, Rolesium . At the annual Basel World Fair, Rolex launched the material in three different sizes. These included the 40mm Reference 16622, 35mm Reference 168622, and the 29mm Reference 169622.
The next update to the Yacht-Master collection came in 2005. That year, Rolex added another two-tone variation to the line, this time in stainless steel and 18-karat yellow gold. They offered the new colorway in the 40mm Reference 16623. Two years later, Rolex made the most significant change to the Yacht-Master line with the addition of the Yacht-Master II . However, the lineage of the original Yacht-Master has continued.

In 2012, Rolex released the next notable upgrade for the Yacht-Master with the Reference 116622. While the model retained its 40mm sizing, it featured an all-new “super case” with different styling. In addition, it boasted an all-platinum bezel as opposed to a combination of platinum and stainless steel. Last but not least, it came equipped with a refined version of the Oyster bracelet featuring an upgraded clasp.
Three years later, Rolex debuted another first for the brand in the Yacht-Master collection’s Reference 116655. This time, instead of a new metal, they introduced their own rigorously designed and tested variation of the rubber strap. The Oysterflex bracele t marked the first-ever rubber strap for the brand. Ever since, it’s become a staple of the Yacht-Master collection.
In the past several years, Rolex has continued to make subtle updated and additions to the Yacht-Master line. One of the latest releases is the Yacht-Master 40 with a multi-color, gem-set bezel. More recently in 2019, Rolex introduced the first 42mm time-and-date Yacht Master Reference 226659.
Deep Dive on Key Features of the Rolex Yacht-Master
For years, 40mm was the standard sizing for the Yacht-Master. The smaller, 35mm variation was the only alternative up until around 2016. Rolex has since replaced it with the 37mm iteration for a smaller option. In addition, it’s only been since 2019 that Rolex has made a larger, 42mm option available.

One of the most notable key features of the Rolex Yacht-Master is the bidirectional, rotatable, 60-minute graduated bezel. Its design helps skippers measure and anticipate the crucial countdown interval leading up to the start of a regatta or sailing race. The screw-down, Triplock crown is another key feature of the Rolex Yacht-Master. This water-resistant system has been a staple of the model since its inception.
With only 100 meters of water resistance, the Yacht-Master is perfect for enjoying a day on the water as opposed to scuba diving. Yet, its in-house, perpetual, mechanical, self-winding movement makes it a robust watch for any occasion. In addition, the option of Oyster bracelet or Oysterflex strap made it versatile enough to take from land to sea.
Who Wears the Rolex Yacht-Master?
The Yacht-Master is a popular choice among many of today’s top entertainers, athletes, and chefs. Some of the Yacht-Master’s famous wearers include TV personality Ellen DeGeneres and film icons like Brad Pitt and Bruce Willis . Athletes across an array of modalities also appreciate the Yacht-Master. You can find it on the wrist of star players like former pro-footballer David Beckham, Atlanta Falcons quarterback Matt Ryan , and former World Number One golfer Justin Thomas. Last but certainly not least, the legendary chef Emeril Lagasse is among the Yacht-Master’s celebrity fans.

Get More Articles Like This in Your Inbox
We're constantly creating great content like this. So, why not get it delivered directly to your inbox? By subscribing you agree to our Privacy Policy but you can unsubscribe at any time.
Written by Crown & Caliber
Crown & Caliber is the smartest way to buy or sell a luxury watch. As an exclusively online marketplace for pre-owned timepieces, Crown & Caliber exists to ensure that when it comes down to the final transaction, buyers and sellers can both win. For sellers, we do all the legwork of valuating, marketing, and selling—for buyers, we put trust back into the act of purchasing sight-unseen with our servicing and authentication process. By emphasizing transparency and placing value on quality, Crown & Caliber has become the preferred marketplace for watch collectors and casual enthusiasts alike.
Rolex Day Date Prices
Rolex gmt master ii prices & rolex gmt master i prices, no comments.
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.
FIFTH WRIST
Owner review: rolex yacht-master 37 268621.
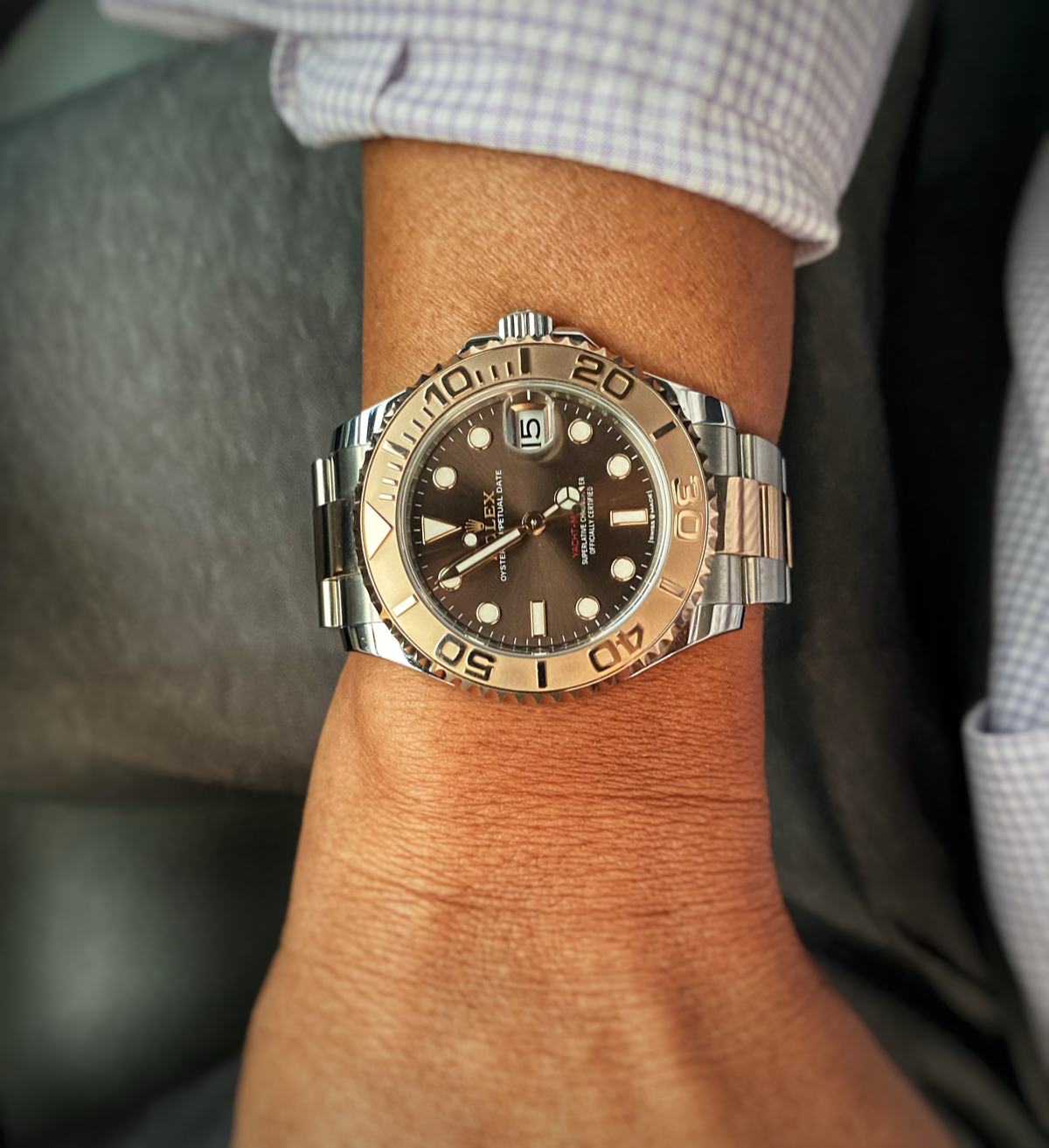

The Yacht-Master line of Rolex has never been a hugely popular series from the acclaimed watch house. That is not necessarily a bad thing though. This was actually the main reason that I got attracted to the Rolex Yacht-Master 37 268621 in the first place.
There are very few of these that you will actually see in the wild.
The Rolex Yacht-Master 37 268621 has such an elegant profile, it is similar to the case of a modern Datejust and Daytona with lugs slopping down and hugging one’s wrist. So when I got a call from my Rolex authorized dealer last year (I waited for a week…. Yes you read it right, waited only for a week) I didn’t think twice and drove myself the very next day to pick it up in person.
I picked up the less popular 37mm two-tone rose gold version and I absolutely love it. The Rolex rose gold is so warm that one tends to get mesmerized by it (at least I do). The elegance of the profile, shine and tone of the rose gold and weight does not disappoint. I wear this in the office and on the beach… literally an incredibly versatile timepiece.

A lot of people might be wondering why I opted for the Rolex Yacht-Master 37 268621 rather than the popular 40mm. I always prefer the more modest sized watches and thought this one was a good fit on my 6.5 inch wrist. I have a number of 40mm watches in my current collection and I thought the 37mm would be a good addition for a more “classy touch”. It is still a mystery to me why this line has not shoot up in popularity and value. Something deep inside me would prefer to keep it that way… a hidden gem that only a few know and appreciate!

the_watch_freak_ph
LEVi A Filipino Watch Nerd ??? Not an expert but a curious soul who loves to learn more about horology, the watch community & watches in general. ?
One response to “Owner review: Rolex Yacht-Master 37 268621”
One of my favorite two tones watch +1
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

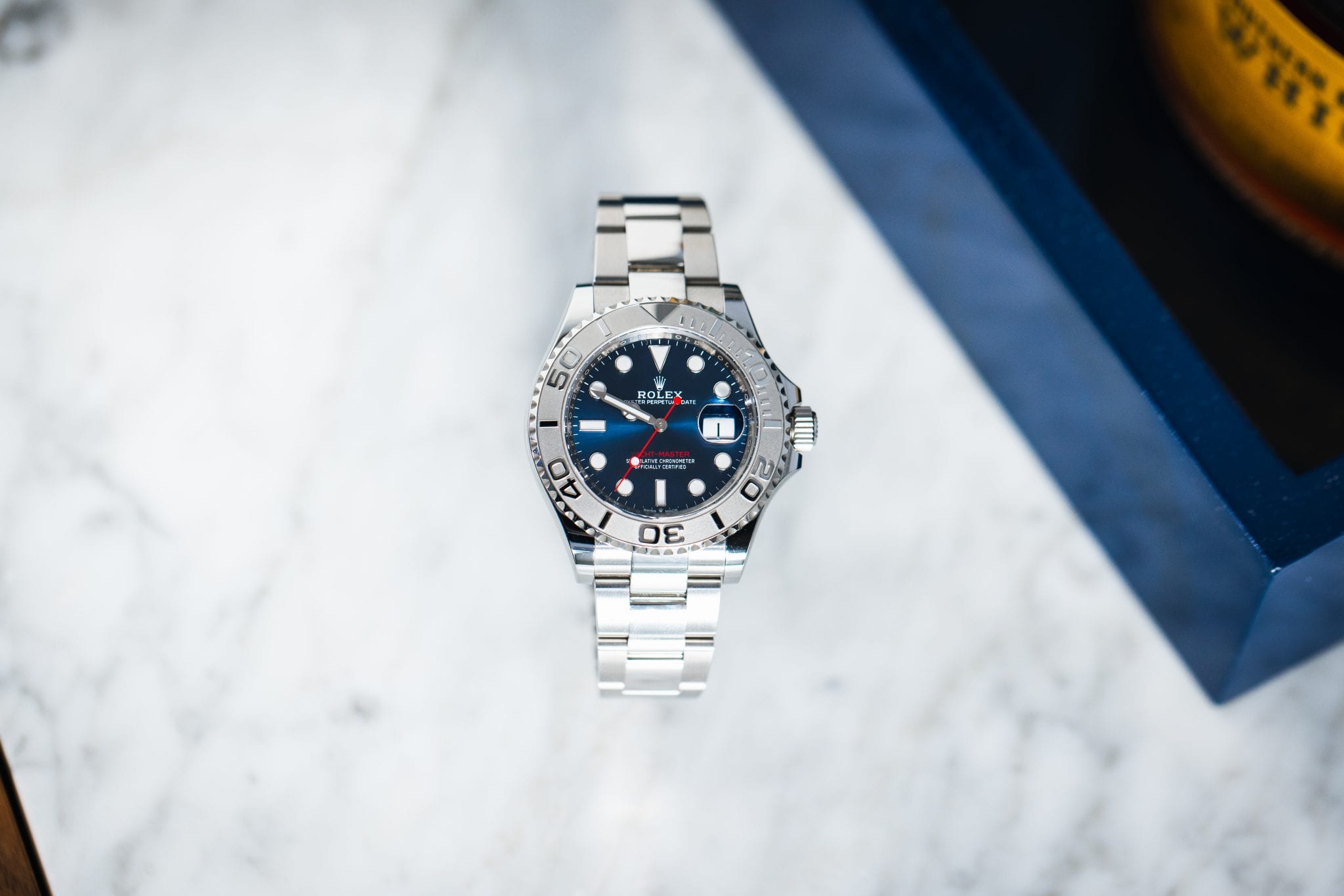
Rolex Yacht-Master 40 Blue Dial Men's Luxury Watch 126622-0002

You May Also Like

Subscribe to our mailing list
- Created with Sketch.
A Closer Look at the Rolex GMT Master II Batman
R olex introduced the 116710BLNR in 2013, with its striking black and blue Cerachrom bezel prompting Rolex afficionados to assign the Rolex GMT Batman, or simply Rolex Batman, moniker. The orginal model remained in production until 2019, when Rolex released the 126710BLNR on a Jubilee bracelet (the Rolex GMT Batgirl). However in 2021 Rolex reintroduced the Rolex Batman model with its Oyster bracelet, therefore offering two options for collectors.
The Rolex GMT Batman has remained extremely popular throughout its two production runs, with owners prizing the combination of trademark Rolex build quality and striking aesthetic. Sotheby's global network of Rolex specialists have sold many Rolex Batman variants across auctions in New York, Paris and Hong Kong. Below we summarize the essential information for this iconic luxury sports watch.

Key Features of the Rolex Batman
- Dual Time Zone: Displays two time zones simultaneously with an additional blue 24-hour hand and a rotatable 24-hour graduated bezel.
- Cerachrom Bezel: The two-tone black and blue Cerachrom bezel is virtually scratch-proof and resistant to fading, maintaining its vibrant appearance over time. The Rolex Batman was Rolex's first two-tone colour Cerachrom bezel (reflecting the difficult of working with the material).
- Material Options: Available in Oystersteel, ensuring durability and corrosion resistance.
- Sizes: Exclusively offered in 40mm, the size provides a perfect balance between wrist presence and comfort, suiting both men and women.
- Dial: The black dial features large hour markers and hands filled with Chromalight for exceptional legibility in any lighting conditions.
- Bracelet: The Oyster bracelet defines the Rolex GMT Batman variant, offering comfort, durability, and a secure fit with the Oysterlock safety clasp.
- Movement: Powered by the Rolex Caliber 3285, an automatic movement with a power reserve of approximately 70 hours, and featuring a Parachrom hairspring for increased precision and resistance to shocks and temperature variations.

Notable Models of the Rolex GMT Batman
- Rolex GMT Master II Batman Reference 116710BLNR: The original model introduced in 2013 with an Oyster bracelet.
- Rolex GMT Master II Batman Reference 126710BLNR: The Rolex Batman was essentially re-released in 2021, featuring the updated Caliber 3285 movement and Oyster bracelet.

Source Your Next Rolex GMT Batman
The Rolex GMT Batman, whether the original 116710BLNR or the newer 126710BLNR released in 2021, remains one of the most sought after watches globally. Sotheby's is on hand to support as a trusted partner, whether that's selling or buying one of these iconic luxury sports watches.
- Browse Rolex GMT Masters available for immediate delivery
- Explore upcoming watch auctions across the globe
- Speak to our specialists about selling your Rolex
- Research your Rolex GMT Master investment using our extensive Rolex sale archive .
Trust our worldwide network of leading Rolex specialists from a globally renowned auction house with a 280 year history.
Shop Rolex GMT-Masters

About the Author
More from sotheby's, stay informed with sotheby’s top stories, videos, events & news..
By subscribing you are agreeing to Sotheby’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe from Sotheby’s emails at any time by clicking the “Manage your Subscriptions” link in any of your emails.
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer

- Français
OYSTER PERPETUAL YACHT-MASTER 42

MASTERING LIGHTNESS
Light and robust, the new Yacht-Master 42, in RLX titanium, is the ally of those who revel in freedom. Especially suited to the demands and pressures of competitive sailing, it delivers exceptional performance.
Rolex is presenting a new version of the Oyster Perpetual Yacht-Master 42. This nautical watch is introduced for the first time in RLX titanium – a particularly strong but lightweight alloy – and is fitted on an Oyster bracelet. The new version stands out for its technical satin finish – a satin finish with a visible grain, a feature of Rolex watches in RLX titanium – which extends to the middle case sides, the edges of the bracelet links and the sides of the clasp cover. The chamfered top edges of the middle case lugs have a high-sheen finish, while the crown guard is polished. With its bidirectional rotatable bezel fitted with a Cerachrom insert in matt black ceramic featuring raised and polished numerals and graduations, the Yacht-Master 42 in RLX titanium remains faithful to the aesthetics of the original model, unveiled in 2019. It is graced with an intense black dial in a fine satin finish, and its Oyster bracelet is equipped with the Easylink comfort extension link. The new version of the Yacht-Master 42 is equipped with calibre 3235, a movement at the forefront of watchmaking technology, enabling it to display the date as well as the hours, minutes and seconds. Like all Rolex watches, the Oyster Perpetual Yacht-Master 42 carries the Superlative Chronometer certification, which ensures excellent performance on the wrist.

THE CALL OF THE OPEN SEAS Launched in 1992, the Yacht-Master was designed specifically for navigators and skippers. Embodying the rich heritage that has bound Rolex and the world of sailing since the 1950s, this Professional-category watch provides a perfect blend of functionality and nautical style, making it equally at home on and off the water. An emblematic nautical timepiece, it is easily recognized by its bidirectional rotatable 60-minute graduated bezel made entirely from precious metal or fitted with a Cerachrom insert in high-technology ceramic.

RLX TITANIUM RLX titanium is a grade 5 titanium alloy specially selected by Rolex. Like all titanium alloys, it is especially lightweight and is noted for its mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. Another characteristic of RLX titanium is the possibility of working it to give a polished or satin finish according to the brand’s specifications. Its high mechanical strength makes it complex to work with, and the decision to use it has required the introduction of special production processes.

HIGH-TECHNOLOGY CERAMIC Rolex played a pioneering role in the development of special ceramics for creating monobloc bezels and bezel inserts. Not only are these materials virtually scratchproof, their colours are also of a rare intensity and are resistant to environmental effects. In addition, thanks to its chemical composition, the high-tech ceramic is inert and cannot corrode. Rolex has developed exclusive expertise and innovative manufacturing methods that grant it complete independence in the production of these ceramic components. On the new version of the Yacht-Master 42, the bidirectional rotatable bezel is fitted with a 60-minute graduated Cerachrom insert in matt black ceramic. Its raised graduations and numerals are first moulded into the ceramic and then polished. The first 15 minutes are graduated minute-by-minute to allow time intervals to be read with great precision. The bezel can also be turned with ease thanks to its knurled edge, which offers excellent grip.

OYSTER CASE, SYMBOL OF WATERPROOFNESS A paragon of robustness and reliability, the 42 mm Oyster case of the new Yacht-Master 42 is guaranteed waterproof to a depth of 100 metres (330 feet). The middle case is crafted from a solid block of RLX titanium. Its case back, edged with fine fluting, is hermetically screwed down with a special tool that allows only Rolex watchmakers to access the movement. The Triplock winding crown, fitted with a triple waterproofness system and protected by an integral crown guard, screws down securely against the case. The crystal, which features a Cyclops lens at 3 o’clock for easy reading of the date, is made of virtually scratchproof sapphire and benefits from an anti-reflective coating. The waterproof Oyster case provides optimal protection for the movement it houses.

PERPETUAL CALIBRE 3235 The new version of the Yacht-Master 42 is equipped with calibre 3235, a movement entirely developed and manufactured by Rolex that was released in 2015 and has been fitted on this model since its launch in 2019. A distillation of technology, this self-winding mechanical movement delivers outstanding performance in terms of precision, power reserve, convenience and reliability. Calibre 3235 incorporates the patented Chronergy escapement, which combines high energy efficiency with great dependability. Made of nickel-phosphorus, this escapement is resistant to strong magnetic fields. The movement is fitted with a blue Parachrom hairspring, manufactured by Rolex in a paramagnetic alloy. The hairspring offers great stability in the face of temperature variations as well as high resistance to shocks. It is equipped with a Rolex overcoil, ensuring the calibre’s regularity in any position. The oscillator is mounted on the Rolex-designed, patented high-performance Paraflex shock absorbers, increasing the movement’s shock resistance. The oscillating weight is now fitted with an optimized ball bearing. Calibre 3235 is equipped with a self-winding system via a Perpetual rotor. Thanks to its barrel architecture and the escapement’s superior efficiency, the power reserve of calibre 3235 extends to approximately 70 hours.
OYSTER BRACELET AND OYSTERLOCK SAFETY CLASP The new version of the Yacht-Master 42, made from RLX titanium, is fitted on an Oyster bracelet. Developed at the end of the 1930s, this three-piece link bracelet remains the most universal in the Oyster Perpetual collection and is known for its robustness. The Oyster bracelet of this new version of the Yacht-Master 42 features the Oysterlock folding safety clasp, which prevents accidental opening. It is also equipped with the Easylink comfort extension link, developed by Rolex, which allows the wearer to easily adjust the bracelet length by approximately 5 mm. The Oyster bracelet in RLX titanium also includes patented ceramic inserts – designed by the brand – inside the links to enhance its flexibility on the wrist and its longevity.

SUPERLATIVE CHRONOMETER CERTIFICATION Like all Rolex watches, the Oyster Perpetual Yacht-Master 42 is covered by the Superlative Chronometer certification redefined by Rolex in 2015. This designation testifies that every watch leaving the brand’s workshops has successfully undergone a series of tests conducted by Rolex in its own laboratories according to its own criteria, following the official certification of the movements by the Swiss Official Chronometer Testing Institute (COSC). The in-house certification tests apply to the fully assembled watch, after casing the movement, guaranteeing superlative performance on the wrist in terms of precision, power reserve, waterproofness and self-winding. The precision of a Rolex Superlative Chronometer is of the order of −2 /+2 seconds per day – the rate deviation tolerated by the brand for a finished watch is significantly smaller than that accepted by COSC for official certification of the movement alone. The Superlative Chronometer status is symbolized by the green seal that comes with every Rolex watch and is coupled with an international five-year guarantee.

Related content

OYSTER PERPETUAL COSMOGRAPH DAYTONA
The emblematic style and technical performance of the Cosmograph Daytona have cemented its iconic status well beyond the motor racing circuits. To mark the 60th anniversary of the watch, Rolex ensures the legend lives on by revisiting the entire range.

PERPETUAL 1908
Elegant, classic and decidedly contemporary, the 1908 immortalizes Rolex’s age-long daring spirit. Its conception is the result of the brand’s comprehensive in-house expertise and unwavering commitment to excellence.

OYSTER PERPETUAL SKY-DWELLER
With its two time zones and annual Saros calendar, the Sky-Dweller is an elegant and trusted companion for world travellers. The range has been updated with numerous enhancements illustrating the role that excellence plays even in the tiniest details.

OYSTER PERPETUAL GMT-MASTER II
The GMT-Master II is available this year in two new versions – yellow Rolesor and 18 ct yellow gold – with a Cerachrom bezel insert in grey and black ceramic, an entirely new colour combination.

OYSTER PERPETUAL EXPLORER 40
The Explorer range is expanded with the arrival of a new 40 mm model. Offering enhanced legibility, this timepiece carries all the qualities that have made the Explorer – one of the brand’s first Professional watches – a reference throughout the decades. Simple, robust and corrosion resistant, the new Explorer 40 is crafted from Oystersteel, a Rolex proprietary alloy.

OYSTER PERPETUAL
Alive with colour, vitality and positivity, the new dials of the Oyster Perpetual in 31 mm, 36 mm and 41 mm are dotted with many-coloured bubbles that joyfully reunite the five hues introduced to the range in 2020.

OYSTER PERPETUAL DAY-DATE 36
With these versions of the Day-Date 36, Rolex brings an unexpected creative twist to one of its iconic models. By displaying a new emotion each day, the watch brings an element of spontaneity into the wearers’ daily life and allows them to invest the reading of time with their changing mood.

The new Day-Date 36 welcomes dials made of decorative stone in shimmering tones that evoke the atmosphere of the Mediterranean coast.
does homework reinforce learning
Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
When celtics star derrick white banged up his smile in the nba finals, this bu alum’s dental office fixed him up, rev. james lawson, crusading confidant of mlk, dies at 95, his first broadway show just earned this cfa alum a tony award nod, kyrie irving signs his dad—bu alum drederick irving—to his shoe line, opening doors: michele courton brown (cas’83), six bu alums to remember this memorial day, american academy of arts & sciences welcomes five bu members, com’s newest journalism grad took her time, could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin.
More From Forbes
Why homework doesn't seem to boost learning--and how it could.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Some schools are eliminating homework, citing research showing it doesn’t do much to boost achievement. But maybe teachers just need to assign a different kind of homework.
In 2016, a second-grade teacher in Texas delighted her students—and at least some of their parents—by announcing she would no longer assign homework. “Research has been unable to prove that homework improves student performance,” she explained.
The following year, the superintendent of a Florida school district serving 42,000 students eliminated homework for all elementary students and replaced it with twenty minutes of nightly reading, saying she was basing her decision on “solid research about what works best in improving academic achievement in students.”
Many other elementary schools seem to have quietly adopted similar policies. Critics have objected that even if homework doesn’t increase grades or test scores, it has other benefits, like fostering good study habits and providing parents with a window into what kids are doing in school.
Those arguments have merit, but why doesn’t homework boost academic achievement? The research cited by educators just doesn’t seem to make sense. If a child wants to learn to play the violin, it’s obvious she needs to practice at home between lessons (at least, it’s obvious to an adult). And psychologists have identified a range of strategies that help students learn, many of which seem ideally suited for homework assignments.
For example, there’s something called “ retrieval practice ,” which means trying to recall information you’ve already learned. The optimal time to engage in retrieval practice is not immediately after you’ve acquired information but after you’ve forgotten it a bit—like, perhaps, after school. A homework assignment could require students to answer questions about what was covered in class that day without consulting their notes. Research has found that retrieval practice and similar learning strategies are far more powerful than simply rereading or reviewing material.
One possible explanation for the general lack of a boost from homework is that few teachers know about this research. And most have gotten little training in how and why to assign homework. These are things that schools of education and teacher-prep programs typically don’t teach . So it’s quite possible that much of the homework teachers assign just isn’t particularly effective for many students.
Even if teachers do manage to assign effective homework, it may not show up on the measures of achievement used by researchers—for example, standardized reading test scores. Those tests are designed to measure general reading comprehension skills, not to assess how much students have learned in specific classes. Good homework assignments might have helped a student learn a lot about, say, Ancient Egypt. But if the reading passages on a test cover topics like life in the Arctic or the habits of the dormouse, that student’s test score may well not reflect what she’s learned.
The research relied on by those who oppose homework has actually found it has a modest positive effect at the middle and high school levels—just not in elementary school. But for the most part, the studies haven’t looked at whether it matters what kind of homework is assigned or whether there are different effects for different demographic student groups. Focusing on those distinctions could be illuminating.
A study that looked specifically at math homework , for example, found it boosted achievement more in elementary school than in middle school—just the opposite of the findings on homework in general. And while one study found that parental help with homework generally doesn’t boost students’ achievement—and can even have a negative effect— another concluded that economically disadvantaged students whose parents help with homework improve their performance significantly.
That seems to run counter to another frequent objection to homework, which is that it privileges kids who are already advantaged. Well-educated parents are better able to provide help, the argument goes, and it’s easier for affluent parents to provide a quiet space for kids to work in—along with a computer and internet access . While those things may be true, not assigning homework—or assigning ineffective homework—can end up privileging advantaged students even more.
Students from less educated families are most in need of the boost that effective homework can provide, because they’re less likely to acquire academic knowledge and vocabulary at home. And homework can provide a way for lower-income parents—who often don’t have time to volunteer in class or participate in parents’ organizations—to forge connections to their children’s schools. Rather than giving up on homework because of social inequities, schools could help parents support homework in ways that don’t depend on their own knowledge—for example, by recruiting others to help, as some low-income demographic groups have been able to do . Schools could also provide quiet study areas at the end of the day, and teachers could assign homework that doesn’t rely on technology.
Another argument against homework is that it causes students to feel overburdened and stressed. While that may be true at schools serving affluent populations, students at low-performing ones often don’t get much homework at all—even in high school. One study found that lower-income ninth-graders “consistently described receiving minimal homework—perhaps one or two worksheets or textbook pages, the occasional project, and 30 minutes of reading per night.” And if they didn’t complete assignments, there were few consequences. I discovered this myself when trying to tutor students in writing at a high-poverty high school. After I expressed surprise that none of the kids I was working with had completed a brief writing assignment, a teacher told me, “Oh yeah—I should have told you. Our students don’t really do homework.”
If and when disadvantaged students get to college, their relative lack of study skills and good homework habits can present a serious handicap. After noticing that black and Hispanic students were failing her course in disproportionate numbers, a professor at the University of North Carolina decided to make some changes , including giving homework assignments that required students to quiz themselves without consulting their notes. Performance improved across the board, but especially for students of color and the disadvantaged. The gap between black and white students was cut in half, and the gaps between Hispanic and white students—along with that between first-generation college students and others—closed completely.
There’s no reason this kind of support should wait until students get to college. To be most effective—both in terms of instilling good study habits and building students’ knowledge—homework assignments that boost learning should start in elementary school.
Some argue that young children just need time to chill after a long day at school. But the “ten-minute rule”—recommended by homework researchers—would have first graders doing ten minutes of homework, second graders twenty minutes, and so on. That leaves plenty of time for chilling, and even brief assignments could have a significant impact if they were well-designed.
But a fundamental problem with homework at the elementary level has to do with the curriculum, which—partly because of standardized testing— has narrowed to reading and math. Social studies and science have been marginalized or eliminated, especially in schools where test scores are low. Students spend hours every week practicing supposed reading comprehension skills like “making inferences” or identifying “author’s purpose”—the kinds of skills that the tests try to measure—with little or no attention paid to content.
But as research has established, the most important component in reading comprehension is knowledge of the topic you’re reading about. Classroom time—or homework time—spent on illusory comprehension “skills” would be far better spent building knowledge of the very subjects schools have eliminated. Even if teachers try to take advantage of retrieval practice—say, by asking students to recall what they’ve learned that day about “making comparisons” or “sequence of events”—it won’t have much impact.
If we want to harness the potential power of homework—particularly for disadvantaged students—we’ll need to educate teachers about what kind of assignments actually work. But first, we’ll need to start teaching kids something substantive about the world, beginning as early as possible.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Donate (opens in a new window)

Curriculum and Instruction
Key Lessons: What Research Says About the Value of Homework
Whether homework helps students — and how much homework is appropriate — has been debated for many years. Homework has been in the headlines again recently and continues to be a topic of controversy, with claims that students and families are suffering under the burden of huge amounts of homework. School board members, educators, and parents may wish to turn to the research for answers to their questions about the benefits and drawbacks of homework. Unfortunately, the research has produced mixed results so far, and more research is needed. Nonetheless, there are some findings that can help to inform decisions about homework. What follows is a summary of the research to date:
The link between homework and student achievement is far from clear.
There is no conclusive evidence that homework increases student achievement across the board. Some studies show positive effects of homework under certain conditions and for certain students, some show no effects, and some suggest negative effects (Kohn 2006; Trautwein and Koller 2003).
Homework appears to have more positive effects for certain groups of students.
- Older students benefit more from homework than younger students.
- Some studies have shown that older students gain more academic benefits from homework than do younger students, perhaps because younger students have less-effective study habits and are more easily distracted (Cooper 1989; Hoover-Dempsey et al. 2001; Leone and Richards 1989; Muhlenbruck et al. 2000).
- Students from low-income homes may not benefit as much from homework as those from higher-income homes.
- Some researchers believe that students from higher-income homes have more resources (such as computers) and receive more assistance with homework, while low-income students may have fewer resources and less assistance and are therefore less likely to complete the homework and reap any related benefits (McDermott, Goldmen and Varenne 1984; Scott-Jones 1984).
- Students with learning disabilities benefit from homework under certain conditions.
- Students with learning disabilities can benefit from homework if appropriate supervision and monitoring are provided (Cooper and Nye 1994; Rosenberg 1989).
- Asian American students may benefit more from homework than do students from other ethnic groups.
- A national study of the influence of homework on student grades across five ethnic groups found that homework had a stronger impact on Asian American students than on students of other ethnicities (Keith and Benson, 1992).
Homework may have nonacademic benefits.
Certain nonacademic benefits of homework have been shown, especially for younger students. Indeed, some primary-level teachers may assign homework for such benefits, which include learning the importance of responsibility, managing time, developing study habits, and staying with a task until it is completed (Cooper, Robinson and Patall 2006; Corno and Xu 2004; Johnson and Pontius 1989; Warton 2001).
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness.
While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night). When students spend more time than this on homework, the positive relationship with student achievement diminishes (Cooper, Robinson, and Patall 2006).
The amount of homework completed by students seems to be more positively associated with student achievement than the amount of homework assigned by teachers.
Some research has shown that students who spend more time on homework score higher on measures of achievement and attitude. Studies that have delved more deeply into this topic suggest, however, that the amount of homework assigned by teachers is unrelated to student achievement, while the amount of homework actually completed by students is associated with higher achievement (Cooper 2001; Cooper, Lindsay, Nye, and Greathouse 1998).
After-school programs that provide homework assistance may improve student behavior, motivation, and work habits but not necessarily academic achievement.
Studies of after-school programs that provide homework assistance have found few definite links to improved student achievement. Several studies, however, noted improvements in student motivation and work habits, which may indirectly affect achievement (Cosden, Morrison, Albanese, and Macias 2001; James-Burdumy et al. 2005).
The effect of parent involvement in homework is unclear. Studies of parent involvement in homework have produced mixed results.
Homework assignments that require interaction between students and parents result in higher levels of parent involvement and are more likely to be turned in than noninteractive assignments. Some studies have shown, however, that parent involvement in homework has no impact on student achievement. Other studies indicate that students whose parents are more involved in their homework have lower test scores and class grades — but this may be because the students were already lower performing and needed more help from their parents than did higher-performing students. (Balli, Wedman, and Demo 1997; Cooper, Lindsay, and Nye 2000; Epstein 1988; Van Voorhis 2003).
There is little research on connections between specific kinds of homework and student achievement.
Most teachers assign homework to reinforce what was presented in class or to prepare students for new material. Less commonly, homework is assigned to extend student learning to different contexts or to integrate learning by applying multiple skills around a project. Little research exists on the effects of these different kinds of homework on student achievement, leaving policymakers with little evidence on which to base decisions (Cooper 1989; Foyle 1985; Murphy and Decker 1989).
Liked it? Share it!
Balli, S. J., Wedman, J. F., & Demo, D. H. (1997). Family involvement with middle-grades homework: Effects of differential prompting. Journal of Experimental Education, 66, 31-48.
Cooper, H. (1989). Homework. White Plains, N.Y.: Longman.
Cooper, H. (2001). Homework for all — in moderation. Educational Leadership, 58, 34-38.
Cooper, H., Lindsay, J. J, Nye, B., & Greathouse, S. (1998). Relationships among attitudes about homework, amount of homework assigned and completed, and student achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(1), 70-83.
Cooper, H., & Nye, B. (1994). Homework for students with learning disabilities: The implications of research for policy and practice. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 27, 470-479.
Cooper, H., Nye, B.A., & Lindsay, J.J. (2000). Homework in the home: How student, family and parenting style differences relate to the homework process. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25(4), 464-487.
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research. Review of Educational Research, 76, 1-62.
Corno, L., & Xu, J. (2004). Homework as the job of childhood. Theory Into Practice, 43, 227-233.
Cosden, M., Morrison, G., Albanese, A. L., & Macias, S. (2001). When homework is not home work: After-school programs for homework assistance. Educational Psychologist, 36(3), 211-221.
Epstein, J. L. (1998). Homework practices, achievements, and behaviors of elementary school students. Baltimore: Center for Research on Elementary and Middle Schools. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED301322]
Foyle, H. C. (1985). The effects of preparation and practice homework on student achievement in tenth-grade American history (Doctoral dissertation, Kansas State University, 1985). Dissertation Abstracts International, 45, 8A.
Hoover-Dempsey, K. V., Battiato, A. C., Walker, J. M. T., Reed, R. P., DeJong, J. M. & Jones, K. P. (2001). Parental involvement in homework. Educational Psychologist, 36, 195-209.
James-Burdumy, S., Dynarski, M., Moore, M., Deke, J., Mansfield, W., Pistorino, C. & Warner, E. (2005). When Schools Stay Open Late: The National Evaluation of the 21st Century Community Learning Centers Program Final Report. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Education/Institute of Education Sciences National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance.
Johnson, J. K., & Pontius, A. (1989). Homework: A survey of teacher beliefs and practices. Research in Education, 41, 71-78.
Keith, T. Z., & Benson, M. J. (1992). Effects of manipulable influences on high school grades across five ethnic groups. Journal of Educational Research, 86, 85-93.
Kohn, A. (2006, September). Abusing research: The study of homework and other examples. Phi Delta Kappan, 8-22.
Leone, C. M., & Richards, M. H. (1989). Classwork and homework in early adolescence: The ecology of achievement. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 18, 531-548.
McDermott, R. P., Goldman, S. V., & Varenne, H. (1984). When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework [Abstract]. Teachers College Record, 85, 391-409.
Muhlenbruck, L., Cooper, H., Nye, B., & Lindsay, J. J. (2000). Homework and achievement: explaining the different strengths of relation at the elementary and secondary school levels. Social Psychology of Education, 3, 295-317.
Murphy, J. & Decker, K. (1989). Teachers’ use of homework in high schools. Journal of Educational Research, 82(5), 261-269.
Rosenberg, M. S. (1989). The effects of daily homework assignments on the acquisition of basic skills by students with learning disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 22, 314-323.
Scott-Jones, D. (1984). Family influences on cognitive development and school achievement. Review of Research in Education, 11, 259-304.
Trautwein, U., & Koller, O. (2003). The relationship between homework and achievement — still much of a mystery. Educational Psychology Review, 15, 115-145.
Van Voorhis, F. L. (2003). Interactive homework in middle school: Effects on family involvements and science achievement. Journal of Educational Research, 96(6), 323-338.
Warton, P. M. (2001). The forgotten voice in homework: Views of students. Educational Psychologist, 36, 155-165.
Related Topics
Homework – top 3 pros and cons.
Pro/Con Arguments | Discussion Questions | Take Action | Sources | More Debates

From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. [ 1 ]
While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word “homework” dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home. Memorization exercises as homework continued through the Middle Ages and Enlightenment by monks and other scholars. [ 45 ]
In the 19th century, German students of the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given assignments to complete outside of the school day. This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann , who encountered the idea in Prussia. [ 45 ]
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies’ Home Journal , decried homework’s negative impact on children’s physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but the prevailing argument was that kids needed time to do household chores. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 45 ] [ 46 ]
Public opinion swayed again in favor of homework in the 1950s due to concerns about keeping up with the Soviet Union’s technological advances during the Cold War . And, in 1986, the US government included homework as an educational quality boosting tool. [ 3 ] [ 45 ]
A 2014 study found kindergarteners to fifth graders averaged 2.9 hours of homework per week, sixth to eighth graders 3.2 hours per teacher, and ninth to twelfth graders 3.5 hours per teacher. A 2014-2019 study found that teens spent about an hour a day on homework. [ 4 ] [ 44 ]
Beginning in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic complicated the very idea of homework as students were schooling remotely and many were doing all school work from home. Washington Post journalist Valerie Strauss asked, “Does homework work when kids are learning all day at home?” While students were mostly back in school buildings in fall 2021, the question remains of how effective homework is as an educational tool. [ 47 ]
Is Homework Beneficial?
Pro 1 Homework improves student achievement. Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicated that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” [ 6 ] Students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework on both standardized tests and grades. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take-home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school. [ 10 ] Read More
Pro 2 Homework helps to reinforce classroom learning, while developing good study habits and life skills. Students typically retain only 50% of the information teachers provide in class, and they need to apply that information in order to truly learn it. Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, co-founders of Teachers Who Tutor NYC, explained, “at-home assignments help students learn the material taught in class. Students require independent practice to internalize new concepts… [And] these assignments can provide valuable data for teachers about how well students understand the curriculum.” [ 11 ] [ 49 ] Elementary school students who were taught “strategies to organize and complete homework,” such as prioritizing homework activities, collecting study materials, note-taking, and following directions, showed increased grades and more positive comments on report cards. [ 17 ] Research by the City University of New York noted that “students who engage in self-regulatory processes while completing homework,” such as goal-setting, time management, and remaining focused, “are generally more motivated and are higher achievers than those who do not use these processes.” [ 18 ] Homework also helps students develop key skills that they’ll use throughout their lives: accountability, autonomy, discipline, time management, self-direction, critical thinking, and independent problem-solving. Freireich and Platzer noted that “homework helps students acquire the skills needed to plan, organize, and complete their work.” [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 49 ] Read More
Pro 3 Homework allows parents to be involved with children’s learning. Thanks to take-home assignments, parents are able to track what their children are learning at school as well as their academic strengths and weaknesses. [ 12 ] Data from a nationwide sample of elementary school students show that parental involvement in homework can improve class performance, especially among economically disadvantaged African-American and Hispanic students. [ 20 ] Research from Johns Hopkins University found that an interactive homework process known as TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) improves student achievement: “Students in the TIPS group earned significantly higher report card grades after 18 weeks (1 TIPS assignment per week) than did non-TIPS students.” [ 21 ] Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, “Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to them.” [ 12 ] Read More
Con 1 Too much homework can be harmful. A poll of California high school students found that 59% thought they had too much homework. 82% of respondents said that they were “often or always stressed by schoolwork.” High-achieving high school students said too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems. [ 24 ] [ 28 ] [ 29 ] Alfie Kohn, an education and parenting expert, said, “Kids should have a chance to just be kids… it’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.” [ 27 ] Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, explained, “More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies.” [ 48 ] Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments. Even parents take shortcuts on homework: 43% of those surveyed admitted to having completed a child’s assignment for them. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] [ 32 ] Read More
Con 2 Homework exacerbates the digital divide or homework gap. Kiara Taylor, financial expert, defined the digital divide as “the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology and those that don’t. Though the term now encompasses the technical and financial ability to utilize available technology—along with access (or a lack of access) to the Internet—the gap it refers to is constantly shifting with the development of technology.” For students, this is often called the homework gap. [ 50 ] [ 51 ] 30% (about 15 to 16 million) public school students either did not have an adequate internet connection or an appropriate device, or both, for distance learning. Completing homework for these students is more complicated (having to find a safe place with an internet connection, or borrowing a laptop, for example) or impossible. [ 51 ] A Hispanic Heritage Foundation study found that 96.5% of students across the country needed to use the internet for homework, and nearly half reported they were sometimes unable to complete their homework due to lack of access to the internet or a computer, which often resulted in lower grades. [ 37 ] [ 38 ] One study concluded that homework increases social inequality because it “potentially serves as a mechanism to further advantage those students who already experience some privilege in the school system while further disadvantaging those who may already be in a marginalized position.” [ 39 ] Read More
Con 3 Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We’ve known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that “homework had no association with achievement gains” when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7 ] Fourth grade students who did no homework got roughly the same score on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) math exam as those who did 30 minutes of homework a night. Students who did 45 minutes or more of homework a night actually did worse. [ 41 ] Temple University professor Kathryn Hirsh-Pasek said that homework is not the most effective tool for young learners to apply new information: “They’re learning way more important skills when they’re not doing their homework.” [ 42 ] In fact, homework may not be helpful at the high school level either. Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, stated, “I interviewed high school teachers who completely stopped giving homework and there was no downside, it was all upside.” He explains, “just because the same kids who get more homework do a little better on tests, doesn’t mean the homework made that happen.” [ 52 ] Read More
Discussion Questions
1. Is homework beneficial? Consider the study data, your personal experience, and other types of information. Explain your answer(s).
2. If homework were banned, what other educational strategies would help students learn classroom material? Explain your answer(s).
3. How has homework been helpful to you personally? How has homework been unhelpful to you personally? Make carefully considered lists for both sides.
Take Action
1. Examine an argument in favor of quality homework assignments from Janine Bempechat.
2. Explore Oxford Learning’s infographic on the effects of homework on students.
3. Consider Joseph Lathan’s argument that homework promotes inequality .
4. Consider how you felt about the issue before reading this article. After reading the pros and cons on this topic, has your thinking changed? If so, how? List two to three ways. If your thoughts have not changed, list two to three ways your better understanding of the “other side of the issue” now helps you better argue your position.
5. Push for the position and policies you support by writing US national senators and representatives .
| 1. | Tom Loveless, “Homework in America: Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report of American Education,” brookings.edu, Mar. 18, 2014 | |
| 2. | Edward Bok, “A National Crime at the Feet of American Parents,” , Jan. 1900 | |
| 3. | Tim Walker, “The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype,” neatoday.org, Sep. 23, 2015 | |
| 4. | University of Phoenix College of Education, “Homework Anxiety: Survey Reveals How Much Homework K-12 Students Are Assigned and Why Teachers Deem It Beneficial,” phoenix.edu, Feb. 24, 2014 | |
| 5. | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), “PISA in Focus No. 46: Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education?,” oecd.org, Dec. 2014 | |
| 6. | Adam V. Maltese, Robert H. Tai, and Xitao Fan, “When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math,” , 2012 | |
| 7. | Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003,” , 2006 | |
| 8. | Gökhan Bas, Cihad Sentürk, and Fatih Mehmet Cigerci, “Homework and Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analytic Review of Research,” , 2017 | |
| 9. | Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, and Xitao Fan, “Homework and Students’ Achievement in Math and Science: A 30-Year Meta-Analysis, 1986-2015,” , 2017 | |
| 10. | Charlene Marie Kalenkoski and Sabrina Wulff Pabilonia, “Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement?,” iza.og, Apr. 2014 | |
| 11. | Ron Kurtus, “Purpose of Homework,” school-for-champions.com, July 8, 2012 | |
| 12. | Harris Cooper, “Yes, Teachers Should Give Homework – The Benefits Are Many,” newsobserver.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 13. | Tammi A. Minke, “Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement,” repository.stcloudstate.edu, 2017 | |
| 14. | LakkshyaEducation.com, “How Does Homework Help Students: Suggestions From Experts,” LakkshyaEducation.com (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 15. | University of Montreal, “Do Kids Benefit from Homework?,” teaching.monster.com (accessed Aug. 30, 2018) | |
| 16. | Glenda Faye Pryor-Johnson, “Why Homework Is Actually Good for Kids,” memphisparent.com, Feb. 1, 2012 | |
| 17. | Joan M. Shepard, “Developing Responsibility for Completing and Handing in Daily Homework Assignments for Students in Grades Three, Four, and Five,” eric.ed.gov, 1999 | |
| 18. | Darshanand Ramdass and Barry J. Zimmerman, “Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework,” , 2011 | |
| 19. | US Department of Education, “Let’s Do Homework!,” ed.gov (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 20. | Loretta Waldman, “Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework,” phys.org, Apr. 12, 2014 | |
| 21. | Frances L. Van Voorhis, “Reflecting on the Homework Ritual: Assignments and Designs,” , June 2010 | |
| 22. | Roel J. F. J. Aries and Sofie J. Cabus, “Parental Homework Involvement Improves Test Scores? A Review of the Literature,” , June 2015 | |
| 23. | Jamie Ballard, “40% of People Say Elementary School Students Have Too Much Homework,” yougov.com, July 31, 2018 | |
| 24. | Stanford University, “Stanford Survey of Adolescent School Experiences Report: Mira Costa High School, Winter 2017,” stanford.edu, 2017 | |
| 25. | Cathy Vatterott, “Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs,” ascd.org, 2009 | |
| 26. | End the Race, “Homework: You Can Make a Difference,” racetonowhere.com (accessed Aug. 24, 2018) | |
| 27. | Elissa Strauss, “Opinion: Your Kid Is Right, Homework Is Pointless. Here’s What You Should Do Instead.,” cnn.com, Jan. 28, 2020 | |
| 28. | Jeanne Fratello, “Survey: Homework Is Biggest Source of Stress for Mira Costa Students,” digmb.com, Dec. 15, 2017 | |
| 29. | Clifton B. Parker, “Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework,” stanford.edu, Mar. 10, 2014 | |
| 30. | AdCouncil, “Cheating Is a Personal Foul: Academic Cheating Background,” glass-castle.com (accessed Aug. 16, 2018) | |
| 31. | Jeffrey R. Young, “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame,” chronicle.com, Mar. 28, 2010 | |
| 32. | Robin McClure, “Do You Do Your Child’s Homework?,” verywellfamily.com, Mar. 14, 2018 | |
| 33. | Robert M. Pressman, David B. Sugarman, Melissa L. Nemon, Jennifer, Desjarlais, Judith A. Owens, and Allison Schettini-Evans, “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background,” , 2015 | |
| 34. | Heather Koball and Yang Jiang, “Basic Facts about Low-Income Children,” nccp.org, Jan. 2018 | |
| 35. | Meagan McGovern, “Homework Is for Rich Kids,” huffingtonpost.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 36. | H. Richard Milner IV, “Not All Students Have Access to Homework Help,” nytimes.com, Nov. 13, 2014 | |
| 37. | Claire McLaughlin, “The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’,” neatoday.org, Apr. 20, 2016 | |
| 38. | Doug Levin, “This Evening’s Homework Requires the Use of the Internet,” edtechstrategies.com, May 1, 2015 | |
| 39. | Amy Lutz and Lakshmi Jayaram, “Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework,” , June 2015 | |
| 40. | Sandra L. Hofferth and John F. Sandberg, “How American Children Spend Their Time,” psc.isr.umich.edu, Apr. 17, 2000 | |
| 41. | Alfie Kohn, “Does Homework Improve Learning?,” alfiekohn.org, 2006 | |
| 42. | Patrick A. Coleman, “Elementary School Homework Probably Isn’t Good for Kids,” fatherly.com, Feb. 8, 2018 | |
| 43. | Valerie Strauss, “Why This Superintendent Is Banning Homework – and Asking Kids to Read Instead,” washingtonpost.com, July 17, 2017 | |
| 44. | Pew Research Center, “The Way U.S. Teens Spend Their Time Is Changing, but Differences between Boys and Girls Persist,” pewresearch.org, Feb. 20, 2019 | |
| 45. | ThroughEducation, “The History of Homework: Why Was It Invented and Who Was behind It?,” , Feb. 14, 2020 | |
| 46. | History, “Why Homework Was Banned,” (accessed Feb. 24, 2022) | |
| 47. | Valerie Strauss, “Does Homework Work When Kids Are Learning All Day at Home?,” , Sep. 2, 2020 | |
| 48. | Sara M Moniuszko, “Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In,” , Aug. 17, 2021 | |
| 49. | Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, “The Worsening Homework Problem,” , Apr. 13, 2021 | |
| 50. | Kiara Taylor, “Digital Divide,” , Feb. 12, 2022 | |
| 51. | Marguerite Reardon, “The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind,” , May 5, 2021 | |
| 52. | Rachel Paula Abrahamson, “Why More and More Teachers Are Joining the Anti-Homework Movement,” , Sep. 10, 2021 |
More School Debate Topics
Should K-12 Students Dissect Animals in Science Classrooms? – Proponents say dissecting real animals is a better learning experience. Opponents say the practice is bad for the environment.
Should Students Have to Wear School Uniforms? – Proponents say uniforms may increase student safety. Opponents say uniforms restrict expression.
Should Corporal Punishment Be Used in K-12 Schools? – Proponents say corporal punishment is an appropriate discipline. Opponents say it inflicts long-lasting physical and mental harm on students.
ProCon/Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 325 N. LaSalle Street, Suite 200 Chicago, Illinois 60654 USA
Natalie Leppard Managing Editor [email protected]
© 2023 Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved
- Social Media
- Death Penalty
- School Uniforms
- Video Games
- Animal Testing
- Gun Control
- Banned Books
- Teachers’ Corner
Cite This Page
ProCon.org is the institutional or organization author for all ProCon.org pages. Proper citation depends on your preferred or required style manual. Below are the proper citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order): the Modern Language Association Style Manual (MLA), the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA), and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Turabian). Here are the proper bibliographic citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order):
[Editor's Note: The APA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
[Editor’s Note: The MLA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]

Science of mind

Why is homework good for your brain?
Did you know that homework has a profound impact on brain development? It’s not just about completing assignments; homework can actually improve brain function and enhance cognitive abilities.
Homework is designed to help students prepare for the future and develop skills that are essential for success in life. It offers several cognitive benefits, including the development of memory and critical thinking skills. By practicing and repeating new skills through homework, students can enhance their memory and retain knowledge for exams and future tests.
But that’s not all. Homework also helps students build suitable study habits, learn time management, realize personal responsibility, work independently, and improve their ability to use resources and conduct research.
Key Takeaways:
- Homework improves brain function and enhances cognitive abilities.
- By practicing and repeating new skills through homework, students can enhance their memory and retain knowledge.
- Homework helps students build suitable study habits, learn time management, and realize personal responsibility.
- Homework fosters independence and the ability to use resources effectively.
- Research shows that designing and assigning homework correctly can optimize its effectiveness as a learning tool.
The Cognitive Benefits of Homework
Homework is not just a task assigned by teachers to keep students occupied after school; it has far-reaching cognitive benefits and contributes to brain growth and development. Through various homework assignments, students have the opportunity to enhance critical thinking skills, memory retention, and problem-solving abilities.
One essential cognitive benefit of homework is its ability to challenge and develop critical thinking skills. By applying the concepts they’ve learned in class to real-life situations, students can deepen their understanding and improve their analytical thinking abilities. This practice fosters a deeper level of comprehension and encourages students to actively engage with the material.
Another cognitive benefit of homework is its positive impact on memory retention. Through practice and repetition of new skills and knowledge, students reinforce the neural connections in their brains, making the information more accessible and easier to recall. This improved memory retention helps students perform better on exams and enhances their overall academic performance.
Homework also plays a crucial role in developing problem-solving abilities. Assignments that require students to think critically and find innovative solutions to complex problems help cultivate their analytical and logical thinking skills. These problem-solving abilities are essential for success in various aspects of life, from academic pursuits to professional careers.
Overall, homework has a profound impact on cognitive development, providing students with opportunities to enhance critical thinking, memory retention, and problem-solving abilities. By engaging in regular homework assignments, students can nurture these essential cognitive skills and lay a solid foundation for their future academic and professional success.
Building Essential Skills Through Homework
Homework plays a vital role in building essential skills that are crucial for academic success and beyond. It provides students with the opportunity to develop effective study habits, learn time management, cultivate personal responsibility, and engage in independent work.
One of the key benefits of homework is the development of study habits. Through regular homework assignments, students learn how to plan their study sessions, set realistic goals, and effectively organize their time. By following consistent study routines, students can maximize their learning potential and improve their overall academic performance.
Time management is another vital skill that homework helps students develop. By juggling multiple assignments and deadlines, students learn to prioritize tasks, allocate their time effectively, and meet their academic obligations. These skills are essential not only for academic success but also for managing responsibilities in other areas of life.
Homework also fosters a sense of personal responsibility. Being accountable for completing assignments on time and to the best of their ability teaches students the importance of taking ownership of their education. It instills a work ethic that can significantly impact their future success, both inside and outside the classroom.
Furthermore, homework promotes independent work and critical thinking skills. Through assignments that require students to apply concepts learned in class, they develop their problem-solving abilities and deepen their understanding of the subject matter. This type of independent work encourages students to think creatively, analyze information critically, and develop their own perspectives.
By engaging in homework, students are actively building these essential skills that will benefit them throughout their education and beyond. The combination of effective study habits, time management, personal responsibility, and independent work fosters self-discipline, resilience, and a lifelong love of learning.

Testimonial:
“Homework has been instrumental in developing my study habits and time management skills. It has taught me the importance of setting goals and staying organized. Through homework, I’ve become more accountable and independent in my learning.” – Jane Smith, High School Student
Homework and Research Skills
When it comes to homework, research skills are essential for academic success. Homework assignments often require students to explore various resources, such as research papers, books, websites, and videos. By delving into these resources, students develop the ability to effectively use different information sources and enhance their understanding of the subject matter.
Research skills acquired through homework not only improve students’ academic performance but also prepare them to navigate the vast amount of information available in the digital age. By honing their research skills, students become adept at finding relevant and reliable information, analyzing different sources, and critically evaluating the credibility and validity of the information they come across.
Research skills acquired through homework contribute to academic success and prepare students for future challenges.
Through homework, students develop the persistence and resilience necessary to delve deep into a topic, locate relevant information, and synthesize their findings in a coherent manner. These skills are not only valuable during their academic journey but will also benefit them throughout their lives as they continue to learn and grow.
Moreover, conducting research for homework assignments instills a sense of curiosity and a thirst for knowledge in students. It encourages them to explore beyond the textbook and develop a broader perspective on the topics they are studying. They learn to ask questions, seek answers, and develop a lifelong love for learning.
Overall, homework assignments that require research skills play a vital role in shaping students’ intellectual growth, fostering critical thinking, and preparing them for the challenges they will face in their future academic and professional endeavors.

| Benefits of Homework and Research Skills |
|---|
| 1. Develops the ability to use various information sources effectively |
| 2. Enhances critical thinking and analytical skills |
| 3. Improves understanding and knowledge retention |
| 4. Encourages curiosity and a love for learning |
| 5. Prepares students for academic and professional challenges |
The Science of Homework Efficiency
When it comes to homework, there is a science behind ensuring its maximum effectiveness as a learning tool. Research has shown that the way homework is designed and assigned can have a significant impact on student performance. To optimize learning outcomes, homework should provide independent learning opportunities and present challenges that facilitate deliberate practice of essential content and skills.
One factor that can greatly affect the efficiency of homework is task switching. Constantly switching between homework and distractions like social media can significantly prolong the time spent on assignments. To overcome this, it is crucial to encourage students to delay gratification by using social media as a reward after completing their assignments. By eliminating distractions and focusing on the task at hand, students can deepen their learning and complete their homework more efficiently.
Adopting a scientific approach to tackling homework can lead to improved academic performance. By implementing strategies that optimize learning, such as organizing study sessions, setting goals, and utilizing resources effectively, students can enhance their understanding of the subject matter and improve their overall learning outcomes. By prioritizing uninterrupted focus and disciplined work, students can transform homework into a valuable learning experience that prepares them for success in their academic endeavors.
Source Links
- https://www.crispebooks.org/
- http://www.math.usf.edu/~mccolm/pedagogy/HWgood.html
- https://www.edutopia.org/blog/homework-sleep-and-student-brain-glenn-whitman
Similar Posts

Why isn’t my brain working?

Can brain health be restored?

Is microwave popcorn bad for your brain?

What are the effects of alcohol and drug abuse on brain health?

How much does brain surgery cost with insurance?

Does lake Michigan have brain eating amoeba?
The case for homework.
- Posted September 29, 2016
- By Matt Weber
This fall, the start of the new school year seemingly brought with it a trend of teachers forgoing homework assignments in order to allow their students more time outside of school for family and play. A number of these announcements took off on social media, with many parents supporting the stance and wishing that their own child's teacher would follow suit. While few would dispute the importance of family and play time for young children, it may be shortsighted to believe that eliminating homework altogether is the answer.
"All children should be doing homework," says Duke University Professor Harris M. Cooper , who has researched and wrote on the topic for over 25 years. While Cooper acknowledges that an excess of homework is both unnecessary and potentially detrimental, the upside of homework is too great to ignore. Not only is it important in reinforcing skills learned during the school day, it also teaches time management, study skills, and independent learning, as well as keeps parents connected to their children's learning.
"Really good homework assignments" in subjects such as math and science, says Cooper, also highlight skills children use in other areas of their life — in sports, games, and everyday tasks like grocery shopping with their parents. "A really good teacher is one that takes the skills that [their students] are learning in the abstract — or more abstract — in their classroom, and uses homework to show them these are the skills they need to enjoy things they do even more," says Cooper.
In this edition of the Harvard EdCast, Cooper evaluates the dissatisfaction with homework practices and discusses all of the reasons why, for children, homework is essential.
About the Harvard EdCast
The Harvard EdCast is a weekly series of podcasts, available on the Harvard University iTunes U page, that features a 15-20 minute conversation with thought leaders in the field of education from across the country and around the world. Hosted by Matt Weber, the Harvard EdCast is a space for educational discourse and openness, focusing on the myriad issues and current events related to the field.

An education podcast that keeps the focus simple: what makes a difference for learners, educators, parents, and communities
Related Articles

After the Journey

What Big Data Means

Notes from Ferguson
- Our Mission
Rethinking Homework for This Year—and Beyond
A schoolwide effort to reduce homework has led to a renewed focus on ensuring that all work assigned really aids students’ learning.

I used to pride myself on my high expectations, including my firm commitment to accountability for regular homework completion among my students. But the trauma of Covid-19 has prompted me to both reflect and adapt. Now when I think about the purpose and practice of homework, two key concepts guide me: depth over breadth, and student well-being.
Homework has long been the subject of intense debate, and there’s no easy answer with respect to its value. Teachers assign homework for any number of reasons: It’s traditional to do so, it makes students practice their skills and solidify learning, it offers the opportunity for formative assessment, and it creates good study habits and discipline. Then there’s the issue of pace. Throughout my career, I’ve assigned homework largely because there just isn’t enough time to get everything done in class.
A Different Approach
Since classes have gone online, the school where I teach has made a conscious effort as a teaching community to reduce, refine, and distill our curriculum. We have applied guiding questions like: What is most important? What is most transferable? What is most relevant? Refocusing on what matters most has inevitably made us rethink homework.
We have approached both asking and answering these questions through a science of learning lens. In Make It Stick: The Science of Successful Learning , the authors maintain that deep learning is slow learning. Deep learning requires time for retrieval, practice, feedback, reflection, and revisiting content; ultimately it requires struggle, and there is no struggle without time.
As someone who has mastered the curriculum mapping style of “get it done to move on to get that next thing done,” using an approach of “slow down and reduce” has been quite a shift for me. However, the shift has been necessary: What matters most is what’s best for my students, as opposed to my own plans or mandates imposed by others.
Listening to Students
To implement this shift, my high school English department has reduced content and texts both in terms of the amount of units and the content within each unit. We’re more flexible with dates and deadlines. We spend our energy planning the current unit instead of the year’s units. In true partnership with my students, I’m constantly checking in with them via Google forms, Zoom chats, conferences, and Padlet activities. In these check-ins, I specifically ask students how they’re managing the workload for my class and their other classes. I ask them how much homework they’re doing. And I adjust what I do and expect based on what they tell me. For example, when I find out a week is heavy with work in other classes, I make sure to allot more time during class for my tasks. At times I have even delayed or altered one of my assignments.
To be completely transparent, the “old” me is sheepish in admitting that I’ve so dramatically changed my thinking with respect to homework. However, both my students and I have reaped numerous benefits. I’m now laser-focused when designing every minute of my lessons to maximize teaching and learning. Every decision I make is now scrutinized through the lens of absolute worth for my students’ growth: If it doesn’t make the cut, it’s cut. I also take into account what is most relevant to my students.
For example, our 10th-grade English team has redesigned a unit that explores current manifestations of systemic oppression. This unit is new in approach and longer in duration than it was pre-Covid, and it has resulted in some of the deepest and hardest learning, as well as the richest conversations, that I have seen among students in my career. Part of this improved quality comes from the frequent and intentional pauses that I instruct students to take in order to reflect on the content and on the arc of their own learning. The reduction in content that we need to get through in online learning has given me more time to assign reflective prompts, and to let students process their thoughts, whether that’s at the end of a lesson as an exit slip or as an assignment.
Joining Forces to Be Consistent
There’s no doubt this reduction in homework has been a team effort. Within the English department, we have all agreed to allot reading time during class; across each grade level, we’re monitoring the amount of homework our students have collectively; and across the whole high school, we have adopted a framework to help us think through assigning homework.
Within that framework, teachers at the school agree that the best option is for students to complete all work during class. The next best option is for students to finish uncompleted class work at home as a homework assignment of less than 30 minutes. The last option—the one we try to avoid as much as possible—is for students to be assigned and complete new work at home (still less than 30 minutes). I set a maximum time limit for students’ homework tasks (e.g., 30 minutes) and make that clear at the top of every assignment.
This schoolwide approach has increased my humility as a teacher. In the past, I tended to think my subject was more important than everyone else’s, which gave me license to assign more homework. But now I view my students’ experience more holistically: All of their classes and the associated work must be considered, and respected.
As always, I ground this new pedagogical approach not just in what’s best for students’ academic learning, but also what’s best for them socially and emotionally. 2020 has been traumatic for educators, parents, and students. There is no doubt the level of trauma varies greatly ; however, one can’t argue with the fact that homework typically means more screen time when students are already spending most of the day on their devices. They need to rest their eyes. They need to not be sitting at their desks. They need physical activity. They need time to do nothing at all.
Eliminating or reducing homework is a social and emotional intervention, which brings me to the greatest benefit of reducing the homework load: Students are more invested in their relationship with me now that they have less homework. When students trust me to take their time seriously, when they trust me to listen to them and adjust accordingly, when they trust me to care for them... they trust more in general.
And what a beautiful world of learning can be built on trust.
Gray Matters: What role should homework play in learning?
Historical Background In the U.S., debates about the value of homework have been steady over the past century. In the beginning half of the 1900’s, homework was not nearly as common. Many school districts banned homework at the elementary and middle school levels in the belief that it only facilitated rote learning. That changed in the 1950’s when the Soviet Union launched Sputnik, creating the perception that the U.S. needed to increase the amount of students’ homework to be competitive in the space race. Over the next 50 years until the present, the popular view of homework switched every 15 years or so between support and condemnation. Today research has enhanced our understanding, but the debate continues.
Homework: What’s the Point? Numerous benefits are attributed to homework: better retention of factual knowledge, development of study habits, increased ability to manage time effectively, and heightened parental involvement. Evaluating exactly what of these benefits can be attributed to homework versus inherent differences in students or the quality of assignments presents obvious challenges. Further confounding research, homework often exacts costs in the form of increased stress and reduced sleep, which can negate potential benefits. Nonetheless, research to date provides guidance on homework’s role in achieving some of these goals.
Research Examples How much homework should be assigned? Although not unanimous, multiple studies on the relationship between homework time and academic achievement have shown that it is not a linear relationship: more homework does not equal more learning. One study of 7,451 13- year-old students administered a test of science and mathematics in addition to a survey of effort spent on homework, homework time, homework frequency, and the general circumstances around how homework was done. Results: student academic gains were associated with homework time up to 1 hour a day, after which increased homework time was associated with worse performance. This result varies with students’ ages.
How does the influence of homework change in different grades? While empirical studies have not yet explicitly compared the role of homework in different ages, a review of the literature reveals clear trends. A meta-analysis of 4,400 studies up until 2003 found that homework time had different effects depending on the grade of students. Results: up to two hours of homework showed the most benefit for high school students, up to an hour of homework showed some benefit for middle school students, and almost no benefit was found among elementary school students.
What homework factors contribute to academic performance? Studies that focus on the circumstances in which students complete homework have found that autonomy and effort are more important predictors of performance than homework time alone. One study of 483 eighth-graders from 20 classes analyzed students’ grades and standardized test scores in mathematics in relation to survey responses on homework effort. Students responded once in November and once in May of the academic year. Results: academic gains in grades and test scores were positively correlated to homework effort. However, other studies suggest that since effort and autonomy are highly correlated with students’ prior achievement, it’s difficult to say if this is a trait of the homework or of a certain kind of student.
How can homework best facilitate learning? Practices from the “ How can I improve longterm learning ” edition of Gray Matters 01 should be implemented in homework design to facilitate learning. For instance, using homework to continue practice on material and skills learned in previous weeks uses distributed practice to improve recall. Homework that offers adequate practice of important skills also helps reinforce skills in a variety of contexts. A survey of school leaders around homework best practices found similar results: homework can facilitate engagement when it is an authentic, engaging extension of the class. Results: homework should be designed intentionally, with reference to most effective forms of practice.
Does the effect of homework change when instruction occurs at home and exercises are done in class? In this case, the question is essentially if homework facilitates learning when it is done as a part class rather than at home. One model that represents this circumstance is the flipped classroom. Case studies done with ninth to twelfth-graders across a variety of subjects showed that achievement increased after implementing a model where students watched videos at home and practiced learning in class. In these schools the percentage of students passing standardized exams increased by up to 12%. Empirical studies comparing in-class work and at home work have repeated research design flaws, however, they generally indicate that in-class exercises have a positive effect for older students. Results: the research is inconclusive, but generally indicates that flipped classroom approaches have positive net benefits for high school students.
How frequently should homework be assigned? The research on frequency is not conclusive, however most studies suggest that classes that receive homework frequently tend to do better on tests of achievement. One such study administered standardized mathematics examinations to 2,939 grade 7 and 8 students across 20 classes. In addition to the exam, students answered questions on frequency of homework and the average amount of time spent on homework each evening. Results: Classes that had more frequent homework assignments had overall higher averages on the achievement tests.
Does homework change students’ attitudes towards school? Studies comparing the attitudes of students who received homework with those who did not receive homework generally found no significant results across a variety of grade levels. One study compared three different models for assigning arithmetic homework to 342 third-graders across twelve classrooms: teachers assigned no homework, assigned homework as usual, and were required to assign a constant amount of homework every night. Students answered questions measuring their attitudes towards school, teacher, arithmetic, spelling, reading, and homework. Results: no significant differences were found between the attitudes of the different groups.
Conclusion The quality of homework and the students who complete it vary significantly, however the general research trends suggest that assigning homework does have benefits at the middle and upper school levels. Frequency of assignment and students’ autonomy in finishing homework were also correlated with student achievement. These results provide guidelines on the appropriate quantity of homework, but how best to incorporate homework content into an overall progression of students’ learning remains for teachers to judge.
“Adolescents’ Homework Performance in Mathematics and Science: Personal Factors and Teaching Practices” by Rubén FernándezAlonso, Javier Suárez-Álvarez, and José Muñiz, Journal of Educational Psychology , 2015, 107(4), 1075.
“Ask the Cognitive Scientist Allocating Student Study Time” by Daniel T. Willingham, American Educator , 2002, 26(2), 37-39.
“Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003” by Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, Review of Educational Research , 2006, 76(1), 1-62.
“Does Homework Improve Learning?” by Alfie Kohn, AlfieKohn.org, 2006. “Effects of Arithmetic Homework upon the Attitudes of Third Grade Pupils Toward Certain School-related Structure” by Norbert Maertens, School Science and Mathematics , 1968, 68(7), 657-662.
“Flipped Learning Model Dramatically Improves Course Pass Rate for At-Risk Students, Clintondale high School, MI: A Case Study” by Pearson Education, May, 2013.
“Flipped Learning Model Increases Student Engagement and Performance, Byron High School, MN: A Case Study” by Pearson Education, June, 2013.
“Homework. Research on Teaching Monograph Series, Homework Versus In-class Supervised Study” by Harris Cooper, 1989, 77- 89.
“If They’d Only Do Their Work!” by Linda Darling-Hammond and Olivia Ifill-Lynch, Educational Leadership, 2008, 63(5), 8-13.
“Research Trends: Why Homework Should Be Balanced” by Youki Terada, Edutopia, 2015, July 31.
“Synthesis of Research on Homework” by Harris Cooper, Educational leadership, 1989, 47(3), 85-91.
“The Homework–Achievement Relation Reconsidered: Differentiating Homework Time, Homework Frequency, and Homework Effort” by Ulrich Trautwein, Learning and Instruction, 2007, 17(3), 372-388.
Gray Matters is dedicated to providing research-based answers to questions commonly raised by faculty and within the education community. Gray Matters is published by the Tiger Works Research & Development group at Avenues.
Find out more about Avenues’ admissions process and begin an online application for one of our global campuses.
About Avenues
Discover the people, places and values that make Avenues unique.
Find your future at Avenues: join the growing team that’s redefining K-12 education around the world.
How Is Homework Helping Students Learn?
- Share article

Practice, or reinforcement of a skill, is part of the educational process. Practice in classwork and homework is an important part of guaranteeing students are learning what is being taught. Skilled, targeted practice is what is planned but the art of practice is both complex and simple.
In sports, theatre, and music programs, a model for how to develop expertise lives right in front of us. To acquire a skill, practice is necessary. Yet, when practice is unsupervised and lacks immediate feedback, frustration can arise, motivation can wane, and bad form can be embedded. Learning is either limited or non-existent without the practice feedback loop ongoing. In sports, a targeted skill is focused on and the coach gives consistent feedback as the player practices that one skill. In the arts the same is true. Skills are identified, modeled, and the students or players or actors, or musicians are given feedback on the skill(s) identified so that practice becomes both targeted and informed. Feedback is key. Encouragement is essential.
Homework is the best example of how educators can improve the use of practice. No matter whether as an educator or a parent, homework as practice remains a standard that might serves many purposes. Teachers use homework to offer students a chance to reinforce what they have learned and what they complete contributes, most often, to a grade. Parents use homework to see what their children are learning and some use it to become partners in the learning experience. Interesting, if it happens that way. Homework has the intention of reinforcement but often lacks the narrow focus for practice. In addition it sends children home without the teacher’s knowledge or confidence that the practice is based on knowledge attained. It can become reinforcement of doubt, frustration, or worse, reinforcement of incorrect information or skills. Doing something over and over is good if it is targeted and informed; if feedback is timely and consistent.
How Teachers Are Taught
After teachers gain their degrees and certification, they rely on professional development opportunities throughout their careers to continue their learning. Often these opportunities have been what has become known as ‘one and done’ professional development opportunities. These were usually selected to impact the broadest sweep of faculty at once. However, the follow-up, reinforcement, and support varies depending on the amount of attention school leaders give following the ‘one and done’. Other ways teachers continue learning is individual. They apply to go to a conference or training, are approved, attend, and return. Whether what is learned is embedded in their future practice is often left up to the teacher. After all, how many new things can a leader keep track of, follow up, and support?
Ericcson and Pool argue that “deliberate practice requires a teacher who can provide practice activities designed to help a student improve his or her performance” (p.98). Deliberate practice is informed practice, guided by “the best performers’ accomplishments and by understanding of what these expert performers do to excel” (p.98).
How do we know for certain, that all homework, particularly in the early grades, teaches what we want it to and what Ericcson and Pool describe? Some might say it teaches responsibility. But for those students who left the classroom without an adequate grasp of the material, it may undermine its intention. Instead it develops frustration and kills motivation. It has the potential of reinforcing the wrong way to do something, or even a belief that ‘I can’t do this’. These happening in the early years can stop students from pushing forward, developing grit, and finding success.
Change the Environment for Teachers’ Learning
Change how we work with teachers so they can change the way they work with their students. No matter the behavior or skill targeted, might we be able to change the environment to be one of learning, continuous learning, for the adults in which targeted practice and feedback are valued and excellence is recognized? The shift in thinking that this can put in motion requires that the leader remain constant in their role that focuses on the agreed upon skills and behaviors that are being practiced. It required consistency and dedication. It invites the development of professional collegiality where those learning new skills practice together and give feedback to each other.
Before shifting the manner in which teachers plan for practice for their students, consider implementing it with the teachers first. Teaching and learning is not an exact science, like playing an instrument or playing tennis. However, we, in education do know the complicated factors that affect learning. Taking that into consideration, isn’t there a way to use deliberate practice where it applies? Rather than assigning independent work because we always have, assign it with the knowledge that the practice will be correct and effective and supported with immediate feedback. Discussions and feedback about what is being implemented and how it will affect the practice of the teacher are essential. Changing the way teachers receive feedback and are asked to practice new, targeted skills offers the model for what you ask them to do with their students. Consider being a model of the change.
A nn Myers and Jill Berkowicz are the authors of The STEM Shift (2015, Corwin) a book about leading the shift into 21st century schools. Ann and Jill welcome connecting through Twitter & Email .
Resource: Ericsson, A. & Pool, R. (2016). Peak: Secrets from the new science of expertise. New York: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Photo courtesy of Pixabay
The opinions expressed in Leadership 360 are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for The Savvy Principal
Get started today.
- Centre Details
- Ask A Question
- Change Location
- Programs & More
The Pros and Cons of Homework

The dreaded word for students across the country—homework.
Homework has long been a source of debate, with parents, educators, and education specialists debating the advantages of at-home study. There are many pros and cons of homework. We’ve examined a few significant points to provide you with a summary of the benefits and disadvantages of homework.
Check Out The Pros and Cons of Homework

Pro 1: Homework Helps to Improve Student Achievement
Homework teaches students various beneficial skills that they will carry with them throughout their academic and professional life, from time management and organization to self-motivation and autonomous learning.
Homework helps students of all ages build critical study abilities that help them throughout their academic careers. Learning at home also encourages the development of good research habits while encouraging students to take ownership of their tasks.
If you’re finding that homework is becoming an issue at home, check out this article to learn how to tackle them before they get out of hand.
Con 1: Too Much Homework Can Negatively Affect Students
You’ll often hear from students that they’re stressed out by schoolwork. Stress becomes even more apparent as students get into higher grade levels.
A study conducted on high school student’s experiences found that high-achieving students found that too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as:
- Weight loss
- Stomach problems
More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies.
It’s been shown that excessive homework can lead to cheating. With too much homework, students end up copying off one another in an attempt to finish all their assignments.
Pro 2: Homework Helps to Reinforce Classroom Learning
Homework is most effective when it allows students to revise what they learn in class. Did you know that students typically retain only 50% of the information teachers provide in class?
Students need to apply that information to learn it.
Homework also helps students develop key skills that they’ll use throughout their lives:
- Accountability
- Time management
- Self-direction
- Critical thinking
- Independent problem-solving
The skills learned in homework can then be applied to other subjects and practical situations in students’ daily lives.
Con 2: Takes Away From Students Leisure Time
Children need free time. This free time allows children to relax and explore the world that they are living in. This free time also gives them valuable skills they wouldn’t learn in a classroom, such as riding a bike, reading a book, or socializing with friends and family.
Having leisure time teaches kids valuable skills that cannot be acquired when doing their homework at a computer.
Plus, students need to get enough exercise. Getting exercise can improve cognitive function, which might be hindered by sedentary activities such as homework.
Pro 3: Homework Gets Parents Involved with Children’s Learning
Homework helps parents track what their children are learning in school.
Also allows parents to see what their children’s academic strengths and weaknesses are. Homework can alert parents to any learning difficulties that their children might have, enabling them to provide assistance and modify their child’s learning approach as necessary.
Parents who help their children with homework will lead to higher academic performance, better social skills and behaviour, and greater self-confidence in their children.
Con 3: Homework Is Not Always Effective
Numerous researchers have attempted to evaluate the importance of homework and how it enhances academic performance. According to a study , homework in primary schools has a minimal effect since students pursue unrelated assignments instead of solidifying what they have already learned.
Mental health experts agree heavy homework loads have the capacity to do more harm than good for students. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. So, unfortunately for students, homework is here to stay.
You can learn more about the pro and cons of homework here.
Need Help with Completing Homework Effectively?
There are many pros and cons of homework, so let our tutors at Oxford Learning can help your family create great homework habits to ensure students are successful at homework.
Contact a location near you to get started today!
Ungrading: What is it?
What your child can gain from a french immersion program, related homework resources.

Homework, Organization, Studying
Homework procrastination: why do students procrastinate.

Understanding Dysgraphia and How Tutoring Can Help

Unwrapping the 12 Days of Holiday Skills


Canadian Attitudes Toward Homework
Find an oxford learning ® location near you, we have over 100 centres across canada.
Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement?

- Share this story on facebook
- Share this story on twitter
- Share this story on reddit
- Share this story on linkedin
- Get this story's permalink
- Print this story
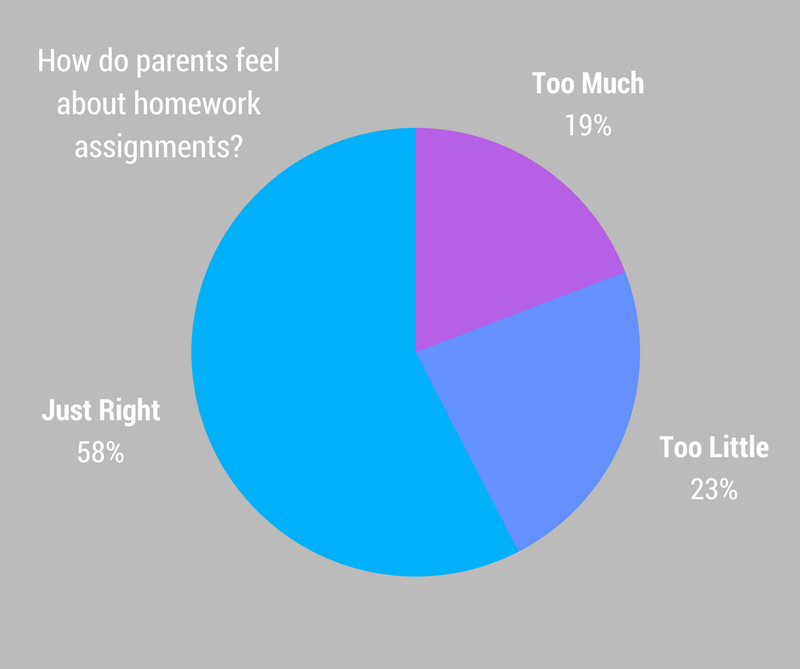
Educators should be thrilled by these numbers. Pleasing a majority of parents regarding homework and having equal numbers of dissenters shouting "too much!" and "too little!" is about as good as they can hope for.
But opinions cannot tell us whether homework works; only research can, which is why my colleagues and I have conducted a combined analysis of dozens of homework studies to examine whether homework is beneficial and what amount of homework is appropriate for our children.
The homework question is best answered by comparing students who are assigned homework with students assigned no homework but who are similar in other ways. The results of such studies suggest that homework can improve students' scores on the class tests that come at the end of a topic. Students assigned homework in 2nd grade did better on math, 3rd and 4th graders did better on English skills and vocabulary, 5th graders on social studies, 9th through 12th graders on American history, and 12th graders on Shakespeare.
Less authoritative are 12 studies that link the amount of homework to achievement, but control for lots of other factors that might influence this connection. These types of studies, often based on national samples of students, also find a positive link between time on homework and achievement.
Yet other studies simply correlate homework and achievement with no attempt to control for student differences. In 35 such studies, about 77 percent find the link between homework and achievement is positive. Most interesting, though, is these results suggest little or no relationship between homework and achievement for elementary school students.
Why might that be? Younger children have less developed study habits and are less able to tune out distractions at home. Studies also suggest that young students who are struggling in school take more time to complete homework assignments simply because these assignments are more difficult for them.
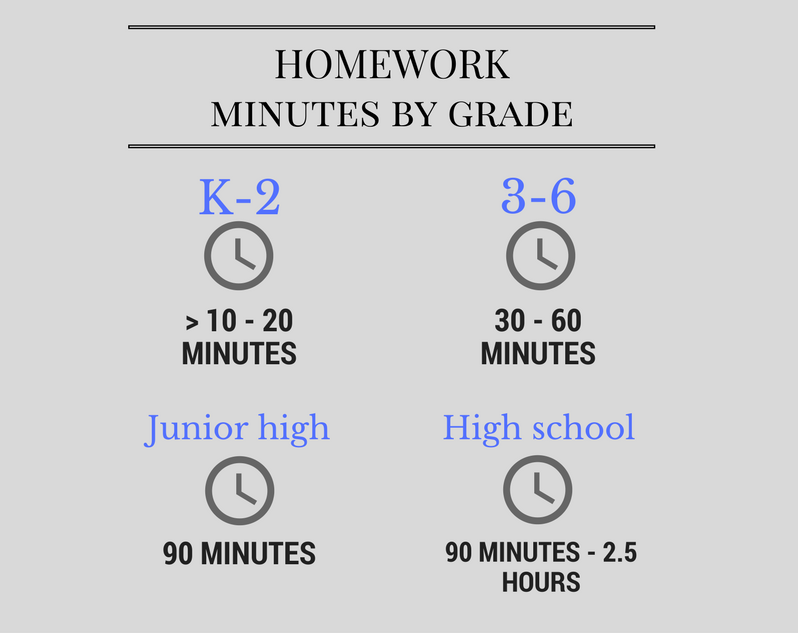
These recommendations are consistent with the conclusions reached by our analysis. Practice assignments do improve scores on class tests at all grade levels. A little amount of homework may help elementary school students build study habits. Homework for junior high students appears to reach the point of diminishing returns after about 90 minutes a night. For high school students, the positive line continues to climb until between 90 minutes and 2½ hours of homework a night, after which returns diminish.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what's going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Opponents of homework counter that it can also have negative effects. They argue it can lead to boredom with schoolwork, since all activities remain interesting only for so long. Homework can deny students access to leisure activities that also teach important life skills. Parents can get too involved in homework -- pressuring their child and confusing him by using different instructional techniques than the teacher.
My feeling is that homework policies should prescribe amounts of homework consistent with the research evidence, but which also give individual schools and teachers some flexibility to take into account the unique needs and circumstances of their students and families. In general, teachers should avoid either extreme.
Link to this page
Copy and paste the URL below to share this page.
- Publications & Products Search
- Appalachia Central Mid-Atlantic Midwest Northeast & Islands
- Northwest Pacific Southeast Southwest West
- REL Work in Progress
- What's New NewsFlash Conferences/Training Bridge Events Early Warning Systems Learning Series RSS Feed
- About Us Staff Help Contact Us
Home > Ask A REL > Response
What does the research say about homework policies and practices?
Following an established REL Northeast & Islands research protocol, we conducted a search for recent research on homework policies and practices. We focused on identifying resources that specifically addressed research on policies and practices for homework for various grade levels based on its impact on student achievement. The sources searched included ERIC and other federally funded databases and organizations, academic research databases, and general Internet search engines (For details, please see the methods section at the end of this memo.)
We have not evaluated the quality of references and the resources provided in this response and we offer them only for your reference. Because our search for references is based on the most commonly used resources of research, it is not comprehensive and other relevant references and resources may exist.
Research References
- Vatterott, C. (2017). One-Size-Doesn’t-Fit-All Homework. Educational Leadership, 74 (6), 34–39. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1132301 From the abstract: “At one elementary school in Massachusetts, students are actually excited about homework. In this article, Cathy Vatterott and educators from Vinal Elementary School explain how--and why--they have made the shift to individua lized homework, "a methodical, standards-based approach that starts with big ideas and enduring understandings from the curriculum." Instead of assigning the same work to every student, teachers use individualized homework to allow for more student agency and a tailored approach to skills practice. The article outlines how students set measurable goals, choose assignments, pursue interests, present their learning, and reflect on their progress. The authors also detail how they address parental concerns and students' needs as they move away from one-size-fits-all homework.”
- Brookings Institution. Brown Center on Education Policy (2014). The 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education: How Well are American Students Learning? With special sections on PISA-Shanghai Controversy, Homework, and the Common Core. Washington, D.C. : Brown Center on Education Policy, Brookings Institution , 3 (3), 1-40. https://www.brookings.edu/research/2014-brown-center-report-on-american-education-how-well-are-american-students-learning-2/ https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED586313 From the introduction : “This year’s Brown Center Report on American Education represents the third installment of volume three and the 13th issue overall since the publication began in 2000. Three studies are presented. All three revisit a topic that has been investigated in a previous Brown Center Report. The topics warrant attention again because they are back in the public spotlight….Part I summarizes the recent controversy involving the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) and its treatment of Shanghai-China….Part II is on homework, updating a study presented in the 2003 Brown Center Report….Part III is on the Common Core State Standards (CCSS).”
- Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C. & Patal, E. A. (2006). Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987-2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1–62. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.3102/00346543076001001 https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ751143 From the abstract: “In this article, research conducted in the United States since 1987 on the effects of homework is summarized. Studies are grouped into four research designs. The authors found that all studies, regardless of type, had design flaws. However, both within and across design types, there was generally consistent evidence for a positive influence of homework on achievement. Studies that reported simple homework-achievement correlations revealed evidence that a stronger correlation existed (a) in Grades 7-12 than in K-6 and (b) when students rather than parents reported time on homework. No strong evidence was found for an association between the homework- achievement link and the outcome measure (grades as opposed to standardized tests) or the subject matter (reading as opposed to math). On the basis of these results and others, the authors suggest future research.”
Additional Organizations to Consult
National Education Association: http://www.nea.org/tools/16938.htm From the website: Research Spotlight on Homework: NEA Reviews of the Research on Best Practices in Education.
Keywords and Search Strings
The following keywords and search strings were used to search the reference databases and other sources:
Homework and student achievement Homework effectiveness Homework benefits
Databases and Resources
We searched ERIC for relevant resources. ERIC is a free online library of over 1.6 million citations of education research sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences. Additionally, we searched Google Scholar, the National Education Association, EBSCOhost, the Institute of Education Sciences and JSTOR.
Reference Search and Selection Criteria
When we were searching and reviewing resources, we considered the following criteria:
Date of the publication : References and resources published for last 15 years, from 2002 to present, were included in the search and review. Search Priorities of Reference Sources : Search priority is given to study reports, briefs, and other documents that are published and/or reviewed by IES and other federal or federally funded organizations, academic databases, including WWC, ERIC, and NCEE. Methodology : Following methodological priorities/considerations were given in the review and selection of the references: (a) study types – randomized control trials, quasi experiments, surveys, descriptive data analyses, literature reviews, policy briefs, etc., generally in this order; (b) target population, samples (representativeness of the target population, sample size, volunteered or randomly selected, etc.), study duration, etc.; (c) limitations, generalizability of the findings and conclusions, etc.
This memorandum is one in a series of quick-turnaround responses to specific questions posed by educational stakeholders in the Northeast & Islands Region (Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, Puerto Rico, Rhode Island, US Virgin Islands, and Vermont), which is served by the Regional Educational Laboratory Northeast & Islands at Education Development Center. This memorandum was prepared by REL Northeast & Islands under a contract with the U.S. Department of Education’s Institute of Education Sciences (IES), Contract ED-IES-17-C-0008, administered by Education Development Center. Its content does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of IES or the U.S. Department of Education nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
How Can You Engage All Students? Find Out Thursday, 7/18 at 10AM PDT | Learn More
- Staff Portal
- Consultant Portal
Toll Free 1-800-495-1550
Local 559-834-2449

- Articles & Books
- Explicit Direct Instruction
- Student Engagement
- Checking for Understanding
- ELD Instruction
- About Our Company
- DataWORKS as an EMO
- About Our Professional Development
- English Learner PD
- Schedule a Webinar
- Homework or No Homework
- Research Review
TO GIVE OR NOT TO GIVE HOMEWORK…That is the question!
The amount of homework students are given differs greatly across grade levels and states. Some students are given hours of work while other students are assigned little or no work to be done at home.
So what’s appropriate? What is the purpose of homework? What are the advantages and disadvantages of homework? How much homework should be assigned? How important is the quality of the assignments? And most importantly: Does homework increase student achievement?
These questions represent the ongoing debate surrounding homework for the past two decades. According to a survey by the University of Michigan , homework has doubled over the last twenty years, especially in the younger grades, due to the school’s requirement to meet higher-than-ever achievement goals for children. Although homework has academic and non-academic advantages and disadvantages, the majority of studies conducted reveal inconclusive evidence that assigning homework increases student achievement. Most studies show positive effects for certain students, others suggest no effects, and some even suggest negative effects according to research by Alfie Kohn , an independent scholar (2006).
Let’s begin with the purpose of homework…
Educators assign homework for different reasons and purposes. Homework is assigned either as practice , preparation , extension , or integration of grade-level skills and concepts.
PRACTICE HOMEWORK reinforces learning from the skills and concepts already taught in the classroom. Practice homework promotes retention and automaticity of the concept , skill, and content taught. Examples include practicing multiplication facts or writing simple sentences in order to commit theses skills and concepts to long-term memory .
PREPARATION HOMEWORK is assigned to introduce content that will be addressed in future lessons. However, research suggests that homework is less effective if it is used to teach new or complex skills. For these types of assignments, students typically become stressed which can create a negative perspective towards learning and school.
EXTENSION HOMEWORK requires students to use previously taught skills and concepts and apply them to new situations or projects. For instance, students may use the concept of area and perimeter to build a flowerbed.
INTEGRATION HOMEWORK requires the student to apply learned skills and concepts to produce a single project like reading a book and writing a report on it.
Homework also serves other purposes not directly related to instruction. Homework can help establish communication between parents and children; it can be used as a form of discipline; and it can inform parents about school topics and activities.
The Homework Debate
The homework debate often focuses on how and why homework affects student learning and achievement. Harris Cooper, a professor of psychology, and colleagues (2006) found there are both positive and negative consequences of homework.
The Benefits
Homework provides practice with content, concepts, and skills taught at school by the teacher. It can foster retention and understanding of the academic content. Some studies suggest that homework correlates with student achievement. Cooper, Robinson, and Patall (2006) discovered a positive correlation between the amount of the homework students do and their achievement at the secondary level. Some studies also suggest that assigning homework improves the achievement of low-performing students and students in low-performing schools. However, the correlation between student achievement and homework given to elementary students is inconclusive. Most research only supports homework for middle and high school students (Cooper 1989a; Kohn 2006).
There are also non-academic reasons for assigning homework. Corno and Xu (2004) discovered that homework fosters independence, develops time-management skills, and teaches responsibility. Assigning homework to primary age students can establish better study habits and skills for secondary education (Bempechat, 2004). Homework promotes a positive attitude towards school and keeps families informed about their child’s learning.
The Potential Harm
Homework also has negative associations. It can lead to boredom if the student has already mastered the skills, and it can lead to loss of interest in school due to burnout. Cheating is involved with homework by either copying another student’s work or when help is received from adults in an attempt to finish all the assignments. Also, assigning excessive amounts of homework may result in unneeded stress and pressure on the child, which affects the student’s emotions, behaviors, thinking ability, and physical health.
The correlation between homework and student achievement is inconsistent. In The Battle Over Homework , Cooper determined that the average correlation between the time primary children spent on homework and achievement was around zero. Not to mention, the amount of homework completed had no effect on test scores. David Baker and Gerald LeTendre, professors of education at Penn State , found that countries that assign minimal amounts of homework, like Japan, were the most successful school systems compared to Greece and Iran school systems where students are given a lot of work.
Another concern surrounding homework is its interference with the student’s time to relax and take their minds off work as well as family time. Students are spending too much time completing homework assignments instead of playing outside or enjoying leisure activities, which teach and enhance important life skills.
In addition, homework decreases the time spent with family. As Alfie Kohn states in The Homework Myth , “ Why should children be asked to work a second shift? It’s unconscionable to send children to work for nearly eight hours a day, then have them go home and work for 2-5 more hours. Secondly, it reduces the amount of time that children could be spending with their families. Family time is especially important to a growing child and without it social problems can crop up and a family unit can be compromised by a lack of time being spent together .”
The Amount of Homework
The frequency and duration of each assignment does not necessarily suggest a correlation between homework and student achievement. “ We found that for kids in elementary school there was hardly any relationship between how much homework young children did and how well they were doing in school, but in middle school the relationship is positive and increases until the kids were doing between an hour to two hours a night, which is right where the 10-minute rule says it’s going to be optimal,” stated Harris Cooper. The 10-minute rule was created by the National PTA which suggests 10 minutes per a grade should be assigned (e.g., 70 minutes for 7 th grade). “After that it didn’t go up anymore. Kids that reported doing more than two hours of homework in middle school weren’t doing any better in school than kids who were doing between an hour to two hours ,” said Harris Cooper.
Quantity Versus Quality
Effective homework is homework with a purpose. According to Cooper, some teachers assign ‘shotgun homework’ : blanket drills, questions, and problems. Students are given homework that is not furthering the concepts and skills. The homework is assigned because it has been drilled into our collective mind that homework produces higher performing students. However, homework is most effective when it covers material already taught, is given for review, or is used to reinforce skills previously learned. Students should not be assigned homework on concepts and skills they do not grasp.
DataWORKS Educational Research recommends assigning homework to provide additional repetitions of the content to promote retention and automaticity . The reason for homework is to practice the content, NOT to learn the content. Students learn the content (skills and concepts) from the lesson taught at school. Students need to be able to complete the work at home without assistance because some students do not have an English-speaking parents or guardians to help them.
In conclusion, research is inconsistent in determining if homework increases student achievement. As educators, the amount, frequency, and the purpose should be considered prior to assigning homework. Homework should be used effectively! Instead of the quantity of homework, educators should improve the quality of the assignments. Homework assignments must be well-designed. So, when assigning homework, please consider the effectiveness of it, homework should positively impact the student learning. Otherwise, the debate about homework will continue without an answer – to give or not to give !
Kohn, Alfie (2007). Rethinking Homework .
Kohn, Alfie. The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing (Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 2006).
Cooper, H. (1989). Homework. White Plains, NY: Longman.
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research . 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1–62.
What is your stance on homework? What do you think is an appropriate amount of homework? Why do you assign homework? Please share your experiences in the comment section below.
Author: patricia bogdanovich.
Patricia has held various positions with DataWORKS since 2002. She currently works as a Curriculum Specialist. Patricia helped develop and create many of the early resources and workshops designed by DataWORKS, and she is an expert in analysis of standards. Patricia plans to blog about curriculum and assessments for CCSS and NGSS, classroom strategies, and news and research from the world of education.
Related posts

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Would you like to explore a topic?
- LEARNING OUTSIDE OF SCHOOL
Or read some of our popular articles?
Free downloadable english gcse past papers with mark scheme.
- 19 May 2022
The Best Free Homeschooling Resources UK Parents Need to Start Using Today
- Joseph McCrossan
- 18 February 2022
How Will GCSE Grade Boundaries Affect My Child’s Results?
- Akshat Biyani
- 13 December 2021
TEACHING TECHNIQUES
Homework: Useful Teaching Tool or Waste of Time?
- May 18, 2021
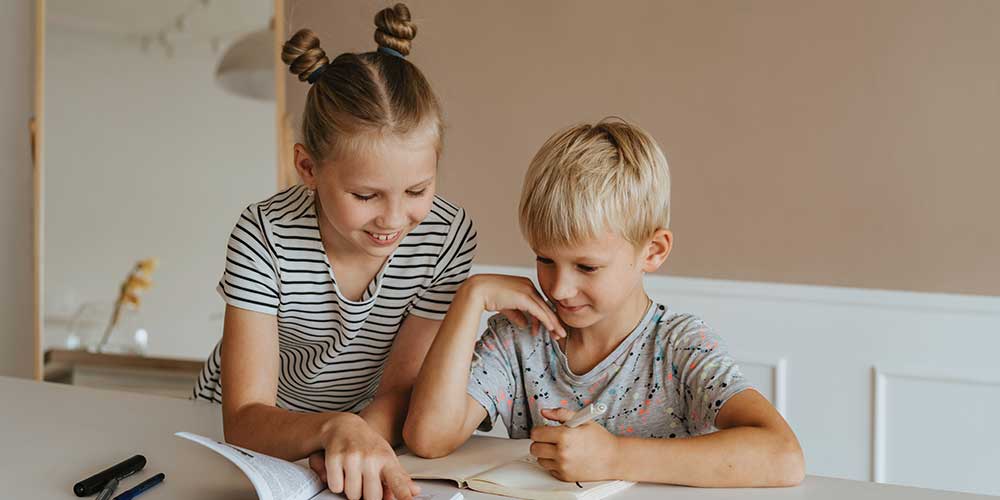

- Helpful or harmful?
How is homework helpful?
- Does homework promote learning?
Downsides of homework
- Should students have homework?
- Stress free homework tips
Homework. How can one little word cause so much trouble? Almost all schools require homework , but should they? Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of homework, plus what the research says you should really be doing after school.
As a pupil in the UK, you will without a doubt encounter homework during your school years. Some kids love it, others… not so much! Many parents struggle to make their child complete their homework and to fit it into their family’s busy schedule, and many kids and teens find homework quite boring. But let’s put our feelings about homework to the side, and focus on a more important question – is homework really necessary?
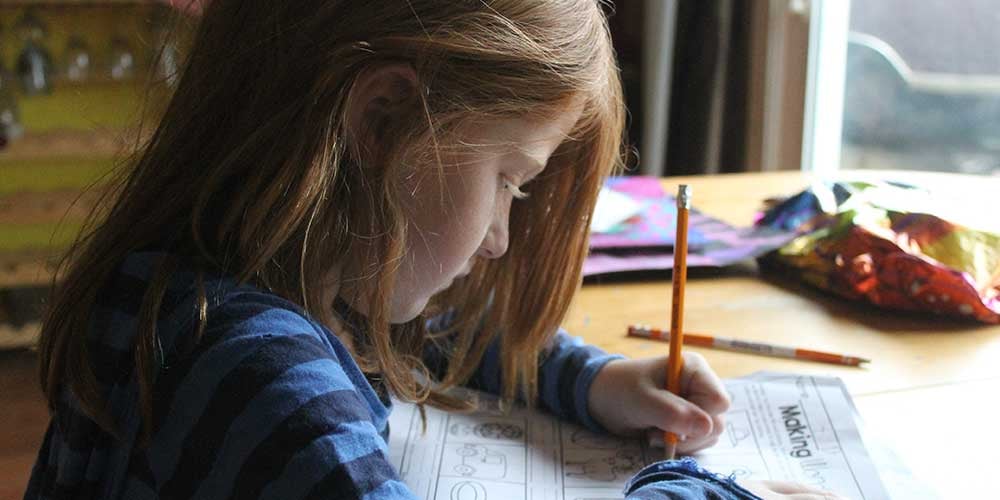

Is homework helpful or harmful?
Well, it depends. There’s loads of debate about homework and whether or not it helps you learn. Researchers have been trying to find the answer to this question since your parents were in school!
It all comes down to the purpose of the homework and the age of the student, as well as their interest in the topic at hand.
For secondary students, homework is useful as a "short and focused intervention .” That means something like a research project that you complete at home. 💻
For primary students, homework can help reinforce skills students are learning in school. It makes sense to practice spelling words at home or working on reading skills , for example.
How does homework promote learning?
One way homework can promote learning is by giving older students a chance to read more content than can be covered in class. For example, a Literature student might read a couple of chapters of a novel at home and then spend the class time discussing its themes with peers. This saves classroom time for the part of learning that’s done with other students.
Research shows that the best homework is closely linked to what you’re learning in the classroom. It should expand your learning and always be something you can complete independently. ✔️
It goes without saying that homework takes time. The more homework you have, the less time you can spend outside or relax.
Homework leaves less time for creative activities that are also very important for brain growth. 🧠
Studies show very little difference in test scores between students who spend lots of time on homework and students who do less homework. For primary school students especially, not many benefits have been found.
So, should students have homework?
In an ideal world, primary students would not have homework. And secondary students would only have short-term homework assignments with a very specific goal, like a book report or a science project.
Since students often do have homework, it shouldn’t take much time - the benefits are the same for a few minutes and a few hours of homework!
Stress-free homework tips
At the end of the day, there may be very little you can do right away about your homework situation. If your teacher assigns it, it must get done – but here are a few tips to make it less stressful:
- It’s a great idea for you to be independent with planning and managing your work time rather than being hounded into starting your homework by your parents. As you get older, it’s up to you to manage yourself – maybe you’d prefer to divide the work up into manageable chunks, for example tackling one subject before dinner and another one after.
- You should have a distraction-free space to work at home. Turn off the television, and keep electronics out of sight to make it easier to stay focused.
- If you’ve had a long school day, it’s a great idea to take some free time after school before starting your homework. You may need a chance to relax and regroup before jumping right into homework.
- If you find yourself struggling with your workload, you should have a chat with your teacher or speak to your parents about it. Homework should closely follow the in-class learning and shouldn’t take more than an hour.
Homework help with GoStudent
If you’re struggling to manage your homework, a GoStudent tutor can help. Our experienced, friendly tutors have a deep understanding of the content they teach, and your tutor can give you the one-on-one support you need to get back on track and be able to finish that homework in no time! 🚀

Popular posts

- By Guy Doza

- By Joseph McCrossan
- In LEARNING TRENDS

- By Akshat Biyani

4 Surprising Disadvantages of Homeschooling
- By Andrea Butler

What are the Hardest GCSEs? Should You Avoid or Embrace Them?
- By Clarissa Joshua
1:1 tutoring to unlock the full potential of your child
More great reads:.

The Best Maths Games 2022
- By Natalie Lever
- August 16, 2022

Five Top Time Management Skills for Tutors
- By Connie Kulis-Page
- July 1, 2022

How to Become a GoStudent Tutor: Follow These Five Easy Steps
- May 19, 2022
Book a free trial session
Sign up for your free tutoring lesson..
Request More Info
Fill out the form below and a member of our team will reach out right away!
" * " indicates required fields
Is Homework Necessary? Education Inequity and Its Impact on Students

The Problem with Homework: It Highlights Inequalities
How much homework is too much homework, when does homework actually help, negative effects of homework for students, how teachers can help.
Schools are getting rid of homework from Essex, Mass., to Los Angeles, Calif. Although the no-homework trend may sound alarming, especially to parents dreaming of their child’s acceptance to Harvard, Stanford or Yale, there is mounting evidence that eliminating homework in grade school may actually have great benefits , especially with regard to educational equity.
In fact, while the push to eliminate homework may come as a surprise to many adults, the debate is not new . Parents and educators have been talking about this subject for the last century, so that the educational pendulum continues to swing back and forth between the need for homework and the need to eliminate homework.
One of the most pressing talking points around homework is how it disproportionately affects students from less affluent families. The American Psychological Association (APA) explained:
“Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs.”
[RELATED] How to Advance Your Career: A Guide for Educators >>
While students growing up in more affluent areas are likely playing sports, participating in other recreational activities after school, or receiving additional tutoring, children in disadvantaged areas are more likely headed to work after school, taking care of siblings while their parents work or dealing with an unstable home life. Adding homework into the mix is one more thing to deal with — and if the student is struggling, the task of completing homework can be too much to consider at the end of an already long school day.
While all students may groan at the mention of homework, it may be more than just a nuisance for poor and disadvantaged children, instead becoming another burden to carry and contend with.
Beyond the logistical issues, homework can negatively impact physical health and stress — and once again this may be a more significant problem among economically disadvantaged youth who typically already have a higher stress level than peers from more financially stable families .
Yet, today, it is not just the disadvantaged who suffer from the stressors that homework inflicts. A 2014 CNN article, “Is Homework Making Your Child Sick?” , covered the issue of extreme pressure placed on children of the affluent. The article looked at the results of a study surveying more than 4,300 students from 10 high-performing public and private high schools in upper-middle-class California communities.
“Their findings were troubling: Research showed that excessive homework is associated with high stress levels, physical health problems and lack of balance in children’s lives; 56% of the students in the study cited homework as a primary stressor in their lives,” according to the CNN story. “That children growing up in poverty are at-risk for a number of ailments is both intuitive and well-supported by research. More difficult to believe is the growing consensus that children on the other end of the spectrum, children raised in affluence, may also be at risk.”
When it comes to health and stress it is clear that excessive homework, for children at both ends of the spectrum, can be damaging. Which begs the question, how much homework is too much?
The National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association recommend that students spend 10 minutes per grade level per night on homework . That means that first graders should spend 10 minutes on homework, second graders 20 minutes and so on. But a study published by The American Journal of Family Therapy found that students are getting much more than that.
While 10 minutes per day doesn’t sound like much, that quickly adds up to an hour per night by sixth grade. The National Center for Education Statistics found that high school students get an average of 6.8 hours of homework per week, a figure that is much too high according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). It is also to be noted that this figure does not take into consideration the needs of underprivileged student populations.
In a study conducted by the OECD it was found that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance .” That means that by asking our children to put in an hour or more per day of dedicated homework time, we are not only not helping them, but — according to the aforementioned studies — we are hurting them, both physically and emotionally.
What’s more is that homework is, as the name implies, to be completed at home, after a full day of learning that is typically six to seven hours long with breaks and lunch included. However, a study by the APA on how people develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work for about only four hours per day. Similarly, companies like Tower Paddle Boards are experimenting with a five-hour workday, under the assumption that people are not able to be truly productive for much longer than that. CEO Stephan Aarstol told CNBC that he believes most Americans only get about two to three hours of work done in an eight-hour day.
In the scope of world history, homework is a fairly new construct in the U.S. Students of all ages have been receiving work to complete at home for centuries, but it was educational reformer Horace Mann who first brought the concept to America from Prussia.
Since then, homework’s popularity has ebbed and flowed in the court of public opinion. In the 1930s, it was considered child labor (as, ironically, it compromised children’s ability to do chores at home). Then, in the 1950s, implementing mandatory homework was hailed as a way to ensure America’s youth were always one step ahead of Soviet children during the Cold War. Homework was formally mandated as a tool for boosting educational quality in 1986 by the U.S. Department of Education, and has remained in common practice ever since.
School work assigned and completed outside of school hours is not without its benefits. Numerous studies have shown that regular homework has a hand in improving student performance and connecting students to their learning. When reviewing these studies, take them with a grain of salt; there are strong arguments for both sides, and only you will know which solution is best for your students or school.
Homework improves student achievement.
- Source: The High School Journal, “ When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math ,” 2012.
- Source: IZA.org, “ Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement? ,” 2014. **Note: Study sample comprised only high school boys.
Homework helps reinforce classroom learning.
- Source: “ Debunk This: People Remember 10 Percent of What They Read ,” 2015.
Homework helps students develop good study habits and life skills.
- Sources: The Repository @ St. Cloud State, “ Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement ,” 2017; Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
- Source: Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
Homework allows parents to be involved with their children’s learning.
- Parents can see what their children are learning and working on in school every day.
- Parents can participate in their children’s learning by guiding them through homework assignments and reinforcing positive study and research habits.
- Homework observation and participation can help parents understand their children’s academic strengths and weaknesses, and even identify possible learning difficulties.
- Source: Phys.org, “ Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework ,” 2018.
While some amount of homework may help students connect to their learning and enhance their in-class performance, too much homework can have damaging effects.
Students with too much homework have elevated stress levels.
- Source: USA Today, “ Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In ,” 2021.
- Source: Stanford University, “ Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework ,” 2014.
Students with too much homework may be tempted to cheat.
- Source: The Chronicle of Higher Education, “ High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame ,” 2010.
- Source: The American Journal of Family Therapy, “ Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background ,” 2015.
Homework highlights digital inequity.
- Sources: NEAToday.org, “ The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’ ,” 2016; CNET.com, “ The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind ,” 2021.
- Source: Investopedia, “ Digital Divide ,” 2022; International Journal of Education and Social Science, “ Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework ,” 2015.
- Source: World Economic Forum, “ COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it ,” 2021.
Homework does not help younger students.
- Source: Review of Educational Research, “ Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003 ,” 2006.
To help students find the right balance and succeed, teachers and educators must start the homework conversation, both internally at their school and with parents. But in order to successfully advocate on behalf of students, teachers must be well educated on the subject, fully understanding the research and the outcomes that can be achieved by eliminating or reducing the homework burden. There is a plethora of research and writing on the subject for those interested in self-study.
For teachers looking for a more in-depth approach or for educators with a keen interest in educational equity, formal education may be the best route. If this latter option sounds appealing, there are now many reputable schools offering online master of education degree programs to help educators balance the demands of work and family life while furthering their education in the quest to help others.
YOU’RE INVITED! Watch Free Webinar on USD’s Online MEd Program >>
Be Sure To Share This Article
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Top 11 Reasons to get Your Master of Education Degree
Free 22-page Book

- Master of Education
Related Posts

The New York Times
The learning network | does your homework help you learn.

Does Your Homework Help You Learn?

Questions about issues in the news for students 13 and older.
- See all Student Opinion »
New research suggests that a lot of assigned homework amounts to pointless busy work that doesn’t help students learn, while more thoughtful assignments can help them develop skills and acquire knowledge. How would you characterize the homework you get?
In the Sunday Review article “The Trouble With Homework,” Annie Murphy Paul reviews the research on homework:
The quantity of students’ homework is a lot less important than its quality. And evidence suggests that as of now, homework isn’t making the grade. Although surveys show that the amount of time our children spend on homework has risen over the last three decades, American students are mired in the middle of international academic rankings: 17th in reading, 23rd in science and 31st in math, according to results from the Program for International Student Assessment released last December. In a 2008 survey, one-third of parents polled rated the quality of their children’s homework assignments as fair or poor, and 4 in 10 said they believed that some or a great deal of homework was busywork. A new study, coming in the Economics of Education Review, reports that homework in science, English and history has “little to no impact” on student test scores. (The authors did note a positive effect for math homework.) Enriching children’s classroom learning requires making homework not shorter or longer, but smarter.
She goes on to enumerate some of the aspects of effective independent assignments, like “retrieval practice,” which basically means doing practice tests to reinforce learning and commit it to memory, and “interleaving,” in which problems are not grouped into sets by type, but rather scattered throughout an assignment, which makes the brain work harder to grasp the material.
Students: Tell us how effective you think your homework is. What kinds of assignments seem pointless? Which ones are confusing or frustrating? Which ones are most engaging and interesting? Which ones are you fairly sure help you learn and grow?
Students 13 and older are invited to comment below. Please use only your first name. For privacy policy reasons, we will not publish student comments that include a last name.
Comments are no longer being accepted.
“I see homework as a big part that helps me learn and grow” that’s what I always said up till I was moved to a different math class. My old math teacher made math easy and fun as well as understandable. But when I was moved I got confused easily, I found it boring, and I even found paying attention hard. Then there’s my English class. I love English with all my heart but my teacher makes me feel like I’m in Preschool! She has hand signs for every rule and if we don’t do them we get more homework! She always puts us into groups and so far every group I’ve been placed in I can’t get along in. One group wouldn’t let me talk and when I gave my opion they scolded me and said I was wrong though it was an opion lesson… Another group was lazy and since I ran out of my medicine that helps me focus, I was lost and told them I need their help to help me keep up with what’s going on yet they let me drag along! History was never my strong point from the start even though my dad is a History teacher. But when I got into a certain class I couldn’t stand it! I was miles behind in homework and around every corner was either homework or projects! I asked for help and I got yelled at! I’m sorry but sometimes homework feels like slave work since I don’t get anything out of good grades except a smile and/or a pat on the back and that’s it. Yes homework can be good for you but there is a limit of how much a student can handle before they collaspe underneath all of that work! But I love it when teachers make homework fun or competive (which we normally do now and days)! Cause that’s when I’m having a blast! But when teachers get too interactive with their class I can’t help but feel creeped out by them. (Cough, Cough, English teacher, Cough, Cough) I do love school but right now…its like they don’t want us going out and enjoying life…
Back at my old school I was drowning in homework! I just couldn’t get the chance to sit back and be young! It was just too much! In every class I had homework! Study this, learn that, solve this, and every where in between! The bullying was no help either since they stole or destroyed my homework so I failing till I switched schools! My suggestion to all you kids who don’t like homework….DON’T GO TO [name of school removed]!!!!!!!! Especially if you’re like me and are considered one of the special kids since the teachers don’t flex to your needs!
At my school , we all think that homework helps people learn in so many different ways. You do your homework to get better grades on test scores because some of the homework you get will have some stuff that can be on test. Another reason is that homework can get you better grades if you just hand it in. You can learn from homework. In my opinion.For example, I had to take notes in algebra yesterday for homework and only took 10 minutes it really help a lot the next day because we had a little mini quiz on it !
Doing my homework every night helps me learn because it helps me remember the lesson gone over in class that day. It also makes it easier to follow the next lesson, which is usually an extension from the lesson the day before.
Homework helps me learn because it’s a review of what we learned in class. Sometimes they give too much work though.
I feel like it all depends on if you understand the work. If a teacher taught you a new topic in class and you didn’t understand it, I dont think you would understand it if you did it again. If you understood it, It would help you because you are repeating the problems.
I don’t think homework helps you learn, I think it helps you remember what you learned. Homework is more of a review of what you did in school during the day, rather than a new subject to learn on a whole.
I personally am not a big fan of homework though, I think that some teachers don’t really realize that we have several other classes which also give us homework, and we sometimes end up with a large amount by the end of the day.
But I’m sure that my procrastination has a lot to do with it as well.
Homework definitely helps me learn. By the time i get home from school some subjects become unfamiliar and homework help reinforce what i learned in class. Better students do their homework and teachers recognize that frequently. Repetition of your homework also helps memorize which you could benefit from on tests and other classwork activities.
Depending on the subject or the assigment, homework can either be redundant or effective. Assignments which make you copy straight out of a textbook are redundant. These assignments are redundant because students hardly put all that much effort into it. By copying a textbook, people aren’t focused on the material, because they are just focusing on getting the assigment done. Straight copying is seen as boring or even in some cases ‘annoying’ by students, which translates into them not learning what they need to learn. Assigments where students are interactive and aren’t just being taught the textbook are interesting and that’s when students learn the most. Writing samples when students are asked for their opinion and to have their voice heard are deemed the most interesting. Thus, being because students then have the ability to share what they’ve learned in their own words and also get to apply their knowledge in their own voice.
On the other hand, when homework is done effectively, the end product will be better grades. If a student neglects to do homework, whether interesting or boring, it will show in their grades. Students who do apply their strongest efforts into their homework will ultimately contribute to better grades.
I think that homework is pointless when the teachers give us homework that is for fun and we have to waist our time doing little projects when we can be doing other more important things like studying. I think that most homework is important I just don’t like it when teachers give too much and it becomes over whelming and I can’t have time to study because it would be too late and then I wouldn’t be able to sleep. If anything I think teachers should give us homework but give us one big homework a week and we work on it for the whole week which it would be due on Friday and then get a test grade for it since it was a big homework. If teachers wouldn’t do that I would love if teachers would give us only three days of homework a week and Fridays we would get a test.
Homework is assigned so that students can practice what they have learned in school and see if they can remember what happened in class. Personally, the homework that has been assigned to me lately has been nothing but busy work that I feel is pointless. The truth is most of the modern day students don’t see the value in doing homework but the discipline and the practice for the real world really are fundamental. The most confusing type of homework assignments that we have come with little to no instructions. When teachers give assignments on things that they haven’t covered yet seems pointless to me since it really isn’t evaluating anything at all. Another type of pointless homework would be the ones in which there is so much repetition that it becomes pointless. In my personal life ive been faced with all types of homework. I believe homework is fundamental to the development of the mind and I will keep doing my homework.
I go to an American school in Bogota, Colombia. Recently in my school I have been getting exaggerated amounts of homework, and most of it has no impact on my learning. I say this because the homework I am assigned is just “busywork” and keeps me up until late hours in the night. The homework I am given is also extremely long and not smart, it is just a very basic review of what we did in class that day. Homework like that is a waste of time since if the student is good and pays attention in class he should know all of the material and shouldn’t be forced to demonstrate it through homework. I believe that what should be improved in not the quantity but the quality of the homework we are assigned. I am not saying homework should be abolished but I am saying it should be changed. If a student is overwhelmed with homework his academic development would also be affected. For example if a student has allot of homework he will probably stay up at night doing it. Maybe he will finish his homework around 10 or 11 in the night. The next day he will have to wake up very early and will only get about 5-6 hours of sleep. In order for the teenage brain to develop correctly a kid needs 8 hours of sleep. So. excessive amount of homework leads to a very tired, unmotivated and less active student. In my school I think the only homework assignments that help me learn are the math ones.
Each subject is different and each grade in school requires a different amount of practice. For example, Math is a subject that I believe needs out-of-classroom practice no matter what grade you are in, or what topic you are covering. It is one of the most essential aptitudes one must acquire in order to be successful in life. Language, whether it be english, spanish, or etc, is also a subject that is vital for an accomplished life. I believe that one must practice in order to become and eloquent speaker and writer, but i only think that a small amount of homework should be given, especially once one reaches the ends of high school. A subject that I feel doesn’t need practice outside of school is history. For me, history is more like a gossip story with dates that “should” be remembered than anything else; therefore, I don’t believe that homework would be necessary to enforce a subject like that.
The idea of having to work all night, studying for a billion exams the next day, getting the college applications going, and practicing a sport isn’t something strange for the average senior at CNG. It seems as if the need to excel at everything might just be the COD of many high school students. As college admissions become more competitive, as more and more people take AP exams and admissions tests there is a greater weight on our shoulders. But is it really worth it? I mean, even if everything goes the way we want it to, was it really worth all our time and energy? There are just better things to do with my life. I would prefer to go deeper into the sciences, write of some philosophical tendency I’m being carried into, do more social work, etc. But I need to commit to an organized agenda, learn the Standards I’m supposed to be learning and show my progress through time. These are fancy ways of creating a level playing field so students can be compared. Is this really what learning has become?
Practice makes perfect some might say. There is no arguing about that. Success in those specific tasks, such as doing homework or working on a particular project that requires zero creativity clearly needs those levels of repetitive practice and great memory. But are we supposed to do this the rest of our lives? I don’t think so. Harris Cooper, a professor from Duke University dedicated to homework research states that “even for high school students, overloading them with homework is not associated with higher grades” (Cooper). I’m sorry, so isn’t homework even doing what its supposed to be doing? The counter-productivity of too much homework, especially in such a critical moment as in college application season, makes the whole educational system lose credibility. Are we being trained to do something we aren’t going to really do or even need in the future? What is the real purpose of doing homework when we aren’t truly learning from it?
Don’t get me wrong. I do believe homework is critical in developing certain skills. How were we supposed to learn basic arithmetic operations without those tons of worksheets and problem sets? Yes, homework is a useful tool but only when used consciously. Statistical evidence seems to agree with this: “teachers in many of the nations that outperform the U.S. on student achievement tests–such as Japan, Denmark and the Czech Republic–tend to assign less homework than American teachers, but instructors in low-scoring countries like Greece, Thailand and Iran tend to pile it on” (Wallis). The need to assign homework, to put a million grades in is too antiquated in my opinion. What’s the problem with guiding classes to a true educational experience and leave behind the limitations of grading, of classifying students, of making them lose all interest, worse yet lose passion for learning and generate hatred towards certain areas of knowledge while capturing valuable time that is needed to explore others?
It depends on what type of homework and the time that it takes to finish it. The homework that I get from English, history, science, and math benefit me and my grades a lot. From my three band classes, and P.E. class, I usually do busy work. I love how the school is run… I learn a lot from the class just itself, and from school assemblies, etc. First, I have to learn before I get my grades… meaning, I don’t care what my grades are like until I actually know and understand the material and knowledge that I learned at school. What we learn from school and from homework are is different. We learn more at school and then apply what we learned in our homework. So most of the time we don’t learn anything that much from homework.
Homework assignments should be provided, but once a month. It allows children to have freedom, and actually feel like life is not all about study and going to a prestigious university.
Homework wastes our time, and in recent articles they say that school’s are killing creativity, and now there is an uproar about homework not providing learning material.
What homework should be is a subjet, say history, and children can choose one that interests them, and they could research it for a month. And after the month is up children can present in class, so that means the child knows thoroughly about their topic and can explain well to their friends, and also they will have an opportunity to listen to other peoples’ research.
I wish we didn’t have homework, because the learning network is providing us with a great amount of resources that homework, in a year, can’t accomplish.
40 hours per week, 8 hours a day, is the legal limit of hours an adult can work in California without being payed overtime. An employee must be payed 150% their usual salary for every hour they work past 8 hours a day. I spend between 34 and 39 hours per week at school, not counting homework (aprox. 10-15 hours per week). My suggestion is that any work assigned to students requiring them to spend more than 40 hours a week on academics be graded with a bonus of 50% the student’s grade. This would encourage students to do well in order to have a higher bonus, and would discourage teachers from assigning so much work (since we all how much giving out bonus points pains them!) As for the questions: I think that homework is effective as long as it will help improve a student’s understanding and execution of course material. As a general rule, I don’t think it’s very useful to be assigned more than one assignment in each category of homework to a class (1 chapter to read, 1 exercise, 1 essay). 5 math exercises is 5 too many if I understand the lesson, and 4 too many if it is the teacher’s goal to find out whether or not I do. As a student, I have a limited amount of time and love to divide up into my work. I find work that leaves the thinking up to the student to be the most engaging and helpful to my understanding: the fewer details on how I should do the assignment, the more I work to make it reflect my understanding of the topic.
It is interesting to write your homework in your free time at home. Homework and assignments are important for innovation and elaboration. Take your time in doing your homework because this will help you understand the lesson more.
i think this is the best amendment ever.
Sense at my school , school just started we do not have that much homework. But I’ve hear a lot of people say that towards the middle of the year is when everyone’s backpack’s become really heavy. Teacher’s start giving more than one homework assignment per class. So I think that homework does not help you learn because you do work at school why do you need to do it again at home? I think teacher’s do that because they want to figure out if you are capable to do the same thing at home and also because they just want us to have some type of work to do at home. Once again I do no think that homework helps you learn.
I personally don’t think homework helps a student learn. I feel if you don’t get what the teacher teaches in class then I personally don’t get the homework at all. If I don’t get the subject then I personally to the homework wrong and I’m sure that other people do it wrong too. My teachers all say that they don’t give so much homework and they really don’t, but since they all give about 20-30 minutes of homework each subject, it piles up.I think that homework is effective as long as it will help improve a student’s understanding and execution of course material. I personally don’t think that homework always helps, but it does.
I think that homework is useful sometimes, but not always. Most of the time, it is just the same thing we did in class, and if we didn’t get it then we still won’t get it at home, primarily because our parents have no clue about how to do it either.
i think that homework should not in are school systems because homework is just practice and i know that practice makes perfect but when you got 5 subjects it add to a lot. I also i believe that all homework (practice) is just studying and unless we have i don’t want to take the time for nothing but another school day
1) What kinds of assignments seem pointless?
I don’t believe that any assignments are pointless, because teachers always have a reason for giving homework. However, teachers often give homework where the effort on the part of the student outweighs the teacher’s goal. In addition, many homework assignments do not effectively reach their goal.
2) Which ones are confusing or frustrating?
Assignments are usually not confusing, although sometimes, when given very easy assignments, I do not understand what the point is (which does not mean that the assignments are pointless — the point is simply mysterious to me). I get most frustrated by homework when I receive virtually identical assignments at regular intervals, but never get feedback from the teacher. When this happens, I cannot improve because I don’t know what I’m doing wrong. For example, our French teacher has given us this assignment three times this year: Comment on a predetermined stanza of a Baudelaire poem. The first two stanzas earned me 17 (out of 20) with no corrections other than grammatical mistakes. For the third assignment, I have written a very similar analysis and I expect to get a very similar grade. If there are 20 possible points and I didn’t get all of them, why did the teacher not provide any comments?
3) Which ones are most engaging and interesting?
Honestly, although I understand the value of homework, I do not enjoy doing it (unless it involves creativity, but with no art, music or creative writing classes in high school, this is extremely rare).
Which ones are you fairly sure help you learn and grow?
I believe all homework helps me learn and grow — the question is whether the amount of growth induced by the homework is worth the effort involved.
Yes, some homework are important. Like learning rhetoric at home to be able to talk about it in class. Doing a math problem to make sure the lesson is understood. But is doing ten exercises on a lesson we did not fully go over because the teacher did not manage to end the lesson on time and now needs us to try to figure it out on our own useful? Is doing forty little problems with the same math equation over and over again necessary? I believe it is not. I believe some teachers are using a lot of useless homework because they must think in some way that it will be beneficent one day or another. They are often wrong. Unless a whole class of twenty students decided they want to be physician, i do not understand why learning what is the kind of relation between the Earth and the Moon, over a dozen of exercises, is in anyway useful. Also, a teacher might think they are doing the right thing, making us practice something that is already learned in class, by giving its students five exercises. Sure, it is not a bad idea. But since all the teachers, or most of them, are looking to do the right thing, five teachers that wants you to practice with some homework exercises, becomes twenty-five exercises for the students. Over something they either understood, or not understood. In any case it’s frustrating. If you understand what it is about then you are just wasting your time doing those exercises. If you did not understand it, you are going to spend ten minutes on each question, usually ending by guessing wrong, when all it could have taken was another clear explanation from the teacher. So yes, homework can be useful, and it often is, but not always.
What's Next
- Audio/Video
- Lecture Topics
- Special Issues
- Standards & Testing
- Follow on Twitter
Does Homework Improve Learning?
Chapter 2 of the homework myth (da capo press, 2006) copyright © 2006 by alfie kohn, by alfie kohn.
Because the question that serves as the title of this chapter doesn’t seem all that complicated, you might think that after all this time we’d have a straightforward answer. You might think that open-minded people who review the evidence should be able to agree on whether homework really does help.
When you think about it, any number of issues could complicate the picture and make it more or less likely that homework would appear to be beneficial in a given study: What kind of homework are we talking about? Fill-in-the-blank worksheets or extended projects? In what school subject(s)? How old are the students? How able and interested are they? Are we looking at how much the teacher assigned or at how much the kids actually did? How careful was the study and how many students were investigated?
Even when you take account of all these variables, the bottom line remains that no definite conclusion can be reached, and that is itself a significant conclusion. The fact that there isn’t anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps. It demonstrates just how superficial and misleading are the countless declarations one hears to the effect that “studies find homework is an important contributor to academic achievement.”
Taken as a whole, the available research might be summarized as inconclusive. But if we look more closely, even that description turns out to be too generous. The bottom line, I’ll argue in this chapter, is that a careful examination of the data raises serious doubts about whether meaningful learning is enhanced by homework for most students. Of the eight reasons that follow, the first three identify important limitations of the existing research, the next three identify findings from these same studies that lead one to question homework’s effectiveness, and the last two introduce additional data that weaken the case even further.
Limitations of the Research
1. At best, most homework studies show only an association, not a causal relationship. Statistical principles don’t get much more basic than “correlation doesn’t prove causation.” The number of umbrellas brought to a workplace on a given morning will be highly correlated with the probability of precipitation in the afternoon, but the presence of umbrellas didn’t make it rain. Also, I’d be willing to bet that kids who ski are more likely to attend selective colleges than those who don’t ski, but that doesn’t mean they were accepted because they ski, or that arranging for a child to take skiing lessons will improve her chances of being admitted. Nevertheless, most research purporting to show a positive effect of homework seems to be based on the assumption that when students who get (or do) more homework also score better on standardized tests, it follows that the higher scores were due to their having had more homework.
There are almost always other explanations for why successful students might be in classrooms where more homework is assigned – let alone why these students might take more time with their homework than their peers do. Even Cooper, a proponent of homework, concedes that “it is equally plausible,” based on the correlational data that comprise most of the available research on the topic, “that teachers assign more homework to students who are achieving better . . . or that better students simply spend more time on home study.”[13] In still other cases, a third variable – for example, being born into a more affluent and highly educated family – might be associated with getting higher test scores and with doing more homework (or attending the kind of school where more homework is assigned). Again, it would be erroneous to conclude that homework is responsible for higher achievement. Or that a complete absence of homework would have any detrimental effect at all.
Sometimes it’s not easy to spot those other variables that can separately affect achievement and time spent on homework, giving the impression that these two are causally related. One of the most frequently cited studies in the field was published in the early 1980s by a researcher named Timothy Keith, who looked at survey results from tens of thousands of high school students and concluded that homework had a positive relationship to achievement, at least at that age. But a funny thing happened ten years later when he and a colleague looked at homework alongside other possible influences on learning such as quality of instruction, motivation, and which classes the students took. When all these variables were entered into the equation simultaneously, the result was “puzzling and surprising”: homework no longer had any meaningful effect on achievement at all.[14] In other words, a set of findings that served – and, given how often his original study continues to be cited, still serves – as a prominent basis for the claim that homework raises achievement turns out to be spurious.
Several studies have actually found a negative relationship between students’ achievement (or their academic performance as judged by teachers) and how much time they spend on homework (or how much help they receive from their parents).[15] But researchers who report this counterintuitive finding generally take pains to explain that it “must not be interpreted as a causal pattern.”[16] What’s really going on here, we’re assured, is just that kids with academic difficulties are taking more time with their homework in order to catch up.
That sounds plausible, but of course it’s just a theory. One study found that children who were having academic difficulties actually didn’t get more homework from their teachers,[17] although it’s possible they spent longer hours working on the homework that they did get. But even if we agreed that doing more homework probably isn’t responsible for lowering students’ achievement, the fact that there’s an inverse relationship seems to suggest that, at the very least, homework isn’t doing much to help kids who are struggling. In any event, anyone who reads the research on this topic can’t help but notice how rare it is to find these same cautions about the misleading nature of correlational results when those results suggest a positive relationship between homework and achievement. It’s only when the outcome doesn’t fit the expected pattern (and support the case for homework) that they’re carefully explained away.
In short, most of the research that’s cited to show that homework is academically beneficial really doesn’t prove any such thing.
2. Do we really know how much homework kids do? The studies claiming that homework helps are based on the assumption that we can accurately measure the number and length of assignments. But many of these studies depend on students to tell us how much homework they get (or complete). When Cooper and his associates looked at recent studies in which the time spent on homework was reported by students, and then compared them with studies in which that estimate was provided by their parents, the results were quite different. In fact, the correlation between homework and achievement completely disappeared when parents’ estimates were used.[18] This was also true in one of Cooper’s own studies: “Parent reports of homework completion were . . . uncorrelated with the student report.”[19] The same sort of discrepancy shows up again in cross-cultural research — parents and children provide very different accounts of how much help kids receive[20] — and also when students and teachers are asked to estimate how much homework was assigned.[21] It’s not clear which source is most accurate, by the way – or, indeed, whether any of them is entirely reliable.
3. Homework studies confuse grades and test scores with learning. Most researchers, like most reporters who write about education, talk about how this or that policy affects student “achievement” without questioning whether the way that word is defined in the studies makes any sense. What exactly is this entity called achievement that’s said to go up or down? It turns out that what’s actually being measured – at least in all the homework research I’ve seen — is one of three things: scores on tests designed by teachers, grades given by teachers, or scores on standardized exams. About the best thing you can say for these numbers is that they’re easy for researchers to collect and report. Each is seriously flawed in its own way.
In studies that involve in-class tests, some students are given homework – which usually consists of reviewing a batch of facts about some topic – and then they, along with their peers who didn’t get the homework, take a quiz on that very material. The outcome measure, in other words, is precisely aligned to the homework that some students did and others didn’t do — or that they did in varying amounts. It’s as if you were told to spend time in the evening learning the names of all the vice presidents of the United States and were then tested only on those names. If you remembered more of them after cramming, the researcher would then conclude that “learning in the evening” is effective.
Here’s one example. Cooper and his colleagues conducted a study in 1998 with both younger and older students (from grades 2 through 12), using both grades and standardized test scores to measure achievement. They also looked at how much homework was assigned by the teacher as well as at how much time students spent on their homework. Thus, there were eight separate results to be reported. Here’s how they came out:
Younger students
Effect on grades of amount of homework assigned No sig. relationship
Effect on test scores of amount of homework assigned No sig. relationship
Effect on grades of amount of homework done Negative relationship
Effect on test scores of amount of homework done No sig. relationship
Older students
Effect on grades of amount of homework done Positive relationship
Of these eight comparisons, then, the only positive correlation – and it wasn’t a large one – was between how much homework older students did and their achievement as measured by grades.[26] If that measure is viewed as dubious, if not downright silly, then one of the more recent studies conducted by the country’s best-known homework researcher fails to support the idea of assigning homework at any age.
The last, and most common, way of measuring achievement is to use standardized test scores. Purely because they’re standardized, these tests are widely regarded as objective instruments for assessing children’s academic performance. But as I’ve argued elsewhere at some length,[27] there is considerable reason to believe that standardized tests are a poor measure of intellectual proficiency. They are, however, excellent indicators of two things. The first is affluence: Up to 90 percent of the difference in scores among schools, communities, or even states can be accounted for, statistically speaking, without knowing anything about what happened inside the classrooms. All you need are some facts about the average income and education levels of the students’ parents. The second phenomenon that standardized tests measure is how skillful a particular group of students is at taking standardized tests – and, increasingly, how much class time has been given over to preparing them to do just that.
In my experience, teachers can almost always identify several students who do poorly on standardized tests even though, by more authentic and meaningful indicators, they are extremely talented thinkers. Other students, meanwhile, ace these tests even though their thinking isn’t particularly impressive; they’re just good test-takers. These anecdotal reports have been corroborated by research that finds a statistically significant positive relationship between a shallow or superficial approach to learning, on the one hand, and high scores on various standardized tests, on the other. What’s more, this association has been documented at the elementary, middle, and high school level.
Standardized tests are even less useful when they include any of these features:
* If most of the questions are multiple-choice, then students are unable to generate, or even justify, their responses. To that extent, students cannot really demonstrate what they know or what they can do with what they know. Multiple-choice tests are basically designed so that many kids who understand a given idea will be tricked into picking the wrong answer.
* If the test is timed, then it places a premium not on thoughtfulness but on speed.
* If the test is focused on “basic skills,” then doing well is more a function of cramming forgettable facts into short-term memory than of really understanding ideas, making connections and distinctions, knowing how to read or write or analyze problems in a sophisticated way, thinking like a scientist or historian, being able to use knowledge in unfamiliar situations, and so on.
* If the test is given to younger children, then, according to an overwhelming consensus on the part of early-education specialists, it is a poor indicator of academic skills. Many children under the age of eight or nine are unable to demonstrate their proficiency on a standardized test just because they’re tripped up by the format.
* If the test is “norm-referenced” (like the Iowa Test of Basic Skills, Terra Nova, Stanford Achievement Test, and others used widely in classrooms and also by researchers), then it was never designed to evaluate whether students know what they should. Instead, its primary purpose is to artificially spread out the scores in order to facilitate ranking students against each other. The question these tests are intended to answer is not “How well are our kids – or our schools – doing?” but “Who’s beating whom?” We know nothing about academic competence in absolute terms just from knowing what percentage of other test-takers a given child has bested. Moreover, the selection of questions for these tests is informed by this imperative to rank. Thus, items that a lot of students answer correctly (or incorrectly) are typically eliminated – regardless of whether the content is important – and replaced with questions that about half the kids will get right. This is done in order to make it easier to compare students to one another.
I’m unaware of any studies that have even addressed the question of whether homework enhances the depth of students’ understanding of ideas or their passion for learning. The fact that more meaningful outcomes are hard to quantify does not make test scores or grades any more valid, reliable, or useful as measures. To use them anyway calls to mind the story of the man who looked for his lost keys near a streetlight one night not because that was where he dropped them but just because the light was better there.
If our children’s ability to understand ideas from the inside out is what matters to us, and if we don’t have any evidence that giving them homework helps them to acquire this proficiency, then all the research in the world showing that test scores rise when you make kids do more schoolwork at home doesn’t mean very much. That’s particularly true if the homework was designed specifically to improve the limited band of skills that appear on these tests. It’s probably not a coincidence that, even within the existing test-based research, homework appears to work better when the assignments involve rote learning and repetition rather than real thinking.[29] After all, “works better” just means “produces higher scores on exams that measure these low-level capabilities.”
Overall, the available homework research defines “beneficial” in terms of achievement, and it defines achievement as better grades or standardized test scores. It allows us to conclude nothing about whether children’s learning improves.
Cautionary Findings
Assume for the moment that we weren’t concerned about basing our conclusions on studies that merely show homework is associated with (as opposed to responsible for) achievement, or studies that depend on questionable estimates of how much is actually completed, or studies that use deeply problematic outcome measures. Even taken on its own terms, the research turns up some findings that must give pause to anyone who thinks homework is valuable.
4. Homework matters less the longer you look. The longer the duration of a homework study, the less of an effect the homework is shown to have.[30] Cooper, who pointed this out almost in passing, speculated that less homework may have been assigned during any given week in the longer-lasting studies, but he offered no evidence that this actually happened. So here’s another theory: The studies finding the greatest effect were those that captured less of what goes on in the real world by virtue of being so brief. View a small, unrepresentative slice of a child’s life and it may appear that homework makes a contribution to achievement; keep watching and that contribution is eventually revealed to be illusory.
6. There is no evidence of any academic benefit from homework in elementary school. Even if you were untroubled by the methodological concerns I’ve been describing, the fact is that after decades of research on the topic, there is no overall positive correlation between homework and achievement (by any measure) for students before middle school – or, in many cases, before high school. More precisely, there’s virtually no research at all on the impact of homework in the primary grades – and therefore no data to support its use with young children – whereas research has been done with students in the upper elementary grades and it generally fails to find any benefit.
The absence of evidence supporting the value of homework before high school is generally acknowledged by experts in the field – even those who are far less critical of the research literature (and less troubled by the negative effects of homework) than I am. But this remarkable fact is rarely communicated to the general public. In fact, it’s with younger children, where the benefits are most questionable, if not altogether absent, that there has been the greatest increase in the quantity of homework!
In 2005, I asked Cooper if he knew of any newer studies with elementary school students, and he said he had come across exactly four, all small and all unpublished. He was kind enough to offer the citations, and I managed to track them down.
The first was a college student’s term paper that described an experiment with 39 second graders in one school. The point was to see whether children who did math homework would perform better on a quiz taken immediately afterward that covered exactly the same content as the homework. The second study, a Master’s thesis, involved 40 third graders, again in a single school and again with performance measured on a follow-up quiz dealing with the homework material, this time featuring vocabulary skills. The third study tested 64 fifth graders on social studies facts.
All three of these experiments found exactly what you would expect: The kids who had drilled on the material – a process that happened to take place at home — did better on their respective class tests. The final study, a dissertation project, involved teaching a lesson contained in a language arts textbook. The fourth graders who had been assigned homework on this material performed better on the textbook’s unit test, but did not do any better on a standardized test. And the third graders who hadn’t done any homework wound up with higher scores on the standardized test.[36] Like the other three studies, the measure of success basically involved memorizing and regurgitating facts.
Such a correlation would be a prerequisite for assuming that homework provides academic benefits but I want to repeat that it isn’t enough to justify that conclusion. A large correlation is necessary, in other words, but not sufficient. Indeed, I believe it would be a mistake to conclude that homework is a meaningful contributor to learning even in high school. Remember that Cooper and his colleagues found a positive effect only when they looked at how much homework high school students actually did (as opposed to how much the teacher assigned) and only when achievement was measured by the grades given to them by those same teachers. Also recall that Keith’s earlier positive finding with respect to homework in high school evaporated once he used a more sophisticated statistical technique to analyze the data.
All of the cautions, qualifications, and criticisms in this chapter, for that matter, are relevant to students of all ages. But it’s worth pointing out separately that absolutely no evidence exists to support the practice of assigning homework to children of elementary-school age – a fact that Cooper himself rather oddly seems to overlook (see chapter 4). No wonder “many Japanese elementary schools in the late 1990s issued ‘no homework’ policies.”[39] That development may strike us as surprising – particularly in light of how Japan’s educational system has long been held out as a model, notably by writers trying to justify their support for homework.[40] But it’s a development that seems entirely rational in light of what the evidence shows right here in the United States.
Additional Research
7. The results of national and international exams raise further doubts about homework’s role. The National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) is often called the nation’s report card. Students who take this test also answer a series of questions about themselves, sometimes including how much time they spend on homework. For any number of reasons, one might expect to find a reasonably strong association between time spent on homework and test scores. Yet the most striking result, particularly for elementary students, is precisely the absence of such an association. Even students who reported having been assigned no homework at all didn’t fare badly on the test.
International comparisons allow us to look for correlations between homework and test scores within each country and also for correlations across countries. Let’s begin with the former. In the 1980s, 13-year-olds in a dozen nations were tested and also queried about how much they studied. “In some countries more time spent on homework was associated with higher scores; in others, it was not.”[43] In the 1990s, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) became the most popular way of assessing what was going on around the world, although of course its conclusions can’t necessarily be generalized to other subjects. Again, the results were not the same in all countries, even when the focus was limited to the final years of high school (where the contribution of homework is thought to be strongest). Usually it turned out that doing some homework had a stronger relationship with achievement than doing none at all, but doing a little homework was also better than doing a lot. [44] This is known as a “curvilinear” relationship; on a graph it looks sort of like an upside-down U.
What about correlations across cultures? Here we find people playing what I’ll later argue is a pointless game in which countries’ education systems are ranked against one another on the basis of their students’ test scores. Pointless or not, “a common explanation of the poor performance of American children in cross-cultural comparisons of academic achievement is that American children spend little time in study.”[46] The reasoning, in other words, goes something like this:
Premise 1: Our students get significantly less homework than their counterparts across the globe.
Premise 2: Other countries whup the pants off us in international exams.
Conclusion: Premise 1 explains Premise 2.
Additional conclusion: If U.S. teachers assigned more homework, our students would perform better.
Every step of this syllogism is either flawed or simply false. We’ve already seen that Premise 1 is no longer true, if indeed it ever was (see chapter 1). Premise 2 has been debunked by a number of analysts and for a number of different reasons.[47] Even if both premises were accurate, however, the conclusions don’t necessarily follow; this is another example of confusing correlation with causation.
But in fact there is now empirical evidence, not just logic, to challenge the conclusions. Two researchers looked at TIMSS data from both 1994 and 1999 in order to be able to compare practices in 50 countries. When they published their findings in 2005, they could scarcely conceal their surprise:
8. Incidental research raises further doubts about homework. Reviews of homework studies tend to overlook investigations that are primarily focused on other topics but just happen to look at homework, among several other variables. Here are two examples:
Second, back in the late 1970s, New Jersey educator Ruth Tschudin identified about three hundred “A+ teachers” on the basis of recommendations, awards, or media coverage. She then set out to compare their classroom practices to those of a matched group of other teachers. Among her findings: the exceptional teachers not only tended to give less homework but also were likely to give students more choices about their assignments.
It’s interesting to speculate on why this might be true. Are better teachers more apt to question the conventional wisdom in general? More likely to notice that homework isn’t really doing much good? More responsive to its negative effects on children and families? More likely to summon the gumption to act on what they’ve noticed? Or perhaps the researchers who reviewed the TIMMS data put their finger on it when they wrote, “It may be the poorest teachers who assign the most homework [because] effective teachers may cover all the material in class.”[52] (Imagine that quotation enlarged and posted in a school’s main office.)
This analysis rings true for Steve Phelps, who teaches math at a high school near Cincinnati. “In all honesty,” he says, “the students are compelled to be in my class for 48 minutes a day. If I can’t get done in 48 minutes what I need to get done, then I really have no business intruding on their family time.”[53] But figuring out how to get it done isn’t always easy. It certainly took time for Phil Lyons, the social studies teacher I mentioned earlier who figured out that homework was making students less interested in learning for its own sake – and who then watched as many of them began to “seek out more knowledge” once he stopped giving them homework. At the beginning of Lyons’s teaching career, he assigned a lot of homework “as a crutch, to compensate for poor lessons. . . . But as I mastered the material, homework ceased to be necessary. A no-homework policy is a challenge to me,” he adds. “I am forced to create lessons that are so good that no further drilling is required when the lessons are completed.”
Lyons has also conducted an informal investigation to gauge the impact of this shift. He gave less and less homework each year before finally eliminating it completely. And he reports that
The results observed by a single teacher in an uncontrolled experiment are obviously not conclusive. Nor is the Harvard physics study. Nor is Tschudin’s survey of terrific teachers. But when all these observations are combined with the surprising results of national and international exams, and when these, in turn, are viewed in the context of a research literature that makes a weak, correlational case for homework in high school – and offers absolutely no support for homework in elementary school – it gradually becomes clear that we’ve been sold a bill of goods.
People who never bought it will not be surprised, of course. “I have a good education and a decent job despite the fact that I didn’t spend half my adolescence doing homework,” said a mother of four children whose concern about excessive homework eventually led to her becoming an activist on the issue.[55] On the other hand, some will find these results not only unexpected but hard to believe, if only because common sense tells them that homework should help. But just as a careful look at the research overturns the canard that “studies show homework raises achievement,” so a careful look at popular beliefs about learning will challenge the reasons that lead us to expect we will find unequivocal research support in the first place. The absence of supporting data actually makes sense in retrospect, as we’ll see in chapter 6 when we examine the idea that homework “reinforces” what was learned in class, along with other declarations that are too readily accepted on faith.
Most proponents, of course, aren’t saying that all homework is always good in all respects for all kids – just as critics couldn’t defend the proposition that no homework is ever good in any way for any child. The prevailing view — which, even if not stated explicitly, seems to be the premise lurking behind our willingness to accept the practice of assigning homework to students on a regular basis — might be summarized as “Most homework is probably good for most kids.” I’ve been arguing, in effect, that even that relatively moderate position is not supported by the evidence. I’ve been arguing that any gains we might conceivably identify are both minimal and far from universal, limited to certain ages and to certain (dubious) outcome measures. What’s more, even studies that seem to show an overall benefit don’t prove that more homework – or any homework, for that matter — has such an effect for most students. Put differently, the research offers no reason to believe that students in high-quality classrooms whose teachers give little or no homework would be at a disadvantage as regards any meaningful kind of learning.
But is there some other benefit, something other than academic learning, that might be cited in homework’s defense? That will be the subject of the following chapter…
For full citations, please see the reference section of The Homework Myth .
1. Cooper et al., p. 70.
2. This early study by Joseph Mayer Rice is cited in Gill and Schlossman 2004, p. 175.
3. Goldstein.
5. Paschal et al.; Walberg et al.
6. Barber, p. 56. Two of the four studies reviewed by Paschal et al. found no benefit to homework at all. The third found benefits at two of three grade levels, but all of the students in this study who were assigned homework also received parental help. The last study found that students who were given math puzzles (unrelated to what was being taught in class) did as well as those who got traditional math homework.
7. Jongsma, p. 703.
8. There is reason to question whether this technique is really appropriate for a topic like homework, and thus whether the conclusions drawn from it would be valid. Meta-analyses may be useful for combining multiple studies of, say, the efficacy of a blood pressure medication, but not necessarily studies dealing with different aspects of complex human behavior. Mark Lepper (1995), a research psychologist at Stanford University, has argued that “the purely statistical effect sizes used to compare studies in a meta-analysis completely and inappropriately ignore the crucial social context in which the conduct and interpretation of research in psychology takes place.” The real-world significance of certain studies is lost, he maintains, when they are reduced to a common denominator. “The use of purely statistical measures of effect size” – overlooking what he calls the “psychological size of effects” – “promotes a[n] illusion of comparability and quantitative precision that is subtly but deeply at odds with the values that define what makes a study or a finding interesting or important.” This concern would seem to apply in the case of distinctive investigations of homework. (Quotations from pp. 414, 415, 420.)
9. Cooper 1999a, 2001. The proportion of variance that can be attributed to homework is derived by squaring the average correlation found in the studies, which Cooper reports as +.19.
10. Cooper et al. 2006.
12. Hofferth and Sandberg, p. 306.
13. Cooper 1999a, p. 100. It’s also theoretically possible that the relationship is reciprocal: Homework contributes to higher achievement, which then, in turn, predisposes those students to spend more time on it. But correlations between the two leave us unable to disentangle the two effects and determine which is stronger.
14. Cool and Keith. Interestingly, Herbert Walberg, an avid proponent of homework, discovered that claims of private school superiority over public schools proved similarly groundless once other variables were controlled in a reanalysis of the same “High School and Beyond” data set (Walberg and Shanahan).
15. For example, see Chen and Stevenson; Epstein; Georgiou; Gorges and Elliott.
16. Epstein and Van Voorhis, pp. 183-84. Also see Walberg et al., pp. 76-77.
17. Muhlenbruck et al. In Cooper et al. 1998, “there was some evidence that teachers in Grades 2 and 4 reported assigning more homework to classes with lower achievement, but students and parents reported that teachers assigned more homework to higher achieving students, especially when grades were the measure of achievement” (p. 80).
18. Cooper et al. 2006, p. 44.
19. Cooper et al. 2001, pp. 190-91.
20. Chen and Stevenson, p. 558.
21. “Several surveys have found that students consistently report their homework time to be higher than teachers’ estimates” (Ziegler 1986, p. 21).
22. Ziegler 1992, p. 602. Cooper (1989a, p. 161), too, describes the quality of homework research as “far from ideal” for a number of reasons, including the relative rarity of random-assignment studies.
23. Dressel, p. 6.
24. For a more detailed discussion about (and review of research regarding) the effects of grades, see Kohn 1999a, 1999b.
25. Cooper 1999a, p. 72. That difference shrank in the latest batch of studies (Cooper et al. 2006), but still trended in the same direction.
26. Cooper et al. 1998. The correlation was .17.
27. See Kohn 1999b, 2000, which includes analysis and research to support the claims made in the following paragraphs.
28. Nevertheless, Cooper criticizes studies that use only one of these measures and argues in favor of those, like his own, that make use of both (see Cooper et al. 1978, p. 71). The problems with tests and grades may be different, but they don’t cancel each other out when the two variables are used at the same time.
29. Cooper 1989a, p. 99. On the other hand, a study reporting a modest correlation between achievement test scores and the amount of math homework assigned also found that “repetitive exercises” of the type intended to help students practice skills actually “had detrimental effects on learning” (Trautwein et al., p. 41).
30. Cooper 1999a, p. 72; 2001, p. 16. The studies he reviewed lasted anywhere from two to thirty weeks.
31. Natriello and McDill. “An additional hour of homework each night results in an increase in English [grade point average] of 0.130” (p. 27).
32. Tymms and Fitz-Gibbon. Quotation appears on p. 8. If anything, this summary understates the actual findings. When individual students’ scores on the English A-level exams were examined, those who worked for more than seven hours a week in a particular subject “tended to get a third of a grade better than students of the same gender and ability who worked less than [two hours] a week, and if students with similar prior achievement are considered, the advantage only amounted to about a fifth of a grade.” When the researchers compared classes rather than individuals – which is probably the more appropriate unit of analysis for a homework study — the average A-level grades in heavy-homework classes were no different than those in light-homework classes, once other variables were held constant (pp. 7-8).
33. Barber, p. 55.
34. Cooper 1989a, p. 109. Why this might be true is open to interpretation. Cooper (2001, p. 20) speculates that it’s because younger children have limited attention spans and poor study skills, but this explanation proceeds from – and seems designed to rescue — the premise that the problem is not with the homework itself. Rather, it’s the “cognitive limitations” of children that prevent them from taking advantage of the value that’s assumed to inhere in homework. While it wouldn’t be sufficient to substantiate this account, it would certainly be necessary to show that homework usually is valuable for older students. If there’s any reason to doubt that claim, then we’d have to revisit some of our more fundamental assumptions about how and why students learn.
35. The unpublished study by C. Bents-Hill et al. is described in Cooper 2001, p. 26.
36. The four, in order, are Finstad; Townsend; Foyle; and Meloy.
37. When Cooper and his colleagues reviewed a new batch of studies in 2006, they once again found that “the mean correlation between time spent on homework and achievement was not significantly different from zero for elementary school students” (Cooper et al. 2006, p. 43).
38. Cooper 1989a, p. 100. The correlations were .02, .07, and .25, respectively.
39. Baker and Letendre, p. 118.
40. For example, see any number of writings by Herbert Walberg. Another possible reason that “elementary achievement is high” in Japan: teachers there “are free from the pressure to teach to standardized tests” (Lewis, p. 201). Until they get to high school, there are no such tests in Japan.
41. See the table called “Average Mathematics Scores by Students’ Report on Time Spent Daily on Mathematics Homework at Grades 4, 8, and 12: 2000,” available from the National Center for Education Statistics at: http://nces.ed.gov/nationsreportcard/mathematics/results/ homework.asp. As far as I can tell, no data on how 2004 NAEP math scores varied by homework completion have been published for nine- and thirteen-year-olds. Seventeen-year-olds were not asked to quantify the number of hours devoted to homework in 2004, but were asked whether they did homework “often,” “sometimes,” or “never” – and here more homework was correlated with higher scores (U.S. Department of Education 2005, p. 63).
42. In 2000, fourth graders who reported doing more than an hour of homework a night got exactly same score as those whose teachers assigned no homework at all. Those in the middle, who said they did 30-60 minutes a night, got slightly higher scores. (See http://nces.ed.gov/ nationsreportcard/reading/results/homework.asp). In 2004, those who weren’t assigned any homework did about as well as those who got either less than one hour or one to two hours; students who were assigned more than two hours a night did worse than any of the other three groups. For older students, more homework was correlated with higher reading scores (U.S. Department of Education 2005, p. 50).
43. Ziegler 1992, p. 604.
44. Mullis et al. 1998, p. 114.
45. Chen and Stevenson, pp. 556-57.
46. Ibid., p. 551.
47. Even at a first pass, TIMSS results suggest that the U.S. does poorly in relative terms only at the high school level, not with respect to the performance of younger students. But TIMSS results really don’t support the proposition that our seniors are inferior. That’s true, first, because, at least on the science test, the scores among most of the countries are actually pretty similar in absolute terms (Gibbs and Fox, p. 87). Second, the participating countries “had such different patterns of participation and exclusion rates, school and student characteristics, and societal contexts that test score rankings are meaningless as an indicator of the quality of education” (Rotberg, p. 1031). Specifically, the students taking the test in many of the countries were older, richer, and drawn from a more selective pool than those in the U.S. Third, when one pair of researchers carefully reviewed half a dozen different international achievement surveys conducted from 1991 to 2001, they found that “U.S. students have generally performed above average in comparisons with students in other industrialized nations” (Boe and Shin; quotation appears on p. 694). Also see the many publications on this subject by Gerald Bracey.
48. Baker and Letendre, pp. 127-28, 130. Emphasis in original.
49. Mullis et al. 2001, chap. 6.
50. Tsuneyoshi, p. 375.
51. Sadler and Tai; personal communication with Phil Sadler, August 2005. The larger study also found that students who took Advanced Placement science courses – and did well on the test – didn’t fare much better in college science courses than those who didn’t take the A.P. classes at all.
52. Baker and Letendre, p. 126.
53. Phelps, personal communication, March 2006.
54. Lyons, personal communication, December 2005.
55. Quoted in Lambert.
56. This New Jersey principal is quoted in Winerip, p. 28.
Copyright © 2006 by Alfie Kohn. Permission must be obtained in order to reprint this chapter in a published work or in order to offer it for sale in any form. Please write to the address indicated on the Contact Us page.

- Conscious and Unconscious Motivations
- Effective Motivation Techniques
- Extrinsic Motivation
- Inspirational Motivational Stories
- Intrinsic Motivation
- Learning and Motivation
- Motivation and Desire
- Motivation and Discipline
- Motivation and Emotions
- Motivation and Goal Setting
- Motivation and Instinct
- Motivation and Willpower
- Motivational Theories
- Procrastination and Motivation
- Understanding Motivation
- Motivation and Lifestyle
- Motivation and Mental Health
- Motivation in Education
- Motivation in Sports
- Motivation in the Workplace
- Practical Applications of Motivation
- Productivity

How does homework enhance understanding and retention of lessons?
Homework has long been a fundamental component of formal education, aiming to reinforce learning through independent study outside of the classroom. Its purpose is to extend the learning process beyond the limited timeframe of a classroom setting, allowing students to engage further with the subject matter. One significant aspect of homework is its role in enhancing understanding and retention of lessons. By requiring students to review and practice what they have learned, homework provides invaluable opportunities to solidify new knowledge, develop essential skills, and deepen comprehension. In this discussion, we will explore the various ways in which homework positively contributes to enhancing students’ understanding and long-term retention of lessons.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Homework in Education
Homework has long been a staple in education, serving as a means to reinforce and extend learning beyond the classroom. While its effectiveness has been debated among educators and parents, there is compelling evidence to suggest that homework can indeed enhance understanding and retention of lessons . In this article, we will delve into the various ways in which homework contributes to the learning process and why it should be considered an integral part of education.
1. Reinforcing Concepts
One of the primary purposes of homework is to reinforce the concepts taught in class. Through practice and application, students can solidify their understanding of the material covered. When they engage with homework assignments, they are given the opportunity to revisit key concepts, apply problem-solving skills, and consolidate their learning. This repetition plays a crucial role in strengthening their knowledge and ensuring that it is retained for the long term.
2. Deepening Understanding
Homework provides students with the chance to delve deeper into a subject and explore it beyond the surface level. In a classroom setting, time constraints often limit the extent to which topics can be explored. However, homework allows students to engage with the material at their own pace, conduct additional research, and gain a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. By delving deeper into the material, students can develop critical thinking skills and form connections that enhance their overall comprehension.
3. Independent Learning
Another benefit of homework is that it promotes independent learning. By completing assignments outside of the classroom, students are encouraged to take responsibility for their own learning and develop self-discipline. They learn to manage their time effectively, set goals, and seek out resources to aid their understanding. This sense of autonomy and self-direction fosters a lifelong love for learning and equips students with valuable skills that extend far beyond their academic journey.
4. Retention of Knowledge
Research suggests that the act of retrieving information from memory strengthens the neural pathways associated with that knowledge. Homework provides the perfect opportunity for students to engage in active recall, as they are required to retrieve information and apply it to solve problems or complete tasks. This process of retrieval enhances long-term retention, ensuring that the lessons learned in the classroom are firmly embedded in the students’ minds.
5. Application of Skills
Homework allows students to apply the skills and knowledge they have acquired in real-world contexts. By tackling authentic problems or engaging in practical tasks, students can see the relevance and applicability of what they have learned. This application of skills not only reinforces understanding but also helps students develop transferable skills that can be utilized beyond the classroom. Whether it is analyzing data, writing essays, or solving mathematical equations, homework provides a platform for students to put their knowledge into action.
In conclusion, homework serves as a valuable tool in enhancing understanding and retention of lessons. By reinforcing concepts, deepening understanding, promoting independent learning, facilitating retention, and encouraging the application of skills, homework plays a vital role in the learning process. However, it is important for educators to strike a balance and ensure that homework assignments are purposeful, meaningful, and manageable. When implemented effectively, homework can truly empower students and contribute to their overall academic success.
6. Feedback and Reflection
Homework provides an avenue for students to receive feedback on their progress and identify areas for improvement. When teachers review and provide feedback on homework assignments, students gain valuable insights into their strengths and weaknesses. This feedback loop allows them to reflect on their learning, make necessary adjustments, and seek further clarification if needed. By actively engaging with feedback, students can enhance their understanding and make strides towards mastery of the subject matter.
7. Preparation for Assessments
Homework plays a crucial role in preparing students for assessments such as quizzes, tests, and exams. By regularly practicing concepts through homework assignments, students become familiar with the types of questions and problems they may encounter in assessments. This familiarity reduces anxiety and helps students feel more confident when approaching exams. Homework also serves as a diagnostic tool for teachers, allowing them to gauge students’ understanding and tailor their instruction accordingly.
8. Parental Involvement
Homework offers an opportunity for parents to be involved in their child’s education. When parents assist their children with homework, they gain insights into their child’s learning progress and can provide additional support and guidance. This partnership between parents and teachers strengthens the educational experience and reinforces the importance of learning beyond the classroom walls.
In conclusion, homework serves as a valuable tool in education by enhancing understanding and retention of lessons. Through the reinforcement of concepts, deepening of understanding, promotion of independent learning, facilitation of retention, encouragement of skill application, provision of feedback and reflection, preparation for assessments, and fostering of parental involvement, homework contributes to the holistic development of students. However, it is essential for educators to strike a balance and ensure that homework assignments are purposeful, meaningful, and manageable, taking into account the individual needs and abilities of students. When implemented effectively, homework can empower students, cultivate a love for lifelong learning, and set them up for success in their academic journey and beyond.
What is the purpose of homework?
Homework serves as an extension of classroom learning, allowing students to practice and apply the knowledge and skills they have acquired during lessons. It provides an opportunity for students to reinforce their understanding of various concepts and foster deeper learning through independent study. Additionally, homework assists in developing important study habits, time management skills, and discipline.
How does homework enhance understanding of lessons?
Homework plays a crucial role in enhancing understanding of lessons by allowing students to revisit and review what they have learned in class. By applying the concepts independently, students can solidify their understanding, identify areas of confusion, and seek clarification if needed. It also helps students to connect different ideas from various lessons, reinforcing a coherent understanding of the subject matter.
Does homework improve retention of lessons?
Absolutely! The act of engaging with homework assignments aids in the retention of lessons. When students actively revisit and practice the material, they are more likely to retain the information in their long-term memory. Regularly spaced intervals of reviewing and recalling the content through homework assignments significantly enhance retention. It reinforces students’ ability to recall and apply the learned knowledge, which is crucial for long-term academic success.
Can homework help in identifying areas of difficulty?
Yes, homework serves as an excellent tool for identifying areas of difficulty and potential gaps in understanding. When students struggle with certain concepts while completing their homework, it highlights the need for further clarification or practice. Teachers can review and provide additional guidance to address these areas of difficulty, promoting a more comprehensive understanding of the lessons. Homework acts as a diagnostic tool, enabling teachers to tailor their instruction to meet the specific needs of students.
Are there any benefits to collaborative homework assignments?
Collaborative homework assignments can offer numerous benefits. When students work together on homework, it encourages discussion, sharing of ideas, and peer learning. This collaborative approach fosters a deeper level of understanding as students explain concepts to one another, ask questions, and engage in problem-solving together. It also enhances communication and teamwork skills, while promoting a sense of community within the classroom.
How can homework be made more effective?
To maximize the effectiveness of homework, it is important to ensure that assignments are meaningful, engaging, and relevant to the lessons taught. Homework should be designed to promote critical thinking, independent problem-solving, and application of knowledge. Providing timely and constructive feedback on completed assignments is also crucial. Additionally, considering the individual needs and abilities of students while assigning homework can help tailor the tasks to their specific learning objectives and enhance overall effectiveness.
How Can You Find Motivation to Apply for a Job?
How can you find motivation for a project, how can you build intrinsic motivation, how can you find motivation for art, the relationship between motivation and discipline: a deeper under, does hypnosis work for motivation.

CS234: Reinforcement Learning Spring 2024

Announcements
- The poster session will be from 11:30am-2:30pm in the Huang Foyer (area outside of NVIDIA auditorium).
Course Description & Logistics
- Lectures will be live every Monday and Wednesday: Videos of the lecture content will also be made available to enrolled students through canvas.
- Lecture Materials (videos and slides) : All standard lecture materials will be delivered through modules with pre-recorded course videos that you can watch at your own time. Each week's modules are listed in the schedule and can be accessed here , and will be posted by the end of Sunday before that week's class. Guest lectures will be presented live and recorded for later watching. Recordings will be available to enrolled students through Canvas.
- 1:1 office hours: Students can sign up for 1:1 office hours with faculty and CAs. These will all be appointment-based so that students need not to wait in queue. See our calendar for times and sign up links. [Office hour schedules will be posted by the end of Tuesday on week 1] --> here . These may be offered in person but will definitely be offered via zoom. -->
- Problem session practice: We will also make available optional additional problem session questions and videos to provide additional opportunities to learn about the material.
- Quizzes: Instead of a large high-stakes midterm, there will be four quizzes over the course. We will drop the lowest score of Quiz 1-3.
- Project: There will be no final project.
- --> Platforms: All assignments and quizzes will be handled through Gradescope, where you will also find your grades. We will send out links and access codes to enrolled students through Canvas. You can find Winter 2023 materials here.
-->
Tabular MDP planning
[Assignment 1 Released]Apr 8 Apr 9 Apr 10 Apr 11 Apr 12 Apr 13 Apr 14 Lecture Materials
-->
-->Policy Evaluation
5:30pm-6:30pm
Q learning and Function Approximation
Assignment 1
[Assignment 2 Released]
Apr 15 Apr 16 Apr 17 Apr 18 Apr 19 Apr 20 Apr 21 Lecture Materials
[Quiz 1]
-->Policy Search 1
Policy Search 2
Apr 22 Apr 23 Apr 24 Apr 25 Apr 26 Apr 27 Apr 28 Lecture Materials
[Quiz 1]
-->Policy Search 3
Offline RL 1
Assignment 2
Apr 29 Apr 30 May 1 May 2 May 3 May 4 May 5 Lecture Materials
[Assignment 2]
-->Offline RL 2
Midterm
[Assignment 3 Released]
Project Proposal
May 6 May 7 May 8 May 9 May 10 May 11 May 12 Lecture Materials
[Assignment 2]
-->Offline RL 3
Exploration 1
May 13 May 14 May 15 May 16 May 17 May 18 May 19 Lecture Materials
[Assignment 2]
-->Exploration 2
Exploration 3
Assignment 3
May 20 May 21 May 22 May 23 May 24 May 25 May 26 Lecture Materials
[Assignment 2]
-->Multi-Agent Game Playing
Guest Lecture
Project Milestone
May 27 May 28 May 29 May 30 May 31 Jun 1 Jun 2 Lecture Materials
[Assignment 2]
-->Memorial Day:
No Class
In-class Quiz
Jun 3 Jun 4 Jun 5 Jun 6 Jun 7 Jun 8 Jun 9 Lecture Materials
Value Alignment
Poster Session
Jun 10 Jun 11 Jun 12 Jun 13 Jun 14 Jun 15 Jun 16 Final Project Report
- Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, Sutton and Barto, 2nd Edition. This is available for free here and references will refer to the final pdf version available here .
- Reinforcement Learning: State-of-the-Art, Marco Wiering and Martijn van Otterlo, Eds. [ link ]
- Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Stuart J. Russell and Peter Norvig.[ link ]
- Deep Learning, Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville. [ link ]
- David Silver's course on Reinforcement Learning [ link ]
Grade Breakdown
- Assignment 1: 10%
- Assignment 2: 18%
- Assignment 3: 18%
- Midterm: 25%
- Course Project: 24%
- Proposal: 1%
- Milestone: 2%
- Poster Presentation: 5%
Late Day Policy
- You can use 5 late days total.
- A late day extends the deadline by 24 hours.
- You are allowed up to 2 late days for assignments 1, 2, 3, project proposal, and project milestone, not to exceed 5 late days total. You may not use any late days for the project poster presentation and final project paper. For group submissions such as the project proposal and milestone, all group members must have the corresponding number of late days used on the assignment, and if one or more members do not have a sufficient amount of late days, all group members will incur a grade penalty of 50% within 24 hours and 100% after 24 hours, as explained below.
- If you use two late days and hand an assignment in after 48 hours, it will be worth at most 50%. If you do not have enough late days left, handing the assignment within 1 day after it was due (adjusting for the late days used) will be worth at most 50%. No credit will be given to assignments handed in after 24 hours they were due (adjusting for any late days. E.g. if you use 2 late days, then after this policy applies 24 hours after your 2 late days, e.g. after 72 hours). Please contact us if you think you have an extremely rare circumstance for which we should make an exception. This policy is to ensure that feedback can be given in a timely manner.
- There will be one midterm and one quiz. See the schedule for the dates.
- Exams will be held in class for on-campus students.
- Conflicts : If you are not able to attend the in class midterm and quizzes with an official reason, please email us at [email protected] , as soon as you can so that an accommodation can be scheduled. (Historically this is either to ask you to take the exam remotely at the same time, or to schedule an alternate exam time).
- Notes for the exams : You are welcome to bring a 1-sided 1 (letter sized) page of handwritten notes to the midterm. For the quiz you are welcome to bring a double sided (letter sized) page of handwritten notes. No calculators, laptops, cell phones, tablets or other resources will be allowed.
Assignments and Submission Process
- Assignments : See Assignments page where all the assignments will be posted.
- Computing Resources : We will have some cloud resources available for later assignments.
- Submission Process : The submission instructions for the assignments can also be found on the Assignments page .
Office Hours
- Individual 1:1 15 minute office hours that you can sign up here . See our calendar for detailed schedules. Video conference links will be provided during sign up.
- Group Office Hours are 5PM-8PM on Wed, Thu, and Fri and will be held on Nooks . We will have small tables where students can work on particular problems together.
- Go to the Zoom Client for Linux page and download the correct Linux package for your Linux distribution type, OS architecture and version.
- Follow the linux installation instructions here .
- Download Zoom installer here .
- Installation instructions can be found here .
- Go to Stanford Zoom and select 'Launch Zoom'.
- Click 'Host a Meeting'; nothing will launch but this will give a link to 'download & run Zoom'.
- Click on 'download & run Zoom' to obtain and download 'Zoom_launcher.exe'.
- Run 'Zoom_launcher.exe' to install.
Communication
Regrading requests.
- If you think that the course staff made a quantifiable error in grading your assignment or exam, then you are welcome to submit a regrade request. Regrade requests should be made on gradescope and will be accepted for three days after assignments or exams are returned.
- Note that while doing a regrade we may review your entire assigment, not just the part you bring to our attention (i.e. we may find errors in your work that we missed before).
Academic Collaboration, AI Tools Usage and Misconduct
Academic accommodation, credit/no credit enrollment.

Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
The research cited by educators just doesn't seem to make sense. If a child wants to learn to play the violin, it's obvious she needs to practice at home between lessons (at least, it's ...
Most teachers assign homework to reinforce what was presented in class or to prepare students for new material. Less commonly, homework is assigned to extend student learning to different contexts or to integrate learning by applying multiple skills around a project. ... Homework for students with learning disabilities: The implications of ...
Washington Post journalist Valerie Strauss asked, "Does homework work when kids are learning all day at home?" While students were mostly back in school buildings in fall 2021, the question remains of how effective homework is as an educational tool. ... Homework helps to reinforce classroom learning, while developing good study habits and ...
used to reinforce the content and skills taught in the classroom. However, nothing can replace the ... Homework does have some beneficial effects. Homework can help students develop effective study habits. Homework can show students that learning can occur at home as well as .
Key Takeaways: Homework improves brain function and enhances cognitive abilities. By practicing and repeating new skills through homework, students can enhance their memory and retain knowledge. Homework helps students build suitable study habits, learn time management, and realize personal responsibility. Homework fosters independence and the ...
What the research. says aboutHOMEWORKWHAT IS HOMEWORK?"Tasks assigned to students by school teachers that are meant to be carried out during non-school hours" (Cooper, 1989, .7 as cited in Hattie, 2009, p. 234). Homework is to be used to practice or reinforce. rning that has already taken place. WHY T.
The Case for Homework. Posted September 29, 2016. By Matt Weber. This fall, the start of the new school year seemingly brought with it a trend of teachers forgoing homework assignments in order to allow their students more time outside of school for family and play. A number of these announcements took off on social media, with many parents ...
A schoolwide effort to reduce homework has led to a renewed focus on ensuring that all work assigned really aids students' learning. I used to pride myself on my high expectations, including my firm commitment to accountability for regular homework completion among my students. But the trauma of Covid-19 has prompted me to both reflect and adapt.
Homework that offers adequate practice of important skills also helps reinforce skills in a variety of contexts. A survey of school leaders around homework best practices found similar results: homework can facilitate engagement when it is an authentic, engaging extension of the class. Results: homework should be designed intentionally, with ...
Practice, or reinforcement of a skill, is part of the educational process. Practice in classwork and homework is an important part of guaranteeing students are learning what is being taught ...
Homework has long been a topic of social research, but rela-tively few studies have focused on the teacher's role in the homework process. Most research examines what students do, and whether and ...
It's been shown that excessive homework can lead to cheating. With too much homework, students end up copying off one another in an attempt to finish all their assignments. Pro 2: Homework Helps to Reinforce Classroom Learning. Homework is most effective when it allows students to revise what they learn in class.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning ...
Homework, when designed and implemented properly, is a valuable tool for reinforcing learning. This essay provides a summary of educational research on homework, discusses the elements of effective homework, and suggests practical classroom applications for teachers. The synthesis of these three areas is intended to supplement the literature on ...
tween the amount of homework students do and their academic achievement. On the opposite side of the argument, researchers such as Kohn (2006), Bennet ... and reinforce learning of simple skills taught in class. In upper elementary grades, homework should play a more direct role in fostering improved achievement in school. Finally, in
PRACTICE HOMEWORK reinforces learning from the skills and concepts already taught in the classroom. ... However, homework is most effective when it covers material already taught, is given for review, or is used to reinforce skills previously learned. Students should not be assigned homework on concepts and skills they do not grasp.
For primary students, homework can help reinforce skills students are learning in school. It makes sense to practice spelling words at home or working on reading skills, for example. How does homework promote learning? One way homework can promote learning is by giving older students a chance to read more content than can be covered in class ...
Homework helps reinforce classroom learning. Students typically retain 50% or less of what they hear, read or see in class; additional engagement with course content helps increase that retention. Source: "Debunk This: People Remember 10 Percent of What They Read," 2015. Homework helps students develop good study habits and life skills.
Better students do their homework and teachers recognize that frequently. Repetition of your homework also helps memorize which you could benefit from on tests and other classwork activities. Alexa S September 14, 2011 ·. Depending on the subject or the assigment, homework can either be redundant or effective.
Cooper (1989a, p. 161), too, describes the quality of homework research as "far from ideal" for a number of reasons, including the relative rarity of random-assignment studies. 23. Dressel, p. 6. 24. For a more detailed discussion about (and review of research regarding) the effects of grades, see Kohn 1999a, 1999b.
Homework has long been a staple in education, serving as a means to reinforce and extend learning beyond the classroom. While its effectiveness has been debated among educators and parents, there is compelling evidence to suggest that homework can indeed enhance understanding and retention of lessons .
Reinforcement Learning: State-of-the-Art, Marco Wiering and Martijn van Otterlo, Eds. Artificial ... For example, such a situation may arise if a student requires extra days to submit a homework due to a medical emergency, or if a student needs to schedule an alternative midterm date due to events such as conference travel etc. ...
Shop New Arrivals
The Rolex Yacht-Master II Reference 116681

2007 was the year Rolex proved that it could only be taunted so much by detractors for the lack of complications in its lineup before it would come out swinging. It has long been the anti-Rolex league’s favorite go-to criticism, holding up the Swiss giant’s catalog of ruggedly simple, almost minimalist, three-hand watches and sneeringly comparing them to the overtly functional pieces from the likes of Patek Philippe or Vacheron Constantin. Did Rolex lack the imagination to compete with the sky charts and moonphases of other watchmakers? Or was it the technical prowess it was missing? Rolex took it with its usual granite stoicism for decades, with the modesty of the Day-Date’s dual calendar or the Daytona’s chronograph seemingly as extravagant as it was prepared to go. Then, the iconic Swiss watch manufacturer released the Rolex Yacht-Master II series.
Vastly different from the original and less complex Yacht-Master, the Rolex Yacht Master II is a vibrant behemoth that contains one of the most technically impressive complications ever made. As a product, it could also serve as the dictionary definition of the word “niche.” Powered by a new caliber that required more than 35,000 hours to devise, the result was a watch that’s sole purpose was to help yacht skippers coordinate the starting procedure of a sailing regatta. The first models of the collection were available in either yellow or white gold. Then In 2011, the Yacht master II ref. 116681 appeared, which is a striking Rolesor variant that blends tough 904L stainless steel with precious 18k Everose gold. If you’re into big watches that make a bold statement on the wrist, then keep reading for everything you need to know about the Rolex Yacht-Master II 116681
Rolex Yacht-Master II 116681

Yacht-Master II Reference 116681 Key Features:
- Reference Number: 116681
- Year of Introduction: 2011
- Case Size: 44mm
- Materials: Everose Rolesor (wo-tone stainless steel and Everose gold)
- Functions: Time w/ running seconds, regatta chronograph featuring a programmable countdown timer with mechanical memory and on-the-fly synchronization
- Dial: White w/ Luminous Hour Markers
- Hands: Straight or Mercedes
- Luminous Material: Chromalight
- Bezel: Ring Command Bezel; blue Cerachrom insert w/ 10-minute scale
- Crystal: Sapphire (Flat)
- Movement: Rolex Cal. 4161 (automatic w/ 72-hour power reserve)
- Water Resistance: 100 meters (330 feet)
- Strap/Bracelet: Oyster Bracelet (two-tone stainless steel and Everose gold)
- Clasp: Oysterlock with 5mm Easylink extension
- Approx. Price (USD): $25,350 (Retail); $30,000 – $35,000 (Pre-Owned)
Click here for our Ultimate Buying Guide on the Rolex Yacht-Master II

Everose Rolesor Yacht Master II Design
While the styles of the Yacht-Master II watches have split opinions and are a world away from the handsome elegance that has been the Rolex hallmark for over 100 years, this technical yet luxurious sports watch has won plenty of fans. Its concept and sheer audacity have also silenced many of the brand’s critics and Rolex has proved that, should it decide to mix it up in the world of complications, it can compete with the best of them.
As mentioned, the first two Rolex Yacht Master II models that debuted in 2007 were in yellow gold (ref. 116688) and white gold (ref. 116689, which was discontinued in 2022). Five years later, Rolex unveiled the Yacht-Master II ref. 116681 as the two-tone Everose gold and stainless steel variant. The combination of the two metals, the bright blue bezel (crafted from Rolex’s ceramic alloy, Cerachrom), and the flashy dial is certainly not the subtlest of Rolex watches, but somehow, the Yacht-Master II 116681 just works.
The Everose gold elements – on the bezel numerals, crown, pushers, snailing around the seconds sub-dial, and center links of the sporty Oyster bracelet – soften some of the brashness of the all-steel or yellow gold versions. As a variant, it’s a definite eye-catcher. It has retained its rather graceful proportions, especially for such a large piece and one that crams in so much functionality. The 44mm case (the biggest case size in the Rolex fleet that’s only shared by the Deepsea) affords a large surface area for the dial designers to play with. And it’s just as well. There is a lot of information displayed on the watch’s face, but the logical placement of each element gives it legible readability.
At the top is a horseshoe-shaped track numbered to ten. The starting gun in a regatta is preceded by a warning signal, often either five or ten minutes beforehand. It informs participants the countdown has begun, and the Yacht-Master II’s curved gauge is there to precisely time the flying start – the long dagger-like hand marks the countdown seconds while the small red arrow-tipped hand displays the countdown minutes.
However, the clever part comes should our yacht skipper need to reset the countdown for any reason. The watch is the first in the world to feature a mechanical memory with both flyback and fly-forward functionality, and it allows the regatta timer to reset to synchronize with the official race timer – either forwards or backwards to the nearest minute. Therefore, should the countdown have been triggered too early or too late, it’s a simple step to bring it back in line.

Rolex Yacht-Master II Dial Update
On the occasion of the 10th anniversary of the Yacht-Master II, Rolex rolled out redesigned dials across the entire collection – including, of course, the Yacht-Master II ref. 116681. So what changed?
First, Rolex replaced the original straight hands with a Mercedes handset, which is much more common across the brand’s sports watches. Also, the hands of the Yacht Master II 116681 went from a dark blue to Everose gold – a nice touch to match the rest of the pink-toned details of the watch. Another dial update that occurred to bring the face of the Yacht-Master II more in line with Rolex’s other sports watches concerns the shape of the hour markers.
Earlier models featured square lume-filled indexes for each hour. However, after the 2017 dial redesign, Yacht-Master II watches now included an inverted triangle and a rectangle at 12 and 6, respectively. Naturally, since the Yacht-Master II 116681 is an Everose Rolesor edition, the hour markers feature Everose gold surrounds.

Yacht-Master II Ring Command Bezel and In-House Caliber
The key to the impressive functionality of the Rolex Yachtmaster II lies in the model’s most conspicuous component: the bright blue Cerachrom bezel with its oversized, pink golden numerals. More than simply being the watch’s border, the bezel is central to its overall operation.
Directly linked to the internal movement, the Ring Command Bezel, to give it its proper title, unlocks the programmable actions of the watch by rotating it counter-clockwise through 90 degrees. With the bezel activated, the crown can be used to set the countdown duration and the two pushers at the two and four o’clock positions start and stop the chronograph and work the flyback function. It sounds like a convoluted affair, but in reality, there is a beautifully designed intuitiveness to getting the most out of the Yacht-Master II.
The Rolex engineers have pared down the process as much as possible, while still retaining all the necessary performance. Underneath everything lies the movement. The original references were released with the Cal. 4160, a heavily reworked version of the Daytona’s Cal. 4130, complete with the vertical clutch that eliminates backlash on the chronograph seconds hand.
By 2013, Rolex had perfected the purpose-built Cal. 4161 specifically for the Yacht-Master II. At the time, it was the company’s most component-heavy movement to date, and the Caliber 4161 is constructed from 360 separate parts. As well as the improved accuracy and shock resistance provided by including Rolex’s proprietary Parachrom hairspring, the 31-jewel, high-beat movement also has a power reserve of 72 hours.

Over A Decade of the Rolex 116681 Yacht-Master II
The Rolex Yacht-Master II ref. 116681 has been a part of the brand’s catalog for over a decade now. Despite the movement update in 2013 to the Caliber 4131 and the dial update that occurred in 2017, Rolex has retained the same reference number since this two-tone variant’s release in 2011. And that’s quite curious given that Rolex has allocated new reference numbers to other watch models that have undergone much more subtle updates. Rolex truly works in mysterious ways!
It’s also interesting to note that in 2022, Rolex discontinued the white gold and platinum Yacht-Master II ref. 116689, which brings the Yacht-Master II lineup down from four references to only three. Perhaps the end of the Rolex Yacht-Master II ref. 116681 is near? Though we don’t wish for that to happen, it’s not uncommon for the modern-day Rolex to replace models after about a decade (or less) of production.
While the Rolex Yacht-Master II 116681 has an undeniable heft and is ultra-luxurious, it can easily be worn all day. Its watertight Oyster case ensures it’s more than a match for the rigors of life on the ocean and its robust self-winding movement is top-notch. As a skipper’s watch, this Rolex Yacht-Master II is in a class all its own. But even if you don’t sail competitively and only ever use the watch’s innovative timing function in the kitchen (if at all,) the steel and Everose gold Yacht-Master II ref. 116681 is a head-turning luxury sports watch that’s unlike any other in Rolex’s lineup.

About Paul Altieri
Paul Altieri is a vintage and pre-owned Rolex specialist, entrepreneur, and the founder and CEO of BobsWatches.com. - the largest and most trusted name in luxury watches. He is widely considered a pioneer in the industry for bringing transparency and innovation to a once-considered stagnant industry. His experience spans over 35 years and he has been published in numerous publications including Forbes, The NY Times, WatchPro, and Fortune Magazine. Paul is committed to staying up-to-date with the latest research and developments in the watch industry and e-commerce, and regularly engages with other professionals in the industry. He is a member of the IWJG, the AWCI and a graduate of the GIA. Alongside running the premier retailer of pre-owned Rolex watches, Paul is a prominent Rolex watch collector himself amassing one of the largest private collections of rare timepieces. In an interview with the WSJ lifestyle/fashion editor Christina Binkley, Paul opened his vault to display his extensive collection of vintage Rolex Submariners and Daytonas. Paul Altieri is a trusted and recognized authority in the watch industry with a proven track record of expertise, professionalism, and commitment to excellence.

Bob's Watches Blog Updates
Sign up and be the first to read exclusive articles and the latest horological news.
Bob's Watches / Rolex Blog / Rolex Info

Recommended Articles

Vintage Watch Reviews Under $30k: The Rolex Explorer Reference 1016

Rolex 1675 GMT-Master Co-Branded Dials

Rolex Oysterdate Precision 6694 Ultimate Buying Guide
You may also like.

Audemars Piguet Royal Oak
Audemars Piguet Royal Oak Selfwinding Chronograph Silver Dial

Rolex Daytona
Rolex Daytona 116500 White Dial

Speedmaster
Omega Speedmaster Date / Day-Date Silver Dial
array assignment in verilog
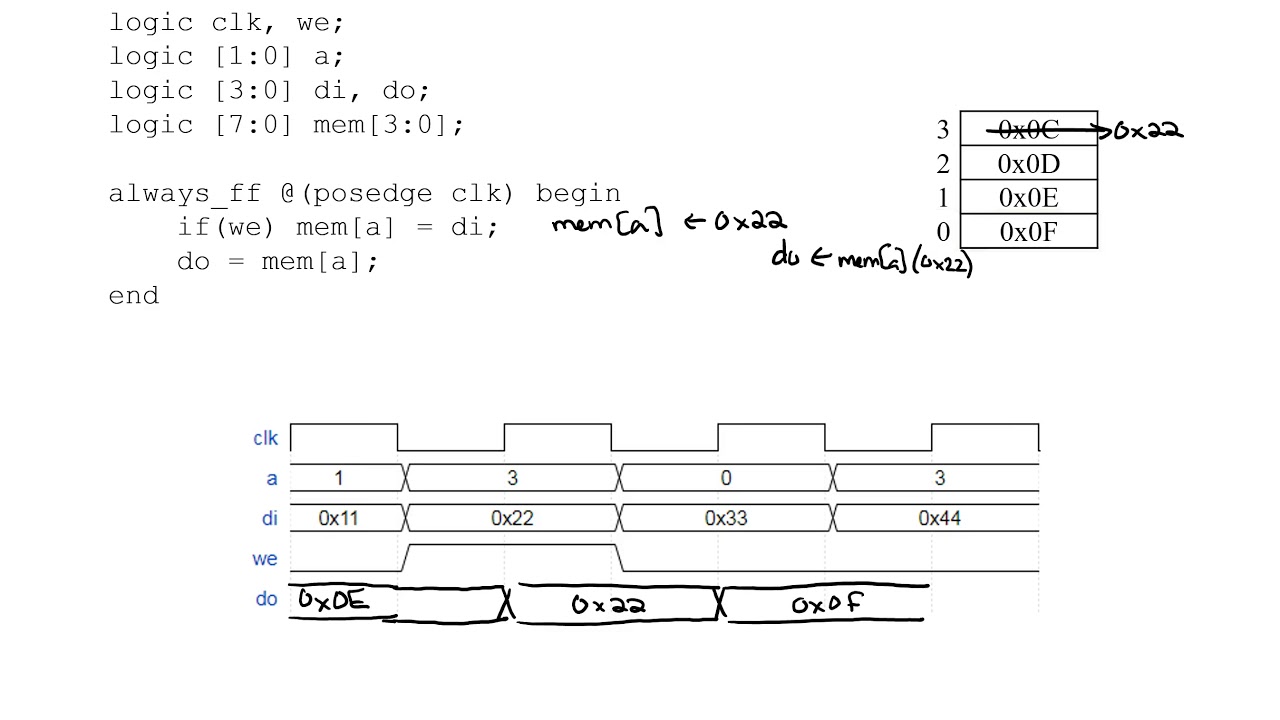
An array can be formed for any of the different data-types supported in Verilog. Note that a memory of n 1-bit reg is not the same as an n-bit vector reg. Array Assignment. y1 = 0; // Illegal - All elements can't be assigned in a single go. y2[0] = 8'ha2; // Assign 0xa2 to index=0.
But when you have 256 values to assign this is a very long process manually organising the code, even with Find/Replace you can only do so much. What I want is the ability to assign values to arrays like you can in System Verilog: reg [15:0] datafile [8] = '{8468,56472,56874,358,2564,8498,4513,9821};
Array initialization is the process of assigning values to an array. In Verilog, arrays can be initialized using the following syntax: data_type array_name [dimension] = {value1, value2, …, valueN}; For example, to initialize a 2D array of integers, we can use the following code:
July 7, 2020. In this post, we talk about the most commonly used data types in Verilog. This includes a discussion of data respresentation, net types, variables types, vectors types and arrays. Although verilog is considered to be a loosely typed language, we must still declare a data type for every port or signal in our verilog design.
An Introduction to SystemVerilog Arrays. This post of the the first of two which talk about SystemVerilog arrays. In this post, we will talk about static arrays, array assignment, loops and packed vs unpacked arrays. In SystemVerilog, we can write arrays which have either a fixed number of elements or a variable number of elements.
Assigning and Copying Verilog Arrays. Verilog arrays can only be referenced one element at a time. Therefore, an array has to be copied a single element at a time. Array initialization has to happen a single element at a time. It is possible, however, to loop through array elements with a generate or similar loop construct.
An array is a group of variables having the same data type. It can be accessed using an index value. An index is a memory address and the array value is stored at that address.
In the example shown below, a static array of 8-bit wide is declared, assigned some value and iterated over to print its value. bit [7:0] m_data; // A vector or 1D packed array. initial begin. // 1. Assign a value to the vector. m_data = 8'hA2; // 2. Iterate through each bit of the vector and print value.
Verilog arrays could only be accessed one element at a time. In SystemVerilog arrays, you can also select one or more contiguous elements of an array. ... Unpacked Array Assignment. All or multiple elements of a SystemVerilog unpacked array can be assigned at once to a list of values. The list can contain values for individual array elements ...
The LHS of an assign statement cannot be a bit-select, part-select or an array reference but can be a variable or a concatenation of variables. reg q; initial begin assign q = 0; #10 deassign q; end force release. These are similar to the assign - deassign statements but can also be applied to nets and variables. The LHS can be a bit-select of ...
How can we read and write values in a multidimensional array in verilog, i had read in this link regarding different operations that can be done on multidimensional array. like if there is a ... <= is a non-blocking assignment used when implying a flip-flop output. = is a blocking assignment used when implementing combinatorial output. example ...
Verilog assign statement. Signals of type wire or a similar wire like data type requires the continuous assignment of a value. For example, consider an electrical wire used to connect pieces on a breadboard. As long as the +5V battery is applied to one end of the wire, the component connected to the other end of the wire will get the required ...
2. So I am trying to assign numbers to an array in verilog, and it goes like this: initial begin. waveforms[0] = 16'b1100100100000000; waveforms[1] = 16'b1000000000000000; waveforms[2] = 16'b1111111111111111; end. And the following codes can pass ModelSim Compiler. However, I have a huge lookup table need to store in this "waveforms", so ...
Verilog Arrays. Verilog arrays are used to group elements into multi-dimensional objects to be manipulated more easily. The Verilog does not have user-defined types, and we are restricted to arrays of built-in Verilog types such as nets, regs, and other Verilog variable types.. An array is a collection of the same types of variables and accessed using the same name plus one or more indices.
To assign an unpacked arrays braces with tick '{ and } are used, ... Verilog Array Assignment. 2. Verilog array assignments. 1. Verilog array of different sized vectors. 0. Verilog assign part of array memory. Hot Network Questions My 5-year-old is stealing food and lying
rolex yachtmaster sizes

.css-1c7en8u{font-size:clamp(1.375rem, 1.25rem + 0.3125vw, 3.125rem);line-height:1.1;margin-bottom:1rem;} Yacht-Master 42 .css-1g7r01k{font-weight:300;font-size:clamp(0.875rem, 0.9375rem + 0.1563vw, 1.25rem);line-height:1.2;text-wrap:balance;}.css-1g7r01k span{display:block;} Oyster, 42 mm, white gold Reference 226659
View in night mode
Discover in 360°
Staying on course
The Oyster Perpetual Yacht-Master 42 in 18 kt white gold with a black dial and an Oysterflex bracelet.
The oysterflex bracelet, highly resistant and durable.
The Yacht-Master’s new Oysterflex bracelet, developed by Rolex and patented, offers a sporty alternative to metal bracelets. The bracelet attaches to the watch case and the Oysterlock safety clasp by a flexible titanium and nickel alloy metal blade.
The blade is overmoulded with high-performance black elastomer which is particularly resistant to environmental effects, very durable and perfectly inert for the wearer of the watch. For enhanced comfort, the inside of the Oysterflex bracelet is equipped with a patented longitudinal cushion system that stabilizes the watch on the wrist and fitted with an 18 kt white gold Oysterlock safety clasp. It also features the Rolex Glidelock extension system, designed by the brand and patented. This inventive toothed mechanism, integrated beneath the clasp, allows fine adjustment of the bracelet length by some 15 mm in increments of approximately 2.5 mm, without the use of tools.
18 kt white gold
Commitment to excellence
By operating its own exclusive foundry, Rolex has the unrivalled ability to cast the highest quality 18 kt gold alloys. According to the proportion of silver, copper, platinum or palladium added, different types of 18 kt gold are obtained: yellow, pink or white.
They are made with only the purest metals and meticulously inspected in an in-house laboratory with state-of-the-art equipment, before the gold is formed and shaped with the same painstaking attention to quality. Rolex's commitment to excellence begins at the source.
Bidirectional Rotatable Bezel
Timing the distance.
The Yacht-Master’s bidirectional rotatable 60-minute graduated bezel is made entirely from precious metals or fitted with a Cerachrom insert in high-tech ceramic. The raised polished numerals and graduations stand out clearly against a matt, sand-blasted background.
This functional bezel – which allows the wearer to calculate, for example, the sailing time between two buoys – is also a key component in the model’s distinctive visual identity.
Exceptional legibility
Like all Rolex Professional watches, the Yacht-Master 42 offers exceptional legibility in all circumstances, and especially in the dark, thanks to its Chromalight display.
The broad hands and hour markers in simple shapes – triangles, circles, rectangles – are filled with a luminescent material emitting a long-lasting glow.
More Yacht-Master technical details
Reference 226659
Model case .css-plfq1t{--iconSize:12px;--iconStrokeWidth:2px;height:var(--iconSize);position:relative;width:var(--iconSize);}.css-plfq1t::before,.css-plfq1t::after{background:currentColor;content:"";display:block;height:var(--iconStrokeWidth);left:0;position:absolute;right:0;top:50%;-webkit-transition:-webkit-transform 0.6s;transition:transform 0.6s;will-change:transform;}html.prefers-reduced-motion .css-plfq1t::before,html.prefers-reduced-motion .css-plfq1t::after{-webkit-transition:none;transition:none;}.css-160voq8 .css-plfq1t::after{-webkit-transform:rotate(90deg);-moz-transform:rotate(90deg);-ms-transform:rotate(90deg);transform:rotate(90deg);}.no-js .css-plfq1t{display:none;}
Oyster, 42 mm, white gold
Oyster architecture
Monobloc middle case, screw-down case back and winding crown
Bidirectional rotatable 60-minute graduated bezel with matt black Cerachrom insert in ceramic, polished raised numerals and graduations
Winding crown
Screw-down, Triplock triple waterproofness system
Scratch-resistant sapphire, Cyclops lens over the date
Water resistance
Waterproof to 100 metres / 330 feet
Perpetual, mechanical, self-winding
3235, Manufacture Rolex
-2/+2 sec/day, after casing
Centre hour, minute and seconds hands. Instantaneous date with rapid setting. Stop-seconds for precise time setting
Paramagnetic blue Parachrom hairspring. High-performance Paraflex shock absorbers
Bidirectional self-winding via Perpetual rotor
Power reserve
Approximately 70 hours
Flexible metal blades overmoulded with high-performance elastomer
Folding Oysterlock safety clasp with Rolex Glidelock extension system
Highly legible Chromalight display with long-lasting blue luminescence
Certification
Superlative Chronometer (COSC + Rolex certification after casing)
Learn how to set the time and other functions of your Rolex watch by consulting our user guides.
Yacht-Master 42
Contact an Official Rolex Jeweler
Only official Rolex jewelers are allowed to sell and maintain a Rolex watch. With the necessary skills, technical know-how and special equipment, they guarantee the authenticity of each and every part of your Rolex and help you make the choice that will last a lifetime.
Watches you may like
These watches have been selected for you. Add them with the heart icon to your favorites.
yachtmaster blue review
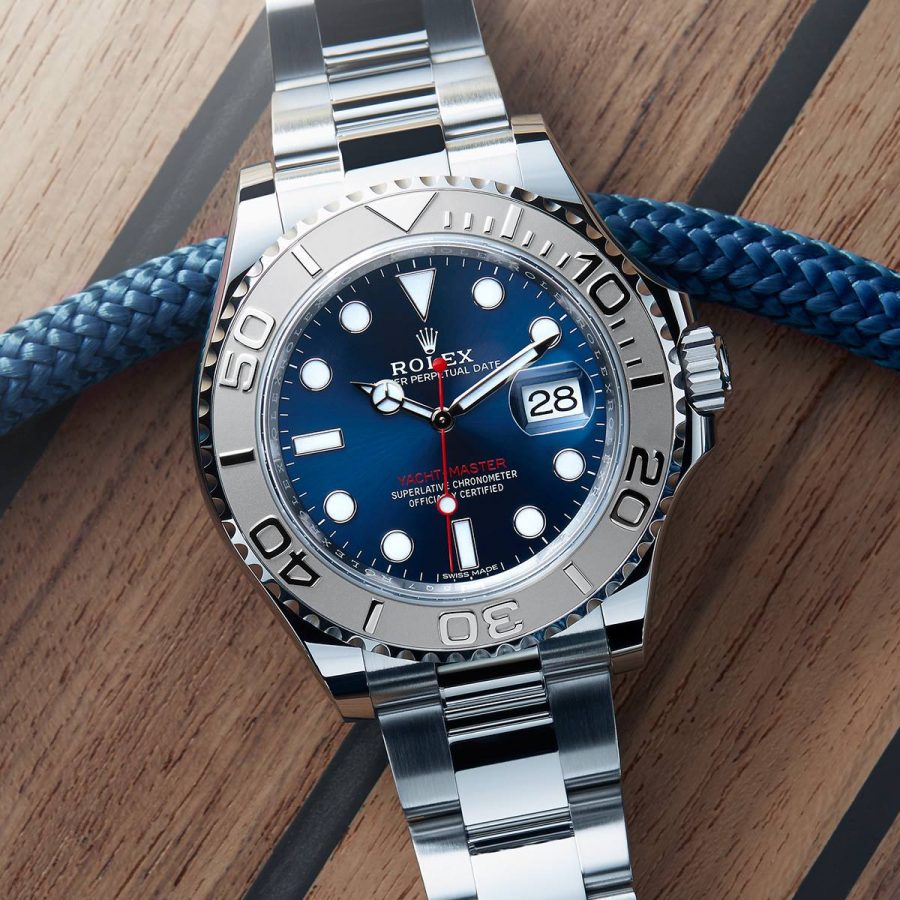

The Everose Rolex Yachtmaster, in Rolex Everose, with Everose Oysterclasp and Oysterflex bracelet, as shown, $22,000 in 37 mm, and $24,950 in 40 mm. For more info, check out Rolex.com. Rolex. A-week-on-the-wrist. For the first time, Rolex is delivering a watch on a rubber strap - except in classic Rolex fashion it's not a rubber strap at all.
My particular Rolex Yacht-Master 40 126622 being Roleisum (Rolex's term for the combination of Platinum and Steel which was first introduced in 1999 with the ref. 16622), in combination with the blue sunburst dial and red accents, gives it such a unique aesthetic it sets it apart in Rolex's catalog. Rolex I think perfected their blue dials ...
Yacht-Master Key Features: - Case Size: 29mm, 35mm, 37mm, 40mm, 42mm - Material Options: Rolesium, Yellow Rolesor, Everose Rolesor, 18k Yellow Gold, 18k Everose Gold, 18k White Gold - Functions: Time with running seconds, date display. - Bezel: 60-minute timing (bi-directional) - Water Resistance: 100 meteres / 330 feet. - Strap/Bracelet: Oyster bracelet, Oysterflex bracelet
Our Yacht-Master 40 blue review compares with the Submariner. Yacht-Master 40 unboxing and 5 reasons it's better than a Submariner.What do you think of the ...
In comparison, the older 2009 model can be purchased from about $5,500 to $7,500, according to Eric. In conclusion, Eric sums up his recommendation regarding the new Rolex Yacht-Master as follows: 'So, if you're looking to get a nice watch in the 9000-dollar area that's pretty versatile, the Yacht-Master with the blue dial. Very nice.
In fact, my Omega Planet Ocean is only 42mm x 15.7mm, and feels much bulkier and heavier than the Yacht-Master II. The case is alternating with polished and satin-finished and features a nautical blue ceramic bezel. The pushers are, as is Rolex's MO, a perfect length. Even though I'm left handed, and therefore wear my watch on my right ...
The Yacht-Master reference 116622 was a part of the Rolex collection from 2012 until 2019, when it was replaced by the 126622. Though it launched with a platinum dial carried over from the preceding reference 16622, the standout for the 2012 model year was a new striking blue dial variation. In 2016, a rhodium dial option was added.
In this review, we dig into the latest generation of the Rolex Yacht-Master 40mm Blue Dial (126622). This is an elegant sport watch from a company that has a...
List of Key Features of the Rolex Yacht-Master. Case: Available in three different sizes - 37mm, 40mm, and 42mm - and two materials - gold or two-tone gold and platinum. Bezel: Bidirectional, rotatable, 60-minute graduated bezel. Crown: Screw-down, Triplock, water-resistant crown system.
With its debut just two years ago at Baselworld 2016, the Yacht-Master ref. 116622 has quickly established itself as a coveted Rolex luxury watch. Part sporty part precious, this modern Rolesium Yacht-Master 40 plays up both sides beautifully. Let's explore all the glorious details.
The current reference of the Rolex Yacht-Master is the Ref 126622. Debuted in 2019 this watch looks like a carbon copy of its predecessor. And from a visual standpoint, it is. Rolex had already tweaked the Yacht-Master quite a bit by this point. So, there was not much left to improve on the case and bracelet.
The two-sided personality Yacht-Master 116622 is meant for yacht-owners, and thereby its name. In this article, we'll go into detail about the Rolex Yacht-Master 126622. Rolex Yacht-Master 126622. As mentioned a new Yacht-Master version was released in 2016, but at Baselworld 2019, Rolex found that the model needed to be updated once again.
A line up of the Oyster Perpetual family, Rolex Yacht master 40 collection is a series of watches with a unique design built to withstand the elements. It was originally designed for diving enthusiasts but is refined enough to fit the daily wearer. The Yacht-Master 40 was first introduced in the 90s. Since then, it has undergone several upgrades.
Before we dive into the depths of this model, let's take a quick look at the dial layout and how it works. In contrast to a conventional chronograph, the Rolex Yacht-Master II features an arc with the numerals 10 to 0 running clockwise. This is joined by a short hand with a triangular tip. The bezel has the same sequence of numbers, as well ...
Rolex Yacht-Master 40 with dark rhodium dial (ref. 116622) Australian pricing. Rolex Yacht-Master 40 in steel and platinum, reference 116622, $14,600. Images by Jason Reekie. Surrounded by its bolder, golder family members, this Rolex Yacht-Master 40 almost snuck past us - but we're mighty glad it didn't.
Discover the Yacht-Master 40 watch in Oystersteel and platinum on the Official Rolex Website. Model:m126622-0002. ... Bright blue dial Exceptional legibility. Like all Rolex Professional watches, the Yacht-Master 40 offers exceptional legibility in all circumstances, and especially in the dark, thanks to its Chromalight display. ...
The watch is powered by a seasoned caliber, the Rolex 3135, used in the very first Yacht-Master in 1992. The 3135 debuted in 1988 in the Submariner. The blue Parachrom balance spring was added to the movement in 2005, five years after it was first introduced in the Cosmograph Daytona. Its paramagnetic alloy resists changes caused by temperature ...
The Yachtmaster 40 Blue, with its distinctive look, can make a great heirloom piece, especially if purchased from an Authorized Dealer (AD) which ensures authenticity and warranty. However, the ceramic Submariner is robust, timeless, and highly coveted, potentially holding its value better in the long term. For a detailed review head over to ...
Hands-On: Rolex Yacht-Master Blue Dial Quick Video Review. 4 Jun 2017 10 Jun 2017 / by Author Donald. In this quick video review of the
The new Seamaster Aqua Terra 150M Ultra Light features details directly inspired by Olympic pole vaulter Armand "Mondo" Duplantis.
Speak with a specialist to learn how you can grow with Birdeye. We are reachable at [email protected] . Read 290 customer reviews of YACHTFISH Fishing Charters, one of the best Fishing businesses at 101 Bay Shore Dr NE Slip Q12, Slip Q12, Saint Petersburg, FL 33701 United States. Find reviews, ratings, directions, business hours, and book ...
Omnia Blue Gentlemen's Club details with ⭐ 27 reviews, 📞 phone number, 📅 work hours, 📍 location on map. Find similar night clubs in St. Petersburg on Nicelocal.
Visitors' opinions on Omnia Blue Gentlemen's Club. I'm a regular I love this place it's amazing. Omnia Blue is a stand-out of the downtown St. Pete area. It's a high-class establishment with a great mix of entertainers across a broad spectrum. Relaxed Dayshifts and a party atmosphere during the nights.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Everose Rolex Yachtmaster, in Rolex Everose, with Everose Oysterclasp and Oysterflex bracelet, as shown, $22,000 in 37 mm, and $24,950 in 40 mm. For more info, check out Rolex.com. Rolex. A-week-on-the-wrist. For the first time, Rolex is delivering a watch on a rubber strap - except in classic Rolex fashion it's not a rubber strap at all.
In fact, my Omega Planet Ocean is only 42mm x 15.7mm, and feels much bulkier and heavier than the Yacht-Master II. The case is alternating with polished and satin-finished and features a nautical blue ceramic bezel. The pushers are, as is Rolex's MO, a perfect length. Even though I'm left handed, and therefore wear my watch on my right ...
Don't trust Hodinkee or Time & Tide? Read an honest owner review of the Rolex Yacht-Master 40 126622 from our community of watch enthusiasts.
The Rolex Yacht-Master is a two-part collection of luxury-oriented sports watches. Here is everything that you need to know before you make your purchase.
Dial In terms of dial options, there's the dark rhodium dial accented with a turquoise seconds hand and the turquoise YACHT-MASTER text or the blue dial with red accents. There's plenty of lume on the Rolesium Yacht-Master for ideal legibility in low light and of course, the signature date window at 3 o'clock along with the Cyclops magnification lens on the sapphire crystal. The Yacht ...
The Yacht-Master also became the first Oyster Professional watch to be made available in a mid-size at 35mm, alongside the ladies and full-size men's models. The Yacht-Master ref. 16623 is a very close brother to the Submariner.
The Rolex Yacht-Master 42 RLX Titanium This year, Rolex launched its commercial version of the Yacht-Master 42 Titanium, which resulted in a slightly different watch from what we've seen on the wrist of Ainslie. More in line with the current white gold and yellow gold YM42, the watch has many distinctive features.
I got this model because I wanted a more 'sporty' Rolex and actually prefer the shape of the lugs and the way the Yachtmaster sits on the wrist, when compared to a Sub and a GMT. I personally love the way the rhodium/slate dial emphasises the light blue of the second hand and the Yachtmaster text.
This Rolex Yacht-Master review assesses both the history of the Yacht-Master as well as its signature design. Learn more in this Yacht-Master review from Crown & Caliber.
Like all Rolex Professional watches, the Yacht-Master 40 offers exceptional legibility in all circumstances, and especially in the dark, thanks to its Chromalight display.
Don't trust Hodinkee? Read an honest owner review of the Rolex Yacht-Master 37 268621 from our community of watch enthusiasts.
The Rolex Yacht Master 40mm M126622-0002 is an authentic Swiss-made Men's luxury watch which features a polished 904L Oystersteel stainless steel case and matching brushed with polished 904L Oystersteel stainless steel oyster bracelet with folding oysterlock safety clasp deployment buckle with Easylink 5mm comfort extension. The blue dial is adorned with luminescent hands and hours markers ...
R olex introduced the 116710BLNR in 2013, with its striking black and blue Cerachrom bezel prompting Rolex afficionados to assign the Rolex GMT Batman, or simply Rolex Batman, moniker. The orginal model remained in production until 2019, when Rolex released the 126710BLNR on a Jubilee bracelet (the Rolex GMT Batgirl). However in 2021 Rolex reintroduced the Rolex Batman model with its Oyster ...
A technical and elegant watch, the Yacht-Master is a reliable nautical instrument on the wrist. Its graduated bidirectional bezel allows for precise measurement and reading of time intervals when navigating. This tool watch benefits from innovations that improve its legibility and wearers' comfort in all circumstances. Graduated bidirectional bezel Precision and legibility on the wrist The ...
The Rolex Yacht-Master 40 is a stunning timepiece that is stylish and functional for the modern man. Our guide will equip you with tips when buying one.
The Yacht-Master 42, made from RLX titanium, is fitted on an Oyster bracelet. Developed at the end of the 1930s, this three-piece link bracelet remains the most universal in the Oyster Perpetual collection and is known for its robustness.
Like all Rolex watches, the Oyster Perpetual Yacht-Master 42 carries the Superlative Chronometer certification, which ensures excellent performance on the wrist. THE CALL OF THE OPEN SEAS Launched in 1992, the Yacht-Master was designed specifically for navigators and skippers.
Model: Yacht-Master II Reference Number: 116688 Serial Number: Random Serial Gender: Men's Metal: Yellow Gold Case Size: 44.00mm Wrist Size: This watch will currently comfortably fit the average male wrist up to 7.50" inches. Movement: Rolex Swiss Automatic Movement with a regatta chronograph function Crystal: Rolex Scratch-Resistant Sapphire ...
The fastest and most secure way to protect the watches and jewelry you love. We've minimized the paperwork and maximized protection, so you can stop worrying about your watches an
Elegantly combining functionality and nautical style, the Yacht-Master is a veritable ally at sea designed for sailors and navigators. More on rolex.com.
Yacht-Master II Ring Command Bezel and In-House Caliber The key to the impressive functionality of the Rolex Yachtmaster II lies in the model's most conspicuous component: the bright blue Cerachrom bezel with its oversized, pink golden numerals.
The fastest and most secure way to protect the watches you love. We've minimized the paperwork and maximized protection, so you can stop worrying about your watches and focus on e
catamaran; gulet; motorboat; powerboat; riverboat; sailboat; trimaran; yacht; yacht. rolex yachtmaster sizes. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter. 426. IMAGES
Like all Rolex Professional watches, the Yacht-Master 42 offers exceptional legibility in all circumstances, and especially in the dark, thanks to its Chromalight display.
The fastest and most secure way to protect the watches and jewelry you love. We've minimized the paperwork and maximized protection, so you can stop worrying about your watches an